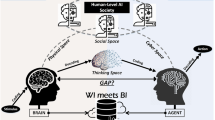
Abstract
Technologies allow the application of knowledge in order to generate solutions to improve the quality of life of human beings. Every day these technologies advance faster, they do not stop, allowing technological innovations to be generated, such as the advances made in artificial intelligence and its applications in different technological tools. Throughout time, since the creation of the Internet, technologies have been developed and implemented that have enabled the evaluation of web 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 (semantic web) and projections to new technological proposals. Among these new technological developments are neural networks that have promoted the management and administration of information. As a model of artificial intelligence, artificial neural networks (RNAs) simulate the behavior of neurons and the neural synapse to solve problems, while not an identical replica, at least it simulates part of the behavior. The studies carried out by Santiago Ramón y Cajal in 1911, through anatomy, made it possible to reveal the structure of nervous tissue in the constitution of the brain, the processing and transmission of information from the transmitter to the receptor, giving adequate response to stimuli. The nervous system is quite complex and even though great efforts have been made in its study, science is still far from fully understanding it. Artificial intelligence models have been supporting new technologies to solve problems, this article presents a proposal for the implementation of one of the artificial intelligence models such as artificial neural networks to the web, generating a new model that projects the intelligent neural web or Web 4.0.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams, W.D.: A multiagent architecture for semantic web resources. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Intelligent Agent Technology (IAT’05) (2005)
Aghaei, S., Nematbakshs, M.Y.(s.f.):. Evolution of the World Wide Web. Int. J. Web Semantic Technol., 8 (2012)
Alexandra Cernian, D.C.: An architecture for a semantic web management system. In: Fourth International Multi-Conference on Computing in the Global Information Technology, 26–30 (2009)
Al-Feel, H., Koutb, M.A.(s.f.): Toward an agreement on semantic web architecture. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol., 806–810 (2009)
Basogain, X.: Redes neuronales artificiales y sus aplicaciones. Bilbao: UPV-EHU, p. 9 (2008)
Berners, T., Hendler, J.A.: The semantic web. Sci. Am. (2001)
BERNERS-LEE (2001). Recuperado el 15 de 04 de 2014, de http://www-sop.inria.fr/: http://www-sop.inria.fr/acacia/cours/essi2006/Scientific%20American_%20Feature%20Article_%20The%20Semantic%20Web_%20May%202001.pdf
Börger, E., Stärk, R.: Abstract State Machines. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-18216-7
Brooke, A., Wei, D.: Architecture for automated annotation and ontology based querying of semantic web resources. Int. Conf. Web Intell. (2005)
Bustamante, E.: El sistema nervioso : desde las neuronas hasta el cerebro humano. Antioquia: Universidad de Antioquia, p. 91 (2007)
CEDE (2014). Obtenido de https://www.mineducacion.gov.co/: https://www.mineducacion.gov.co/sistemasdeinformacion/1735/articles-254702_Informe_determinantes_desercion.pdf
D’Aquin, M.A.: Watson, More Than a Semantic Web Search Engine. IOS Press (2015)
Dai, W., Abrahams, B.: A multiagent architecture for semantic web resources. Int. Conf. Intell. Agent Technology
Davies, J., Studer, R., Warren, P.: Semantic Web Technologies: Trends and Research in Ontology-based Systems. Wiley, Chichester (2006)
Dinero (s.f.): Recuperado el 30 de noviembre de 2017, de (2017). http://www.dinero.com/edicion-impresa/caratula/articulo/porcentaje-y-contribucion-de-las-pymes-en-colombia/231854
Djelloul, B., Mimoun, M.: Towards re-engineering web applications into semantic web services. IEEE Xplore, 350–353 (2010)
Fernández, L.: Procedimiento semi-automático para transformar la web en web semántica (2009). Obtenido de https://gc.scalahed.com/: https://gc.scalahed.com/recursos/files/r161r/w23877w/Transformar_la_web_en_web_semantica.pdf
Galey, J.: Aplicación web semántica para la gestión de referencias bibliográficas. Universidad Rey Juan Carlos (2010)
Georgieva, R.: Ontology-based information representation. Technische Universität München, 16 (2005)
Harth, A., Janik, M., Staab, S.: Semantic web architecture. In: Domingue, J., Fensel, D., Hendler, J.A. (eds.) Handbook of Semantic Web Technologies, pp. 43–75. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-92913-0_2
Huang, R., Zhuang, Y., Zhou, J., Cao, Q.: Semantic web-based context-aware service selection in task-computing. IEEE Comput. Soc., 97–101 (2008)
Huhns, M.: Agents as web services. IEEE Internet Comput. 6(4), 93–94 (2002)
Huhns, M.N.: Agents as web services. IEEE Internet Comput., 93–95 (2018)
Iman, K., Hassan, A.: An architecture for context-aware semantic web services. IEEE Comput. Soc., 779–780 (2008)
Kifer, M., Lausen, G., Wu, J.: Logical foundations of object-oriented and frame-based languages. J. ACM 42(4), 741–843 (1995)
Li, D., Finin, T., Joshi, A., Peng, Y., Cost, R.S., Sachs, J.: Swoogle: a semantic web search and metadata engine. ACM (2010)
Li, L.: The design of semantic web services discovery model based on multi proxy, pp. 186–189. IEEE (2009)
Martinez, G.: Definición de una red neuronal para clasificación por medio de un programa evolutivo. Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Biomédica, pp. 4–11 (2001)
Matthews, B.: Semantic web technologies. JISC Technol. Stand. Watch (2014)
McIlraith, S.A., Son, T.C., Zeng, H.: Semantic web services. IEEE Intell. Syst. (2001)
Nath, K., Iswary, R.: What comes after web 3.0? Web 4.0 and the future. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Appl. (IJAIA) (2015)
Portafolio (2017). Obtenido de http://www.portafolio.co/negocios/empresas/cerca-90-mil-empresas-han-cerrado-ano-49120
Ramón, Y., Cajal, S.: Histologie du Système Nerveux. París: Maloine (1911)
Rodriguez: Complejidad de los Datos en las RNA. M.A Cruz-Chávez, J.C Zavala Díaz(Eds), pp. 229–235 (2009)
Roebuck: Web 3.0 - the Semantic Web (2011)
Rosenblatt, F.: “The Perceptron: a probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain. Psychol. Rev., pp 386–408 (1958)
Semanticwebbuilder (2016). Obtenido de Semanticwebbuilder: http://www.semanticwebbuilder.org.mx/es_mx/swb/Web_Semantica_Blog
Wilde, S.: Customer Knowledge Management: Improving Customer Relationship through Knowledge Application. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16475-0
Zhao, J., Goble, C., Stevens, R.A.: Mining taverna's semantic web of provenance. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Corredor, B.Y.A., Crespo, R.G., Marín, C.E.M., Martelo, C.A.S. (2024). A Projection Neuronal Smart WEB. In: Montenegro, C., Rocha, Á., Cueva Lovelle, J.M. (eds) Management, Tourism and Smart Technologies. ICMTT 2023. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 773. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44131-8_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44131-8_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-44130-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-44131-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)