Abstract
Purpose: The paper explored the potential of Burnt clay grinding pot waste powder (BCGPWP) as a partial replacement for Ordinary Portland Cement for concrete production.
Design/Methodology/Approach: Given such aim, chemical analysis was conducted on the (BCGPWP)in the Ghana Water Company laboratory. One hundred and five (105) concrete cubes were prepared and tested for compressive and split tensile strength. The mix ratio for the specimen were 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and 30% respectively. A concrete mix ratio of 1:2:4 was used. The (BCGPWP) percentages formed part of the one-part cement. The concrete specimen was cured for twenty-eight (28) days under the shed, covered with woolen material and sprinkle with water on them every day. The compressive and split tensile tests were done on the 7, 14, 21 and 28 days.
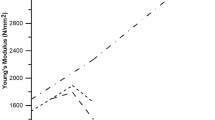
Findings: It was established that the sample contains about eight essential oxides found in Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC). The constituents were Calcium oxide (CaO), Silica oxide (Sio2), Iron oxide(fe2O3), Aluminium oxide (Al2O3), Magnesium oxide (MgO), and Sodium oxide (Na2O), Potassium Oxide (K2O) and Sulphur Oxide (SO3). On the 28th day of testing, the control specimen had 17.05 N/mm2, 5% replacement had 16.53%, 10% replacement also recorded 16.55 N/mm2 with 15% declining to 7.46 N/mm2. Twenty percent went up to 17.57 N/mm2 with 25% registering a compressive strength of 15.18 N/mm2 while the 30% recorded 15.35 N/mm2.
Implications/Research Limitations: The study could not ascertain the type of clay used for the production of the traditional burnt clay grinding pot. Again, the study could not unearth the temperature at which the pot/pot waste were subjected to before it came out of the fire.
Practical Implications: The usage of Burnt clay grinding pot waste powder as a partial replacement for Ordinary Portland Cement for concrete production will help to reduce the cost of construction.
Social Implications: It will help in improving the environment by recycling waste into construction materials for use.
Originality/Value: The use of burnt clay grinding pot waste powder as a partial replacement for Ordinary Portland Cement for concrete production is a novelty in construction material development.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullahi, M.: Properties of some fine aggregates in minna. Niger. Environs Leonardo J. Sci. 8, 1–6 (2006)
Agbede, I.O., Manasseh, J.: (2008) Use of cement-sand admixture in laterite bricks production for low-cost housing. Leonardo Electron. J. Prctices Technol. 12, 163–174 (2008)
Sholanke, A.B., Fagbenl, I.O., Aderonmu, P.A., Ajagbe, M.A.: Sandcrete block and brick production in nigeria - prospects and challenges. IIARD Int. J. Geogr. Environ. Manage. 1(8) (2015). ISSN 2505–8821
.Graphic online. Graphic online Housing deficit now 2 million units (2021). (https://www.graphic.com.gh/news/general-news/housing-deficit-now-2-million-units-minister.html).Accessed 19 Apr 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nimo-Boakye, A., Nana-Addy, E., Adinkrah-Appiah, K. (2023). Burnt Clay Grinding Pot Waste Powder as a Partial Replacement of Ordinary Portland Cement for Concrete Production. In: Aigbavboa, C., et al. Sustainable Education and Development – Sustainable Industrialization and Innovation. ARCA 2022. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25998-2_73
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25998-2_73
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25997-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25998-2
eBook Packages: Business and ManagementBusiness and Management (R0)