Abstract
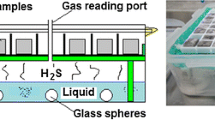
This chapter introduces a methodology to measure the rate of gaseous H2S transferring from sewer atmosphere to the exposed concrete surface. This facilitates the monitoring of sulfide-induced corrosion processes on concrete at various corrosion stages. In comparison to many existing methods, this methodology has the advantages of rapid measurement and non-destruction of the concrete sample. The H2S uptake rate (SUR) for a concrete coupon can be determined by measuring the gaseous H2S concentrations over time in a temperature- and humidity-controlled gas-tight reactor. The reliability of this method was evaluated by carrying out repeated tests on concrete coupons previously exposed to different corrosion conditions. The method could be applied to perform various research activities related to microbiologically influenced concrete corrosion, for instance, (1) understand sulfide uptake activity by concrete; (2) differentiate chemical and biological driven sulfide uptake activity; (3) evaluate the effectiveness of concrete control techniques; (4) estimate concrete corrosion rate in sewer systems; (5) investigate important factors affecting sulfide-induced concrete corrosion, particularly temperature, fluctuating gaseous H2S concentrations, oxygen concentrations, surface pH and relative humidity (RH).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aesoy, A., Osterhus, S.W., Bentzen, G.: Controlled treatment with nitrate in sewers to prevent concrete corrosion. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2, 137–144 (2002)
Buisman, C., Uspeert, P., Janssen, A., Lettinga, G.: Kinetics of chemical and biological sulphide oxidation in aqueous solutions. Water Res. (Oxford) 24, 667–671 (1990)
Cayford, B.I., Dennis, P.G., Keller, J., Tyson, G.W., Bond, P.L.: High-throughput amplicon sequencing reveals distinct communities within a corroding concrete sewer system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78, 7160–7162 (2012)
Cayford, B.I., Jiang, G., Keller, J., Tyson, G., Bond, P.L.: Comparison of microbial communities across sections of a corroding sewer pipe and the effects of wastewater flooding. Biofouling 33, 780–792 (2017)
Cayford, B.I., Dennis, P.G., Tyson, G.W., Bond, P.L.: Microbial communities involved in the corrosion of concrete sewer infrastructure. In: 14th International Symposium on Microbial Ecology (ISME14) (2012)
Chen, G.-H., Leung, D.H.-W.: Utilization of oxygen in a sanitary gravity sewer. Water Res. 34, 3813–3821 (2000)
Chen, K.Y., Morris, J.C.: Kinetics of oxidation of aqueous sulfide by oxygen. Environ. Sci. Technol. 6, 529–537 (1972)
Harremoës, P.: The significance of pore diffusion to filter denitrification. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 42, 377–388 (1976)
Jensen, H.S., Lens, P.N.L., Nielsen, J.L., Bester, K., Nielsen, A.H., Hvitved-Jacobsen, T., Vollertsen, J.: Growth kinetics of hydrogen sulfide oxidizing bacteria in corroded concrete from sewers. J. Hazard. Mater. 189, 685–691 (2011)
Jiang, G., Sun, X., Keller, J., Bond, P.L.: Identification of controlling factors for the initiation of corrosion of fresh concrete sewers. Water Res. 80, 30–40 (2015)
Jiang, G., Zhou, M., Chiu, T.H., Sun, X., Keller, J., Bond, P.L.: Wastewater-enhanced microbial corrosion of concrete sewers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50, 8084–8092 (2016)
Jiang, G., Bond, P., Keller, J.: Long term investigation of concrete corrosion processes in sewers. In: Ozwater’13, pp. 1–5 (2013)
Joseph, A.P., Keller, J., Bustamante, H., Bond, P.L.: Surface neutralization and H2S oxidation at early stages of sewer corrosion: influence of temperature, relative humidity and H2S concentration. Water Res. 46, 4235–4245 (2012)
Li, X., Bond, P.L., O’Moore, L., Wilkie, S., Hanzic, L., Johnson, I., Mueller, K., Yuan, Z., Jiang, G.: Increased resistance of nitrite-admixed concrete to microbially induced corrosion in real sewers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 2323–2333 (2020)
Li, X., Johnson, I., Mueller, K., Wilkie, S., Hanzic, L., Bond, P.L., O’Moore, L., Yuan, Z., Jiang, G.: Corrosion mitigation by nitrite spray on corroded concrete in a real sewer system. Sci. Total Environ. 806, 151328 (2022)
Li, X., O'Moore, L., Song, Y., Bond, P.L., Yuan, Z., Wilkie, S., Hanzic, L. and Jiang, G.: The rapid chemically induced corrosion of concrete sewers at high H2S concentration. Water. Res. 162, 95–104 (2019)
Millero, F.J., Hubinger, S., Fernandez, M., Garnett, S.: Oxidation of H2S in seawater as a function of temperature, pH, and ionic strength. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 439–443 (1987)
Nielsen, A.H., Hvitved-Jacobsen, T., Vollertsen, J.: Kinetics and stoichiometry of sulfide oxidation by sewer biofilms. Water Res. 39, 4119–4125 (2005)
Nielsen, A.H., Vollertsen, J., Jacobsen, T.H.: Chemical sulfide oxidation of wastewater—effects of pH and temperature. Water Sci. Technol. 50, 185–192 (2004)
Satoh, H., Odagiri, M., Ito, T., Okabe, S.: Microbial community structures and in situ sulfate-reducing and sulfur-oxidizing activities in biofilms developed on mortar specimens in a corroded sewer system. Water Res. 43, 4729–4739 (2009)
Sun, X., Jiang, G., Bond, P.L., Keller, J.: Impact of fluctuations in gaseous H2S concentrations on sulfide uptake by sewer concrete: the effect of high H2S loads. Water Res. 81, 84–91 (2015)
Sun, X., Jiang, G., Bond, P.L., Keller, J.: Periodic deprivation of gaseous hydrogen sulfide affects the activity of the concrete corrosion layer in sewers. Water Res. 157, 463–471 (2019)
Sun, X., Jiang, G., Bond, P.L., Keller, J., Yuan, Z.: A novel and simple treatment for control of sulfide induced sewer concrete corrosion using free nitrous acid. Water Res. 70, 179–187 (2015)
Sun, X., Jiang, G., Bond, P.L., Wells, T., Keller, J.: A rapid, non-destructive methodology to monitor activity of sulfide-induced corrosion of concrete based on H2S uptake rate. Water Res. 59, 229–238 (2014)
Sun, X., Jiang, G., Chiu, T.H., Zhou, M., Keller, J., Bond, P.L.: Effects of surface washing on the mitigation of concrete corrosion under sewer conditions. Cem. Concr. Compos. 68, 88–95 (2016)
Tamimi, A., Rinker, E.B., Sandall, O.C.: Diffusion coefficients for hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, and nitrous oxide in water over the temperature range 293–368 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 39, 330–332 (1994)
Vollertsen, J., Nielsen, A.H., Jensen, H.S., Wium-Andersen, T., Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.: Corrosion of concrete sewers—the kinetics of hydrogen sulfide oxidation. Sci. Total Environ. 394, 162–170 (2008)
Wells, T., Melchers, R.: An observation-based model for corrosion of concrete sewers under aggressive conditions. Cem. Concr. Res. 61, 1–10 (2014)
Wells, P.T., Melchers, R.: Findings of a 4 year study of concrete sewer pipe corrosion. In: Corrosion and prevention. Darwin, Northern Territory, Australia (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sun, X., Jiang, G., Keller, J., Bond, P., Li, X. (2023). Testing of Sulfide Uptake Rate (SUR) and Its Applications. In: Jiang, G. (eds) Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Concrete Sewers . Engineering Materials. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-29941-4_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-29941-4_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-29940-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-29941-4
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)