Abstract
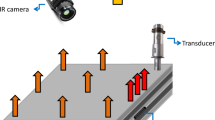
This article presents a novel infrared thermographic approach for damage detection by utilizing the heat generated around damage sites during vibrations below 1000 Hz induced by lightweight piezoelectric actuators. In this research, the optimal location of excitation was first investigated through finite element analyses, where two generalized equations were obtained to describe the relationship between the excitation and the resulting displacement response. These observations were then verified experimentally on an aerospace-grade composite plate, followed by vibrothermographic tests conducted on the same structure to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed damage detection process employing only a single lightweight piezoelectric disk as the actuator.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chi, X.: Modal-based vibrothermography for damage detection and structural health monitoring. PhD thesis, University of Bristol (2022)
Renshaw, J., Chen, J.C., Holland, S.D., Bruce Thompson, R.: The sources of heat generation in vibrothermography. NDT & E Int. 44(8), 736–739 (2011)
Stinchcomb, W.W.: Mechanics of Nondestructive Testing. Springer New York, NY, USA (1980)
Henneke II, E.G., Reifsnider, K.L., Stinchcomb, W.W.: Vibrothermography: investigation, development, and application of a new nondestructive evaluation technique. Engineering Science and Mechanics Department, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, Tech report (1986)
Henneke II, E.G., Jones, T.S.: Detection of damage in composite materials by vibrothermography. In: Nondestructive Evaluation and Flaw Criticality for Composite Materials (1979)
Henneke II, E.G., Reifsnider, K.L., Stinchcomb, W.W.: Thermography — an NDI method for damage detection. JOM. 31(9), 11–15 (1979)
Stepinski, T., Uhl, T., Staszewski, W.: Advanced Structural Damage Detection: From Theory to Engineering Applications. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Chichester, West Sussex, UK (2013)
Ibarra-Castanedo, C., Genest, M., Guibert, S., Piau, J.-M., Maldague, X.P.V., Bendada, A.: Inspection of aerospace materials by pulsed thermography, lock-in thermography, and vibrothermography: a comparative study. Thermosense XXIX. 6541, 321–329 (2007)
Mignogna, R.B., Green, R.E., Duke, J.C., Henneke II, E.G., Reifsnider, K.L.: Thermographic investigation of high-power ultrasonic heating in materials. Ultrasonics. 19(4), 159–163 (1981)
Montanini, R., Freni, F.: Correlation between vibrational mode shapes and viscoelastic heat generation in vibrothermography. NDT & E Int. 58, 43–48 (2013)
Holland, S.D., Uhl, C., Ouyang, Z., Bantel, T., Li, M., Meeker, W.Q., Lively, J., Brasche, L., Eisenmann, D.: Quantifying the vibrothermographic effect. NDT & E Int. 44(8), 775–782 (2011)
Morbidini, M., Cawley, P., Barden, T., Almond, D., Duffour, P.: Prediction of the thermosonic signal from fatigue cracks in metals using vibration damping measurements. J. Appl. Phys. 100(10), 104905 (2006)
Holland, S.D., Uhl, C., Renshaw, J.: Vibrothermographic crack heating: a function of vibration and crack size. AIP Conf. Proc. 1096(1), 489–494 (2009)
Krapez, J.-C., Taillade, F., Balageas, D.: Ultrasound-lockin-thermography NDE of composite plates with low power actuators. Experimental investigation of the influence of the lamb wave frequency. Quant. InfraRed Thermogr. J. 2(2), 191–206 (2005)
Solodov, I., Rahammer, M., Derusova, D., Busse, G.: Highly-efficient and noncontact vibro-thermography via local defect resonance. Quant. InfraRed Thermogr. J. 12(1), 98–111 (2015)
Bai, G., Lamboul, B., Roche, J.-M., Baste, S.: Investigation of multiple cracking in glass/epoxy 2D woven composites by vibrothermography. Quant. InfraRed Thermogr. J. 13(1), 35–49 (2016)
Kang, B., Cawley, P.: Low power PZT exciter for thermosonics. AIP Conf. Proc. 894(1), 484–491 (2007)
Kang, B., Cawley, P.: Multi-mode excitation system for thermosonic testing of turbine blades. AIP Conf. Proc. 975(1), 520–527 (2008)
Kang, B., Lee, H., Lee, C.: Performance of a small PZT exciter for thermosonic non-destructive testing. In: INTELEC 2009 – 31st International Telecommunications Energy Conference, pp. 1–4 (2009, October)
Renshaw, J., Holland, S.D., Barnard, D.J.: Viscous material-filled synthetic defects for vibrothermography. NDT & E Int. 42(8), 753–756 (2009)
Pye, C.J., Adams, R.D.: Heat emission from damaged composite materials and its use in nondestructive testing. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 14(5), 927–941 (1981)
Pye, C.J., Adams, R.D.: Detection of damage in fibre reinforced plastics using thermal fields generated during resonant vibration. NDT Int. 14(3), 111–118 (1981)
Homma, C., Rothenfusser, M., Baumann, J., Shannon, R., Thompson, D.O., Chimenti, D.E.: Study of the heat generation mechanism in acoustic thermography. AIP Conf. Proc. 820(1), 566–573 (2006)
Rantala, J., Wu, D., Busse, G.: Amplitude-modulated lock-in vibrothermography for NDE of polymers and composites. Res. Nondestruct. Eval. 7(4), 215–228 (1996)
Harwood, N., Cummings, W.M.: Thermoelastic Stress Analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA (1991)
Morbidini, M., Cawley, P., Barden, T.J., Almond, D.P., Duffour, P.: A new approach for the prediction of the thermosonic signal from vibration records. AIP Conf. Proc. 820(1), 558–565 (2006)
Ewins, D.J.: Modal Testing: Theory, Practice and Application, 2nd edn. Research Studies Press Ltd., Baldock, Hertfordshire, UK (2000)
Meola, C., Boccardi, S., Carlomagno, G.M.: Infrared Thermography in the Evaluation of Aerospace Composite Materials. Woodhead Publishing, Duxford, UK (2015)
Chi, X., Di Maio, D., Lieven, N.A.J.: Modal-based vibrothermography using feature extraction with application to composite materials. Struct. Health Monit. 19(4), 967–986 (2020)
Chi, X., Di Maio, D., Lieven, N.A.J.: Health monitoring of bolted joints using modal-based vibrothermography. SN Appl. Sci. 2(8), 1446 (2020)
Chi, X., Zhang, Y., Di Maio, D., Lieven, N.A.J.: Viability of image compression in vibrothermography. Exp. Tech. 45(3), 345–362 (2021)
Chi, X., Di Maio, D., Lieven, N.A.J.: Frictional heating as an estimator of modal damping and structural degradation: a vibrothermographic approach. In: 12th Defence Science and Technology International Conference on Health and Usage Monitoring (2021)
Talai, S.M., Desai, D.A., Heyns, P.S.: Infrared thermography applied to the prediction of structural vibration behaviour. Alex. Eng. J. 58(2), 603–610 (2019)
Han, X., Zeng, Z., Li, W., Islam, M.S., Lu, J., Loggins, V., Yitamben, E., Favro, L.D., Newaz, G., Thomas, R.L.: Acoustic chaos for enhanced detectability of cracks by sonic infrared imaging. J. Appl. Phys. 95(7), 3792–3797 (2004)
Favro, L.D., Han, X., Ouyang, Z., Sun, G., Sui, H., Thomas, R.L.: Infrared imaging of defects heated by a sonic pulse. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71(6), 2418–2421 (2000)
Li, M., Holland, S.D., Meeker, W.Q.: Quantitative multi-inspection-site comparison of probability of detection for vibrothermography nondestructive evaluation data. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 30(3), 172–178 (2011)
Vaddi, J., Reusser, R., Holland, S.D.: Characterization of piezoelectric stack actuators for vibrothermography. AIP Conf. Proc. 1335(1), 423–429 (2011)
Vaddi, J., Holland, S.D., Reusser, R.: Transducer degradation and high amplitude behavior of broadband piezoelectric stack transducer for vibrothermography. AIP Conf. Proc. 1430(1), 552–558 (2012)
Vaddi, J.S., Holland, S.D., Kessler, M.R.: Absorptive viscoelastic coatings for full field vibration coverage measurement in vibrothermography. NDT & E Int. 82, 56–61 (2016)
Demy, P., Golinval, J.-C., Simon, D.: Damage detection in composites by vibrothermography and local resonances. Mech. Ind. 14(2), 137–143 (2013)
Holland, S.D.: First measurements from a new broadband vibrothermography measurement system. AIP Conf. Proc. 894(1), 478–483 (2007)
Lamboul, B., Passilly, F., Roche, J.-M., Balageas, D.: Ultrasonic vibrothermography using low-power actuators: an impact damage detection case study. AIP Conf. Proc. 1650(1), 319–326 (2015)
Solodov, I., Bai, J., Bekgulyan, S., Busse, G.: A local defect resonance to enhance acoustic wave-defect interaction in ultrasonic nondestructive evaluation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99(21), 211911 (2011)
Parvasi, S.M., Xu, C., Kong, Q., Song, G.: Detection of multiple thin surface cracks using vibrothermography with low-power piezoceramic-based ultrasonic actuator—a numerical study with experimental verification. Smart Mater. Struct. 25(5), 055042 (2016)
Zhu, L., Guo, X.: Vibro-thermography of debonding defects in composite plates. In: Conference on Quantitative Infrared Thermography – QIRT Asia 2017, Daejeon (2017)
Renshaw, J., Holland, S.D., Bruce Thompson, R.: Measurement of crack opening stresses and crack closure stress profiles from heat generation in vibrating cracks. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93(8), 081914 (2008)
Russell, S.S., Henneke II, E.G.: Dynamic effects during vibrothermographic NDE of composites. NDT Int. 17(1), 19–25 (1984)
Wang, C.-Y., Yew, C.H.: Impact damage in composite laminates. Comput. Struct. 37(6), 967–982 (1990)
Bull, D.J., Spearing, S.M., Sinclair, I., Helfen, L.: Three-dimensional assessment of low velocity impact damage in particle toughened composite laminates using micro-focus X-ray computed tomography and synchrotron radiation laminography. Compos. A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 52, 62–69 (2013)
Yang, F.J., Cantwell, W.J.: Impact damage initiation in composite materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70(2), 336–342 (2010)
Richardson, M.O.W., Wisheart, M.J.: Review of low-velocity impact properties of composite materials. Compos. A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 27(12), 1123–1131 (1996)
Tai, N.H., Yip, M.C., Lin, J.L.: Effects of low-energy impact on the fatigue behavior of carbon/epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 58(1), 1–8 (1998)
Sjoblom, P.O., Hartness, J.T., Cordell, T.M.: On low-velocity impact testing of composite materials. J. Compos. Mater. 22(1), 30–52 (1988)
de Vries, E.: Mechanics and mechanisms of ultrasonic metal welding. PhD thesis, The Ohio State University (2004)
Crawley, E.F., de Luis, J.: Use of piezoelectric actuators as elements of intelligent structures. AIAA J. 25(10), 1373–1385 (1987)
PI Ceramic: Displacement modes of piezoelectric actuators. https://www.piceramic.com/en/piezo-technology/properties-piezo-actuators/displacement-modes. Accessed 16 Sept 2022
Dimitriadis, E.K., Fuller, C.R., Rogers, C.A.: Piezoelectric actuators for distributed vibration excitation of thin plates. J. Vib. Acoust. 113(1), 100–107 (1991)
Kim, T.-W., Kim, J.-H.: Optimal distribution of an active layer for transient vibration control of a flexible plate. Smart Mater. Struct. 14(5), 904–916 (2005)
Ramesh Kumar, K., Narayanan, S.: The optimal location of piezoelectric actuators and sensors for vibration control of plates. Smart Mater. Struct. 16(6), 2680–2691 (2007)
Aldraihem, O.J., Singh, T., Wetherhold, R.C.: Optimal size and location of piezoelectric actuator/sensors: practical considerations. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 23(3), 509–515 (2000)
Sadri, A.M., Wright, J.R., Wynne, R.J.: Modelling and optimal placement of piezoelectric actuators in isotropic plates using genetic algorithms. Smart Mater. Struct. 8(4), 490–498 (1999)
Swann, C., Chattopadhyay, A.: Optimization of piezoelectric sensor location for delamination detection in composite laminates. Eng. Optim. 38(5), 511–528 (2006)
Hexcel Corporation: HexPly® 8552 epoxy matrix product data sheet (2020)
Marlett, K.: Hexcel 8552S AS4 plain weave fabric Prepreg 193 gsm & 38% RC qualification material property data report. National Institute for Aviation Research, Wichita State University, Tech report (2011)
Speakman, J.R., Ward, S.: Infrared thermography: principles and applications. Zoology. 101, 224–232 (1998)
Nicodemus, F.E.: Directional reflectance and emissivity of an opaque surface. Appl. Opt. 4(7), 767–775 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Society for Experimental Mechanics, Inc.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chi, X., Di Maio, D., Lieven, N.A.J. (2024). Low-Frequency Vibrothermography Using Lightweight Piezoelectric Actuators: The Location of Excitation and Application to Composite Materials. In: Allen, M., Blough, J., Mains, M. (eds) Special Topics in Structural Dynamics & Experimental Techniques, Volume 5. SEM 2023. Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-37007-6_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-37007-6_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-37006-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-37007-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)