Abstract
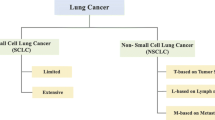
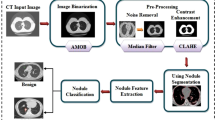
The main objective of the proposed work is to develop an automated CAD system for classification of lung nodules using various classifiers from CT images. The classification of nodule and non-nodule patterns in CT is one of the most significant processes during the detection of lung nodule. This helps in detecting the disease at early stage thereby decrease the mortality rate. The developed CAD systems consist of segmentation, feature extraction and classification. For Segmentation we used Fuzzy C Means (FCM) for effective extraction infected region. Later, we extracted features through First order statistics (FOS) and Second order statistics (SOS) and fed into classifiers like DS, RF and BPNN. The experimentation is conducted on LIDC-IDRI dataset and results outperforms well with BPNN when compare to other classifiers.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari, R., Ziarati, K.: A rank based particle swarm optimization algorithm with dynamic adaptation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 235(8), 2694–2714 (2011)
Aoyama, M., Li, Q., Katsuragawa, S., Li, F., Sone, S.: Computerized scheme for determination of the likelihood measure of malignancy for pulmonary nodules on low- dose ct images. Med. Phys. 30(3), 387–394 (2003)
Armato, S.G., Giger, M.L., Moran, C.J., Blackburn, J.T., Doi, K., MacMahon, H.: Computerized detection of pulmonary nodules on ct scans. Radiographics 19(5), 1303–1311 (1999)
Armato, S.G., et al.: Guest editorial: Lungx chal- lenge for computerized lung nodule classification: Reflections and lessons learned. J. Med. Imag. 2(2), 1–5 (2015)
Armato, S.G., et al.: The lung image database consortium (lidc) and image database resource initiative (idri): A completed reference database of lung nodules on Ct scans. Med. Phys. 38(2), 915–931 (2011)
Arumugam, M.S., Rao, M.: On the performance of the particle swarm optimiza- tion algorithm with various inertia weight variants for computing optimal control of a class of hybrid systems. In: Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society (2006)
Choi, W.-J., Choi, T.-S.: Automated pulmonary nodule detection based on three-dimensional shape-based feature descriptor. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 113(1), 37–54 (2014)
Criminisi, A., Shotton, J., Bucciarelli, S.: Decision forests with long-range spatial context for organ localization in CT volumes. In: MICCAI Workshop on Probabilistic Models for Medical Image Analysis, Vol. 1 (2009)
Cross, G.R., Jain, A.K.: Markov random field texmre models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1, 25–39 (1983)
Da Silva Sousa, J.R.F., Silva, A.C., de Paiva, A.C., Nunes, R.A.: Methodology for automatic detection of lung nodules in computerized tomography images. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 98(1), 1–14 (2010)
Dai, S., Lu, K., Dong, J., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y.: A novel approach of lung segmen- tation on chest ct images using graph cuts. Neurocomputing 168, 799–807 (2015)
Daneshmand, F., Mehrshad, N., Massinaei, M.: A new approach for froth image seg- mentation using fuzzy logic. In First Iranian Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis (PRIA). IEEE (2013)
Dawoud, A.: Lung segmentation in chest radiographs by fusing shape information in iterative thresholding. IET Comput. Vision 5(3), 185–190 (2011)
Sluimer, I., Prokop, M., van Ginneken, B.: Toward automated segmentation of the pathological lung in CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 24(8), 1025–1038 (2005)
Deep, G., Kaur, L., Gupta, S.: Lung nodule segmentation in ct images using ro- tation invariant local binary pattern. Int. J. Sig. Image Process. 4(1), 20 (2013)
Dehmeshki, J., Amin, H., Valdivieso, M., Ye, X.: Segmentation of pulmonary nodules in thoracic ct scans: A region growing approach. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 27(4), 467–480 (2008)
Dehmeshki, J., Ye, X., Lin, X., Valdivieso, M., Amin, H.: Automated detection of lung nodules in ct images using shape-based genetic algorithm. Comput. Med. Imag. Graph. 31(6), 408–417 (2007)
Delogu, P., Cheran, S., De Mitri, I., De Nunzio, G., Fantacci, M., Fauci, F., Gargano, G., Torres, E. L., Massafra, R., Oliva, P., et al.: Preprocessing methods for nodule detection in lung ct. In International Congress Series, Vol. 1281. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2005)
Dheepak, G., Premkumar, S., Ramachandran, R.: Lung cancer detection by using artificial neural network and fuzzy clustering method (2015)
Doi, K.: Computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging: Historical review, current status and future potential. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 31(4), 198–211 (2007)
Dolejsi, M., Kybic, J., Polovincak, M., Tuma, S.: The lung time: Annotated lung nodule dataset and nodule detection framework. In: SPIE Medical Imaging. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2009)
Elizabeth, D., Nehemiah, H., Raj, C.R., Kannan, A.: Computer-aided diagno- sis of lung cancer based on analysis of the significant slice of chest computed tomography image. IET Image Process. 6(6), 697–705 (2012)
Enquobahrie, A.A., Reeves, A.P., Yankelevitz, D.F., Henschke, C.I.: Auto- mated detection of small pulmonary nodules in whole lung ct scans. Acad. Radiol. 14(5), 579–593 (2007)
Balakrishna, K., Rao, M.: Tomato plant leaves disease classification using KNN and PNN. Int. J. Comput. Vis. Image Process. 9(1), 51–63 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4018/IJCVIP.2019010104
Farag, A., Ali, A., Graham, J., Farag, A., Elshazly, S., Falk, R.: Evaluation of geometric feature descriptors for detection and classification of lung nodules in low dose ct scans of the chest. In IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro. IEEE (2011)
Farag, A. A., Abdelmunim, H., Graham, J., Farag, A. A., Elshazly, S., El-Mogy, S., El-Mogy, M., Falk, R., Al-Jafary, S., Mahdi, H. et al.: Variational approach for segmentation of lung nodules. In IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). IEEE (2011b)
Gambhir, S., et al.: Analytical decision model for the cost-effective management of solitary pulmonary nodules. J. Clin. Oncol. 16(6), 2113–2125 (1998)
Garro, B. A. and R. A. Vazquez (2015). Designing artificial neural networks using particle swarm optimization algorithms. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 61 (2015)
Golosio, B., et al.: A novel multithreshold method for nodule detection in lung ct. Med. Phys. 36(8), 3607–3618 (2009)
Gomathi, M., Thangaraj, P.: A computer aided diagnosis system for detection of lung cancer nodules using extreme learning machine. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2(10), 5770–5779 (2010)
Gomathi, M., Thangaraj, P.: A computer aided diagnosis system for lung cancer detection using support vector machine. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 7(12), 1532 (2010)
Gonalves, L., Novo, J., Campilho, A.: Hessian based approaches for 3d lung nodule segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 61, 1–15 (2016)
Gould, M.K., et al.: Evaluation of individuals with pulmonary nodules: when is it lung cancer. Chest 143(5 Suppl), 93S-120S (2013)
Grigorescu, S.E., Petkov, N., Kruizinga, P.: Comparison of texmre features based on gabor filters. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 11(10), 1160–1167 (2002)
Gu, Y., et al.: Automated delineation of lung tumors from ct images using a single click ensemble segmentation approach. Pattern Recog. 46(3), 692–702 (2013)
Gudise, V. G., Venayagamoorthy, G. K.: Comparison of particle swarm optimization and backpropagation as training algorithms for neural networks. In Swarm Intelligence Symposium. IEEE (2003)
Hua, P., Song, Q., Sonka, M., Hoffman, E. A., Reinhardt, J. M.: Segmentation of pathological and diseased lung tissue in ct images using a graph-search algorithm. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro. IEEE (2011)
Jacobs, C., Murphy, K., Twellmann, T., de Jong, P. A., van Ginneken, B.: Computer- aided detection of solid and ground glass nodules in thoracic ct images using two independent cad systems. In: The Fourth International Workshop on Pulmonary Image Analysis (2011)
Shen, S., Bui, A.A., Cong, J., Hsu, W.: An automated lung segmentation approach using bidirectional chain codes to improve nodule detection accuracy. Comput. Biol. Med. 57, 139–149 (2015)
Shen, S., Sandham, W., Granat, M., Sterr, A.: Mri fuzzy segmentation of brain tissue using neighborhood attraction with neural-network optimization. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 9(3), 459–467 (2005)
Shi, Y., Eberhart, R.: A modified particle swarm optimizer. In: Evolutionary Computation Proceedings, 1998. IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence, The 1998 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE (1998)
Shih-Chung, B.L., Freedman, M.T., Lin, J.-S., Mun, S.K.: Automatic lung nodule detection using profile matching and back-propagation neural network techniques. J. Dig. Imaging 6(1), 48–54 (1993)
Yuan, J.: Active contour driven by local divergence energies for ultrasound image segmentation. IET Image Process. 7(3), 252–259 (2013)
Zhou, S., Cheng, Y., Tamura, S.: Automated lung segmentation and smoothing techniques for inclusion of juxtapleural nodules and pulmonary vessels on chest ct images. Biomed. Sig. Process. Control 13, 62–67 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kumar, Y.H.S., Smithashree, K.P. (2022). An Automated CAD System for Classification of Lung Module. In: Guru, D.S., Y. H., S.K., K., B., Agrawal, R.K., Ichino, M. (eds) Cognition and Recognition. ICCR 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1697. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22405-8_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22405-8_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-22404-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-22405-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)