Abstract
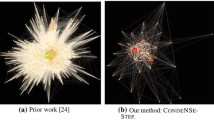
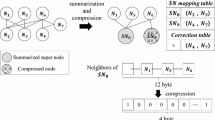
Real-world graphs can be difficult to interpret and visualize beyond a certain size. To address this issue, graph summarization aims to simplify and shrink a graph, while maintaining its high-level structure and characteristics. Most summarization methods are designed for homogeneous, undirected, simple graphs; however, many real-world graphs are ornate; with characteristics including node labels, directed edges, edge multiplicities, and self-loops. In this paper we propose TG-sum, a versatile yet rigorous graph summarization model that (to the best of our knowledge, for the first time) can handle graphs with all the aforementioned characteristics (and any combination thereof). Moreover, our proposed model captures basic sub-structures that are prevalent in real-world graphs, such as cliques, stars, etc. Experiments demonstrate that TG-sum facilitates the visualization of real-world complex graphs, revealing interpretable structures and high-level relationships. Furthermore, TG-sum achieves better trade-off between compression rate and running time, relative to existing methods (only) on comparable settings.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
\(L_\mathbb {N}(k)=2\log k +1\) bits are required to encode an arbitrarily large natural number k, using the variable-length prefix-free encoding; see, Ex. 2.4 in [12].
- 2.
References
Adamic, L.A., Glance, N.: The political blogosphere and the 2004 us election: divided they blog. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Link Discovery, pp. 36–43 (2005)
Adler, M., Mitzenmacher, M.: Towards compressing web graphs. In: Data Compression Conference IEEE Computer Society (2001)
Akoglu, L.: Quantifying political polarity based on bipartite opinion networks. In: ICWSM (2014)
Andoni, A., Indyk, P.: Near-optimal hashing algorithms for approximate nearest neighbor in high dimensions. Commun. ACM, pp. 117–122 (2008)
Besta, M., Hoefler, T.: Survey and taxonomy of lossless graph compression and space-efficient graph representations (2018). arxiv:1806.01799
Boldi, P., Vigna, S.: The webgraph framework i: compression techniques. In: WWW, pp. 595–602 (2004)
Buehrer, G., Chellapilla, K.: A scalable pattern mining approach to web graph compression with communities. In: WSDM, pp. 95–106. ACM (2008)
Chong, E.K., Zak, S.H.: An introduction to optimization. John Wiley & Sons (2004)
Cook, D.J., Holder, L.B.: Substructure discovery using minimum description length and background knowledge. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 1, 231–255 (1993)
Dunne, C., Shneiderman, B.: Motif simplification: improving network visualization readability with fan, connector, and clique glyphs. In: SIGCHI, pp. 3247–3256 (2013)
Giles, C.L., Bollacker, K.D., Lawrence, S.: CiteSeer: an automatic citation indexing system. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Digital Libraries, pp. 89–98 (1998)
Grünwald, P.D.: The Minimum Description Length Principle. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA (2007)
Kang, U., Faloutsos, C.: Beyond ‘caveman communities’: hubs and spokes for graph compression and mining. In: ICDM, pp. 300–309 (2011)
Khan, K.U., Nawaz, W., Lee, Y.K.: Set-based approximate approach for lossless graph summarization. Computing 97(12) (2015)
Koutra, D., Kang, U., Vreeken, J., Faloutsos, C.: Summarizing and understanding large graphs. Statist. Anal. Data Min. 8(3), 183–202 (2015)
LeFevre, K., Terzi, E.: Grass: graph structure summarization. In: SDM, pp. 454–465. SIAM (2010)
Liakos, P., Papakonstantinopoulou, K., Sioutis, M.: Pushing the envelope in graph compression. In: CIKM, pp. 1549–1558 (2014)
Liu, Y., Safavi, T., Dighe, A., Koutra, D.: Graph summarization methods and applications: a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 51(3), 1–34 (2018)
Liu, Z., Yu, J.X., Cheng, H.: Approximate homogeneous graph summarization. Info. Media Tech. 7(1), 32–43 (2012)
Navlakha, S., Rastogi, R., Shrivastava, N.: Graph summarization with bounded error. In: SIGMOD, pp. 419–432. ACM (2008)
Oughtred, R., et al.: The biogrid interaction database 47(D1), D529–D541 (2019)
Pattabiraman, B., Patwary, M.M.A., Gebremedhin, A.H., Liao, W.K., Choudhary, A.: Fast algorithms for the maximum clique problem on massive sparse graphs. In: International Workshop. AMWG (2013)
Riondato, M., García-Soriano, D., Bonchi, F.: Graph summarization with quality guarantees. Data Min. Knowl. Disc. 31(2), 314–349 (2017)
Shin, K., Ghoting, A., Kim, M., Raghavan, H.: SWeG: lossless and lossy summarization of web-scale graphs. In: WWW, pp. 1679–1690. ACM (2019)
Tian, Y., Hankins, R., Patel, J.: Efficient aggregation for graph summarization. In: SIGMOD (2008)
Toivonen, H., Zhou, F., Hartikainen, A., Hinkka, A.: Compression of weighted graphs. In: KDD (2011)
Ying, Z., You, J., Morris, C., Ren, X., Hamilton, W., Leskovec, J.: Hierarchical graph representation learning with differentiable pooling. In: NeurIPS, pp. 4800–4810 (2018)
Zhu, L., Ghasemi-Gol, M., Szekely, P., Galstyan, A., Knoblock, C.A.: Unsupervised entity resolution on multi-type graphs. In: International Semantic Web Conference, pp. 649–667 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work has been sponsored by the U.S. National Science Foundation CAREER 1452425 and the PwC Risk and Regulatory Services Innovation Center at Carnegie Mellon University. Any conclusions expressed in this material are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views, expressed or implied, of the funding parties.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Berberidis, D., Liang, P.J., Akoglu, L. (2023). Summarizing Labeled Multi-graphs. In: Amini, MR., Canu, S., Fischer, A., Guns, T., Kralj Novak, P., Tsoumakas, G. (eds) Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. ECML PKDD 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 13714. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26390-3_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26390-3_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-26389-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-26390-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)