Abstract
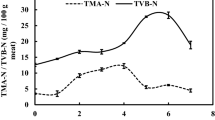
Spoilage dynamics and safety of fresh deep-water pink shrimp, Parapenaeus longirostris, are of paramount importance for its storage and commercialization in good sanitary conditions, owing to its high perishability and limited shelf life. This study focused on the analysis of physicochemical indices, microbiota growth and sensory analysis during storage of deep-water pink shrimp in ice at 5 °C. The specimens were kept for 13 d in a perforated plastic box covered with ice that allowed the melted water to drain; new ice was added every 8–12 h. A sensory analysis panel assessed several attributes to develop a species-specific, 14-demerit points Quality Index Method (QIM) scheme. Water content remained at ca. 80% and water activity values ranged 0.98–1.00 during the experiment, confirming the high perishability potential of the samples. Unexpectedly, there were no significant changes in the concentrations of TVBN and TMA during this storage trial. Despite this, the abundances of mesophilic and psychrotrophic bacteria increased consistently from ca. 3.0–3.5 log CFU/g to about 6.9–7.4 log CFU/g. The absence of increase in nitrogen-based compounds despite microbiota proliferation might be related to a leaching process due to melting ice (that needs to be further experimented). Moreover, Enterobacteriaceae were not present in any of the samples analyzed, indicating good sanitary and hygienic conditions during handling and storage and safety of samples. Data suggests that deep-water pink shrimp should not be stored in ice at 5 °C more than 7 days before consumption. Food safety is critical to food security and public health, thus relevant to United Nations’ SDG 1 (No poverty) and SDG 2 (Zero hunger).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisher, W., Schneider, M., Bauchot, M.L.: Identification des espèces pour les besoins de la pêche. Mediterranée et mer Noire. Fishes FAO. Volume I–II (1987)
Parapenaeus longirostris (Lucas, 1846). Deep-water rose shrimp. https://www.sealifebase.se/summary/Parapenaeus-longirostris.html. Accessed 23 Nov 2022
FAO 2023. Parapenaeus longirostris Lucas,1846. Fisheries and Aquaculture Division, Rome. https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/aqspecies/2598/en. Accessed 12 Mar 2023
Gillett, R. Global Study of shrimp fisheries. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper 475 (2008)
DGPA. Recursos da Pesca 2021. Direção-Geral de Recursos Naturais, Segurança e de Serviços Marítimos, Lisboa (2022)
Rosa, R., Nunes, M.L.: Nutritional quality of red shrimp, Aristeus antennatus (Risso), pink shrimp, Parapenaeus longirostris (Lucas), and Norway lobster, Nephrops norvegicus (Linnaeus). J. Sci. Food Agric. 84, 89–94 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.1619
Küçükgülmez, A., Baykal, M., Kadak, A.E., Cukurova, M.C.: Quality changes in crustaceans during and after processing. In: Genç, I.Y., Esteves, E., Diler, A. (eds.) Handbook of Seafood: Quality and Safety Maintenance and Application, pp. 127–137. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., New York (2016)
Ashie, I.N.A., Smith, J.P., Simpson, B.K., Haard, N.F.: Spoilage and shelf-life extension of fresh fish and shellfish. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 36(1–2), 87–121 (1996)
Gram, L., Dalgaard, P.: Fish spoilage bacteria–problems and solutions. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 13(3), 262–266 (2002)
Flick, G.J., Granata, L.A.: Biological safety of fresh and processed shellfish. SRAC Publication, 4901 (2010)
Huq, K.A., Rahaman, S.M.B., Islam, B., Shaha, B.K., Ghosh, A.K., Sayeed, A.B.: Quality aspects of frozen shrimp product in processing industry: a case study in Khulna, Bangladesh. Bangladesh Res. Publ. J. 3(2), 945962 (2009)
Hossain, A., Mandal, S.C., Rahman, M.S., Rahman, M., Hasan, M.: Microbiological quality of processed frozen black tiger shrimps in fish processing plant. World J. Fish Marine Sci. 2(2), 124–128 (2010)
Lagartinho, J.: Estudo da deterioração da gamba Parapenaeus longirostris (Lucas, 1846). MSc dissertation, Departamento de Engenharia Alimentar, Instituto Superior de Engenharia, Universidade do Algarve, Faro (2010)
Gonçalves, A.C., Lopez-Caballero, M.E., Nunes, M.L.: Quality changes of deepwater pink shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris) packed in modified atmosphere. J. Food Sci. 68(8), 2586–2590 (2003)
EU. Regulamento (CE) 2074/2005 da Comissão. Jornal Oficial da União Europeia L 338, 27–59 (2005)
EU. Regulamento (CE) 1022/2008 da Comissão. Jornal Oficial da União Europeia L 277, 18–20 (2008)
EC. Regulation (EC) 2406/96 of the Commission. Official Journal of the European Communities, 334(1), 1–15 (1996)
Esteves, E.: Relating sensory and instrumental analyses of well-known and emerging fish and seafood products. In: Genç, I.Y., Esteves, E., Diler, A. (eds.) Handbook of Seafood: Quality and Safety Maintenance and Applications, pp. 31–64. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., New York (2016)
Esteves, E., Aníbal, J.: Sensory evaluation of seafood freshness using the quality index method: a meta-analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 337, 108934 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108934
Howgate, P.: A history of the development of sensory methods for the evaluation of freshness of fish. J. Aquatic Food Prod. Technol. 24(5), 516–532 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/10498850.2013.783897
Conway, E.J., Byrne, A.: An absorption apparatus for the micro-determination of certain volatile substances. I. The micro-determination of ammonia. Biochem. J. 27, 419–429 (1933)
IPQ. NP 2930. Produtos da pesca e da aquicultura. Determinação do teor de azoto básico volátil total (ABVT). Instituto Português da Qualidade, Lisboa (2009)
ISO. ISO 6887-3: Microbiology of the food chain—Preparation of test samples, initial suspension, and decimal dilutions for microbiological examination—Part 3: Specific rules for the preparation of fish and fishery products. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva (2003)
IPQ. NP 4405. Microbiologia Alimentar: Regras gerais para contagem de microrganismos: Contagem de colónias a 30 °C. Instituto Português de Qualidade, Lisboa (2002)
ISO. ISO 17410: Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs – Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Psychrotrophic Microorganisms. International Organization for Standardization, Genève (2001)
IPQ. NP 4137. Microbiologia Alimentar: Regras gerais para determinação de Enterobacteriaceae sem revitalização. Técnicas do número mais provável e de contagem de colónias. Instituto Português de Qualidade, Lisboa (1991)
Laghmari, H., Marrakchi, A.: Appréciation organoleptique et physico-chimique de la crevette rose Parapenaeus longirostris (Lucas, 1846) conservée sous glace et à température ambiante. Rev. Méd. Vétérinaire 156(4), 221–226 (2005)
Martinsdóttir, E., Sveinsdóttir, K., Luten, J., Schelvis-Smit, R., Hyldig, G.: Sensory evaluation of fish freshness. QIM Eurofish, Ijmuden (2001)
Oliveira, V.M., Freitas, M.Q., São-Clemente, S.C., Mársico, E.T.: Método do Índice de Qualidade (MIQ) desenvolvido para camarão (Litopenaeus vannamei) cultivado. Rev. Ciências Vida 29(1), 60–71 (2009)
Zeng, Q.Z., Thorarinsdottir, K.A., Olafsdottir, G.: Quality changes of shrimp (Pandalus borealis) stored under different cooling conditions. J. Food Sci. 70(7), 459–466 (2005)
IPQ. NP EN ISO 8589. Sensory analysis. General guidance for the design of test rooms (ISO 8589:2007/Amd 1:2013). Instituto Português da Qualidade, Lisboa (2014)
Baranyi, J., Roberts, T.A.: A dynamic approach to predicting bacterial growth in food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 23, 277–294 (1994)
Baty, F., Delignette-Muller, M.L.: nlsMicrobio: data sets and nonlinear regression models dedicated to predictive microbiology. R package version 0.0-1 (2013)
Ritz, C., Streibig, J.C.: Nonlinear Regression with R. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-09616-2
Sveinsdóttir, K., Hyldig, G., Martinsdóttir, E., Jørgensen, B., Kristbergsson, K.: Quality index method (QIM) scheme developed for farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Food Qual. Prefer. 14, 237–245 (2003)
Rossini, K., Verdu, S., Cariou, V., Qannari, E.M., Fogliatto, F.S.: PLS discriminant analysis applied to conventional sensory profiling data. Food Qual. Prefer. 23, 18–24 (2012)
Mevik, B.-H., Wehrens, R., Liland, K.H.: PLS: partial least squares and principal component regression. R package version 2.6-0 (2016)
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria (2022). https://www.R-project.org/
Cui, H., Xue, C., Xue, Y., Su, W., Li. Z., Cong, H.: Development of shelf-stable, ready-to-eat (RTE) shrimps (Litopenaeus vannamei) using water activity lowering agent by response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. Technol. 50, 1137–1143 (2013)
Cadun, A., Cakli, S., Kisla, D.: A study of marination of deepwater pink shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris, Lucas, 1846) and its shelf life. Food Chem. 90, 53–59 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.03.024
Hall, G.M.: Fish Processing – Sustainability and New Opportunities. Wiley-Blackwell Publishing Ltd. (2011)
Huidobro, A., Lopez-Caballero, M., Mendes, R.: Onboard processing of deepwater pink shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris) with liquid ice: effect on quality. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 214, 469–475 (2002)
Moura, A.F.P., Mayer, M.D.B., Landgraf, M., Tenuta-Filho, A.: Qualidade química e microbiológica de camarão-rosa comercializado em São Paulo. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 5(2), 203–208 (2003)
Shamshad, S.I., Kher-Un-Nisa, Riaz, M., Zuberi, R., Qadri, R.B.: Shelf life of shrimp (Penaeus merguiensis) stored at different temperatures. J. Food Sci. 55(5), 1201–1205 (1990)
Fatima, R., Khan, M.A., Qadri, R.B.: Shelf life of shrimp Penaeus merquiensis stored in Ice (0 °C) and partially frozen (−3 °C). J. Sci. Food Agric. 42, 235–247 (1988)
Kirschnik, P.G., Viegas, E.M.M., Valenti, W.C., Oliveir, C.A.F.: Shelf-life of tail meat of the giant river prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii, stored on ice. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 15(2), 57–71 (2006)
Nirmal, N.P., Benjakul, S.: Effect of ferulic acid on inhibition of polyphenoloxidase and quality changes of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) during iced storage. J. Food Chem. 116, 323–331 (2009)
Kirschnik, P.G., Viegas, E.M.M.: Alterações na qualidade do camarão de água doce Macrobrachium rosenbergii durante estocagem em gelo. J. Ciência Tecnol. Alimentos 24(3), 407–412 (2004)
Akintola, S.L., Bakare, S.B.: Effects of ice storage on the biochemical composition of Macrobrachium vollenhovenii (Herklots, 1857). J. Fish. Aquatic Sci. 8, 213–217 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3923/jfas.2013.213.217
Mendes, R., Huidobro, A., Lopez-Caballero, M.E.: Indole levels in deepwater pink shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris) from the Portuguese coast. Effects of temperature abuse. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 214, 125–130 (2002)
Salvi, D.: Study of Quality deterioration of shrimp by chemical, microbial and electronic nose analysis. AIT thesis, Bangkok, Thailand (2005)
Castro, P., Padrón, J.C.P., Cansino, M.J.C., Velázquez, E.S., Larriva, R.M.: Total volatile base nitrogen and its use to assess freshness in European sea bass stored in ice. J. Food Control 17, 245–248 (2006)
Grigorakis, K., Alexis, M., Gialamas, I., Nikolopoulou, D.: Sensory, microbiological, and chemical spoilage of cultured common sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) stored in ice: a seasonal differentiation. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 219, 584–587 (2004)
Hernández, M.D., López, M.B., Álvarez, A., Ferrandini, E., García, B.G., Garrido, M.D.: Sensory, physical, chemical and microbiological changes in aquacultured meagre (Argyrosomus regius) fillets during ice storage. Food Chem. 114, 237–245 (2009)
Aníbal, J., Lagartinho, J., Esteves, E.: Is total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) a reliable spoilage indicator for the deep-water shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris)? In: International Meeting on Marine Resources (IMMR'12), Escola Superior de Turismo e Tecnologia do Mar, Instituto Politécnico de Leiria, Peniche, Portugal (2012)
Anastasio, A.: Correlations between pH, total volatile basic nitrogen, trimethylamine and sensory evaluation in fresh fish slices. Arch. Lebensmittel Hygiene 50(3), 63–66 (1999)
Kyrana, V.R., Lougovois, V.P.: Sensory, chemical and microbiological assessment of farm-raised European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) stored in melting ice. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 37, 319–328 (2002)
Papadopoulos, V., Chouliara, I., Badeka, A., Savvaidis, I.N., Kontominas, M.G.: Effect of gutting on microbiological, chemical, and sensory properties of aquacultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) stored in ice. Food Microbiol. 20(4), 411–420 (2003)
Kornacki, J.L., Johnson, J.L.: Enterobacteriaceae, coliforms, and Escherichia coli as Quality and safety Indicators. In: Downes, F.P., Ito, K. (eds.) Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination, pp. 68–81. American Public Health Association (2001)
ICMSF. Microorganisms in Foods. 2. Sampling for Microbiological Analysis: Principles and Specific Applications, 2nd edn. University of Toronto Press, Toronto (1986)
Ho, M.L., Cheng, H.H., Jiang, S.T.: Effect of modified ice storage on the shelf-life of shrimp. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Fish. Oceanogr. 52, 479–488 (1986)
Lannelongue, M., Finne, G., Hanna, M.O., Nickelson, R., Vanderzant, C.: Storage characteristics of brown shrimp (Penaeus aztecus) stored in retail packages containing CO2-enriched atmospheres. J. Food Sci. 47, 911–923 (1982)
Layrisse, M.E., Matches, J.R.: Microbiological and chemical changes of spotted shrimp (Pandalus platyceros) stored under modified atmospheres. J. Food Protect. 47(6), 453–457 (1984)
Oliveira, V.M.: Estudo da qualidade do camarão branco do Pacífico (Litopenaeus vannamei) inteiro e descabeçado estocado em gelo. Ph.D. thesis, Universidade Federal Fluminense (2005)
Khodanazary, A.: Freshness assessment of shrimp Metapenaeus affinis by quality index method and estimation of its shelf life. Int. J. Food Properties 22(1), 309–319 (2019)
Gonçalves, A.A., de Lima, J.T.A.X., de Paula, F.E.R.: Development of quality index method (QIM) scheme for spiny lobster (Panulirus Argus, Latreille, 1804) stored in ice. Food Control 47, 237–245 (2015)
Tam, L.N., Khue, D.N., Thanh, N.B., Thi, T.T.V.: Towards improved quality benchmarking and shelf life evaluation of black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Food Chem. 235, 220–226 (2017)
Acknowledgments
This study also received Portuguese national funds from FCT - Foundation for Science and Technology through projects UIDB/04326/2020, UIDP/04326/2020 and LA/P/0101/2020 (Eduardo Esteves). Jaime Aníbal would like to acknowledge the support of national funds through Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT), under the project LA/P/0069/2020 granted to the Associate Laboratory ARNET and UID/00350/2020 CIMA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Universidade do Algarve
About this paper
Cite this paper
Esteves, E., Lagartinho, J., Aníbal, J. (2023). Freshness, Spoilage Dynamics and Safety of Deep-Water Pink Shrimp, Parapenaeus longirostris, Stored in Ice. In: Semião, J.F.L.C., Sousa, N.M.S., da Cruz, R.M.S., Prates, G.N.D. (eds) INCREaSE 2023. INCREaSE 2023. Advances in Sustainability Science and Technology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44006-9_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44006-9_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-44005-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-44006-9
eBook Packages: Business and ManagementBusiness and Management (R0)