Abstract
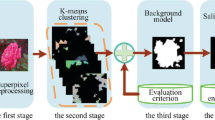
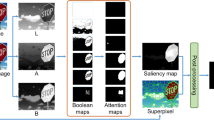
The study of salient image is related to the method for detecting the most prominent area within the image. There were numbers of methods applied in describing the image saliency, and the models’ integration with the learning techniques has been able to provide tremendous achievement on the results of salient object detection. However, the approach that is able to describe the saliency existence has never been seriously discussed, and therefore, many models are still unable to produce correct detection for the non-salient image. The non-salient image is a type of image that does not contain any important information. This paper presents a method that can describe the saliency existence of images based on the boundary compactness hypothesis with fact that the compactness of a non-salient image is spatially distributed as being referred to its boundary compared to the salient image. The saliency features were extracted from the image background measurement that consists of boundary contrast compactness and boundary spatial distribution compactness. These compactness components were computed for all image’s superpixel patches and compared with its boundary patches. As these features were computed in the spatial domain, the fast Fourier transform is applied to obtain the saliency features in the frequency domain. Experimental results show that the proposed approach achieve the highest mean difference ratio of 21.65 compared to the state-of-the-art approaches in putting distinct value to identify the saliency existence.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achanta R, Shaji A, Smith K, Lucchi A, Fua P, Süsstrunk S (2012) SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(11):2274–2282
Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F, Susstrunk S (2009) Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1597–1604
Borji A, Sihite DN, Itti L (2012) Salient object detection: a benchmark. In: Fitzgibbon A, Lazebnik S, Perona P, Sato Y, Schmid C (eds) Computer vision—ECCV 2012. ECCV 2012. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 7573. Springer, Heidelberg
Borji A, Cheng MM, Jiang H, Li J (2019) Salient object detection: a survey. Comp Visual Media 1–26
Islam MA, Kalash M, Bruce NDB (2018) Revisiting salient object detection: simultaneous detection, ranking, and subitizing of multiple salient objects. In: IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7142–7150
Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E (1998) A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20(11):1254–1259
Jiang H, Wang J, Yuan Z, Wu Y, Zheng N, Li S (2013a) Salient object detection: a discriminative regional feature integration approach. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Jiang B, Zhang L, Lu H, Yang C, Yang MH (2013b) Saliency detection via absorbing Markov chain. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1665–1672
Jiang H, Cheng MM, Li SJ et al (2019) Joint salient object detection and existence prediction. Front Comput Sci 778–788
Kim J, Han D, Tai YW, Kim J (2016) Salient region detection via high-dimensional color transform and local spatial support. IEEE Trans Image Process 883–890
Kruthiventi SSS, Gudisa V, Dholakiya JH, Babu RV (2016) Saliency unified : a deep architecture for simultaneous eye fixation prediction and salient object segmentation. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5781–5790
Liang M, Hu X (2015) Feature selection in supervised saliency predictio. IEEE Trans Cybern 45(5):914–926
Lin W, Niu Y, Lin J, Chen Y (2017) Learning from neighbours for saliency optimization. In: Computing conference, pp 1406–1409
Liu T, Sun J, Zheng NN, Tang X, Shum HY (2007) Learning to detect a salient object. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–8
Nadzri NZ, Marhaban MH, Ahmad SA (2019) Improved salient object detection via boundary components affinity. Pertanika J Sci Technol 27(4):1735–1758
Pan J, Canton-Ferrer C, Mcguinness K, OConnor NE, Torres J, Sayrol E (2017) SalGAN: visual saliency prediction with adversarial networks. In: Computer vision and patter recognition, pp 1–9
Perazzi F, Krähenbühl P, Pritch Y, Hornung A (2012). Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 733–740
Wang P, Wang J, Zeng G, Feng J, Zha H, Li S (2012) Salient object detection for searched web images via global saliency. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Wei Y, Wen F, Zhu W, Sun J (2012) Geodesic saliency using background priors. In: Fitzgibbon A, Lazebnik S, Perona P, Sato Y, Schmid C (eds) Computer vision—ECCV 2012. ECCV 2012. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 7574. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 29–42
Xia C, Li J, Chen X, Zheng A, Zhang Y (2017) What is and what is not a salient object? Learning salient object detector by ensembling linear exemplar regressors. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 4399–4407
Yan Q, Xu L, Shi J, Jia J (2013) Hierarchical saliency detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1155–1162
Yang C, Zhang L, Lu H, Ruan X, Yang MH (2013). Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3166–3173
Zhang Q, Lin J, Li W et al (2018) Salient object detection via compactness and objectness cues. Vis Comput 34:473–489
Zhang J et al (2015) Salient object subitizing. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 4045–4054
Zhao R, Ouyang W, Li W, Wang X (2015) Saliency detection by multi-context deep learning. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1265–1274
Zhu W, Liang S, Wei Y, Sun J (2014) Saliency optimization from robust background detection. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2814–2821
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Nadzri, N.Z., Marhaban, M.H., Ahmad, S.A., Ishak, A.J. (2023). Feature Presentation of Image Saliency Existence Based on Boundary Compactness Hypothesis. In: Ismail, A., Nur Zulkipli, F., Mohd Daril, M.A., Öchsner, A. (eds) Materials Innovations and Solutions in Science and Technology. Advanced Structured Materials, vol 173. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26636-2_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26636-2_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-26635-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-26636-2
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)