Abstract
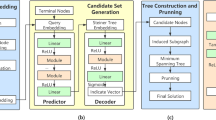
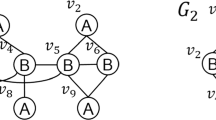
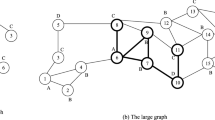
Reconstructing a subgraph through an embedding is very useful for many subgraph-level tasks, e.g., subgraph matching and minimum Steiner tree problem. To support subgraph reconstruction, a naive approach is materializing subgraph embeddings for all possible candidate subgraphs in advance, which is impractical since the subgraphs are exponential to the size of the input graph. Therefore, it is desired to devise a subgraph embedding based on which the subgraph can be reconstructed. To the end, we develop a novel reversible subgraph embedding in this paper. By importing the compressed sensing theory into learning node embeddings, we design a reversible read-out operation such that the aggregation vector can be recovered according to the subgraph embedding, where the aggregation vector acts as a bridge between the adjacency matrix and subgraph embedding. To reconstruct the structure of the subgraph from the decoded aggregation vector, we present a bijective rule by applying a simple transformation between binary number and decimal number with a scale operation. We conduct extensive experiments over real graphs to evaluate the proposed subgraph embedding. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method greatly and consistently outperforms the baselines in three tasks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolghasemi, V., Ferdowsi, S., Sanei, S.: A gradient-based alternating minimization approach for optimization of the measurement matrix in compressive sensing. Signal Process. 92(4), 999–1009 (2012)
Abu-El-Haija, S., Perozzi, B., Al-Rfou, R., Alemi, A.A.: Watch your step: learning node embeddings via graph attention. In: NeurIPS, pp. 9198–9208 (2018)
Adhikari, B., Zhang, Y., Ramakrishnan, N., Prakash, B.A.: Sub2vec: feature learning for subgraphs. In: PAKDD, pp. 170–182 (2018)
Ahmed, N., Natarajan, T., Rao, K.R.: Discrete cosine transform. IEEE Trans. Comput. 100(1), 90–93 (1974)
Bai, Y., Xu, D., Sun, Y., Wang, W.: GLSearch: maximum common subgraph detection via learning to search. In: ICML, vol. 139, pp. 588–598 (2021)
Balalau, O., Goyal, S.: SubRank: subgraph embeddings via a subgraph proximity measure. In: PAKDD, pp. 487–498 (2020)
Candes, E.J., Tao, T.: Decoding by linear programming. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 51(12), 4203–4215 (2005)
Fey, M., Lenssen, J.E., Weichert, F., Müller, H.: SplineCNN: fast geometric deep learning with continuous b-spline kernels. In: CVPR, pp. 869–877 (2018)
Ge, Y., Bertozzi, A.L.: Active learning for the subgraph matching problem. In: Big Data, pp. 2641–2649 (2021)
Grover, A., Leskovec, J.: node2vec: scalable feature learning for networks. In: SIGKDD, pp. 855–864 (2016)
Hao, Z., et al.: ASGN: an active semi-supervised graph neural network for molecular property prediction. In: SIGKDD, pp. 731–752. ACM (2020)
Huang, K., Zitnik, M.: Graph meta learning via local subgraphs. In: NeurIPS (2020)
Iwata, Y., Shigemura, T.: Separator-based pruned dynamic programming for steiner tree. In: AAAI, pp. 1520–1527 (2019)
Izadi, M.R., Fang, Y., Stevenson, R., Lin, L.: Optimization of graph neural networks with natural gradient descent. arXiv preprint arXiv:2008.09624 (2020)
Izadi, M.R., Fang, Y., Stevenson, R., Lin, L.: Optimization of graph neural networks with natural gradient descent. CoRR abs/2008.09624 (2020)
Jin, W., Ma, Y., Liu, X., Tang, X., Wang, S., Tang, J.: Graph structure learning for robust graph neural networks. In: SIGKDD, pp. 66–74. ACM (2020)
Kim, D., Oh, A.: Efficient representation learning of subgraphs by subgraph-to-node translation. CoRR abs/2204.04510 (2022)
Leskovec, J., Kleinberg, J., Faloutsos, C.: Graph evolution: densification and shrinking diameters. TKDD 1(1), 2-es (2007)
Ou, M., Cui, P., Pei, J., Zhang, Z., Zhu, W.: Asymmetric transitivity preserving graph embedding. In: SIGKDD, pp. 1105–1114 (2016)
Perozzi, B., Al-Rfou, R., Skiena, S.: Deepwalk: online learning of social representations. In: SIGKDD, pp. 701–710 (2014)
Sen, P., Namata, G., Bilgic, M., Getoor, L., Galligher, B., Eliassi-Rad, T.: Collective classification in network data. AI Mag. 29(3), 93–93 (2008)
Sun, S., Luo, Q.: In-memory subgraph matching: an in-depth study. In: SIGMOD, pp. 1083–1098. ACM (2020)
Tang, J., Qu, M., Wang, M., Zhang, M., Yan, J., Mei, Q.: Line: large-scale information network embedding. In: WWW, pp. 1067–1077 (2015)
Velickovic, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Liò, P., Bengio, Y.: Graph attention networks. In: ICLR, OpenReview.net (2018)
Wang, C., Liu, Z.: Graph representation learning by ensemble aggregating subgraphs via mutual information maximization. CoRR abs/2103.13125 (2021)
Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Qin, L., Wang, W., Zhang, W., Lin, X.: Reinforcement learning based query vertex ordering model for subgraph matching, pp. 245–258 (2022)
Xu, K., Hu, W., Leskovec, J., Jegelka, S.: How powerful are graph neural networks? In: ICLR (2018)
Yin, Y., Wei, Z.: Scalable graph embeddings via sparse transpose proximities. In: SIGKDD, pp. 1429–1437 (2019)
Zhang, J.: Segmented graph-BERT for graph instance modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.03283 (2020)
Zhang, J., Meng, L.: Gresnet: graph residual network for reviving deep gnns from suspended animation. CoRR abs/1909.05729 (2019)
Zhang, Z., Cui, P., Wang, X., Pei, J., Yao, X., Zhu, W.: Arbitrary-order proximity preserved network embedding. In: SIGKDD, pp. 2778–2786 (2018)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61902074).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yang, B., Zheng, W. (2023). Subgraph Reconstruction via Reversible Subgraph Embedding. In: Wang, X., et al. Database Systems for Advanced Applications. DASFAA 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13945. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30675-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30675-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-30674-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-30675-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)