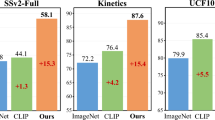
Abstract
Image-based visual-language (I-VL) pre-training has shown great success for learning joint visual-textual representations from large-scale web data, revealing remarkable ability for “zero-shot” generalisation. This paper presents a simple but strong baseline to efficiently adapt the pre-trained I-VL model for video understanding tasks, with minimal training. Specifically, we propose to optimise a few random vectors, termed as “continuous prompt vectors”, that convert video-related tasks into the same format as the pre-training objectives. In addition, to bridge the gap between static images and videos, temporal information is encoded with lightweight Transformers stacking on top of frame-wise visual features. Experimentally, we conduct extensive ablation studies to analyse the critical components. On ten public benchmarks of action recognition, action localisation, and text-video retrieval, across closed-set, few-shot, and zero-shot scenarios, we achieve competitive or state-of-the-art performance to existing methods, despite optimising significantly fewer parameters. Due to space limitation, we refer the readers to the arXiv version at https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04478.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anne Hendricks, L., Wang, O., Shechtman, E., Sivic, J., Darrell, T., Russell, B.: Localizing moments in video with natural language. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2017)
Bain, M., Nagrani, A., Varol, G., Zisserman, A.: Frozen in time: a joint video and image encoder for end-to-end retrieval. Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2021)
Bertasius, G., Wang, H., Torresani, L.: Is space-time attention all you need for video understanding? In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (2021)
Bishay, M., Zoumpourlis, G., Patras, I.: TARN: temporal attentive relation network for few-shot and zero-shot action recognition. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (2019)
Brattoli, B., Tighe, J., Zhdanov, F., Perona, P., Chalupka, K.: Rethinking zero-shot video classification: end-to-end training for realistic applications. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2020)
Brown, T., et al.: Language models are few-shot learners. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2020)
Buch, S., Escorcia, V., Ghanem, B., Fei-Fei, L., Niebles, J.C.: End-to-end, single-stream temporal action detection in untrimmed videos. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (2019)
Cao, K., Ji, J., Cao, Z., Chang, C.Y., Niebles, J.C.: Few-shot video classification via temporal alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2020)
Carreira, J., Noland, E., Hillier, C., Zisserman, A.: A short note on the kinetics-700 human action dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.06987 (2019)
Carreira, J., Zisserman, A.: Quo Vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2017)
Chao, Y.W., Vijayanarasimhan, S., Seybold, B., Ross, D.A., Deng, J., Sukthankar, R.: Rethinking the faster R-CNN architecture for temporal action localisation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2018)
Croitoru, I., et al.: TeachText: crossmodal generalized distillation for text-video retrieval. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2021)
Dwivedi, S.K., Gupta, V., Mitra, R., Ahmed, S., Jain, A.: ProtoGAN: towards few shot learning for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2019)
Feichtenhofer, C.: X3D: expanding architectures for efficient video recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2020)
Feichtenhofer, C., Fan, H., Malik, J., He, K.: SlowFast networks for video recognition. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2019)
Feichtenhofer, C., Pinz, A., Zisserman, A.: Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Frome, A., et al.: Devise: a deep visual-semantic embedding model. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2013)
Gabeur, V., Sun, C., Alahari, K., Schmid, C.: Multi-modal transformer for video retrieval. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12349, pp. 214–229. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58548-8_13
Gan, C., Yang, T., Gongi, B.: Learning attributes equals multi-source domain generalization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Gan, C., Yang, Y., Zhu, L., Zhao, D., Zhuang, Y.: Recognizing an action using its name: a knowledge-based approach. Int. J. Comput. Vision 120, 61–77 (2016)
Gao, P., et al.: Clip-adapter: better vision-language models with feature adapters. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.04544 (2021)
Gao, T., Fisch, A., Chen, D.: Making pre-trained language models better few-shot learners. In: Association for Computational Linguistics (2021)
Gao, Z., Wang, L., Zhang, Q., Niu, Z., Zheng, N., Hua, G.: Video imprint segmentation for temporal action detection in untrimmed videos. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2019)
Ha, D., Dai, A., Le, Q.: Hypernetworks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (2016)
Han, T., Xie, W., Zisserman, A.: Temporal alignment network for long-term video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2022)
Hara, K., Kataoka, H., Satoh, Y.: Can spatiotemporal 3d CNNs retrace the history of 2d CNNs and ImageNet? In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2018)
Heilbron, F.C., Escorcia, V., Ghanem, B., Niebles, J.C.: ActivityNet: a large-scale video benchmark for human activity understanding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2015)
Jain, M., Van Gemert, J.C., Mensink, T., Snoek, C.G.: Objects2action: classifying and localizing actions without any video example. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2015)
Jain, M., Van Gemert, J.C., Snoek, C.G.: What do 15,000 object categories tell us about classifying and localizing actions? In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2015)
Jia, C., et al.: Scaling up visual and vision-language representation learning with noisy text supervision. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (2021)
Jia, M., et al.: Visual prompt tuning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.12119 (2022)
Jiang, Y.G., et al.: THUMOS challenge: action recognition with a large number of classes (2014). https://crcv.ucf.edu/THUMOS14/
Jiang, Z., Xu, F.F., Araki, J., Neubig, G.: How can we know what language models know? Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 8, 423–438 (2020)
Ju, C., Zhao, P., Chen, S., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Tian, Q.: Divide and conquer for single-frame temporal action localization. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2021)
Ju, C., Zhao, P., Chen, S., Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., Tian, Q.: Adaptive mutual supervision for weakly-supervised temporal action localization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.02357 (2021)
Kay, W., et al.: The kinetics human action video dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.06950 (2017)
Kuehne, H., Jhuang, H., Garrote, E., Poggio, T., Serre, T.: HMDB: a large video database for human motion recognition. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2011)
Lei, J., et al.: Less is more: ClipBERT for video-and-language learning via sparse sampling. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2021)
Lester, B., Al-Rfou, R., Constant, N.: The power of scale for parameter-efficient prompt tuning. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (2021)
Li, X.L., Liang, P.: Prefix-tuning: optimizing continuous prompts for generation. In: Association for Computational Linguistics (2021)
Li, Y., hung Hu, S., Li, B.: Recognizing unseen actions in a domain-adapted embedding space. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (2016)
Lin, C., et al.: Learning salient boundary feature for anchor-free temporal action localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2021)
Lin, J., Gan, C., Han, S.: TSM: temporal shift module for efficient video understanding. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2019)
Lin, T., Liu, X., Li, X., Ding, E., Wen, S.: BMN: boundary-matching network for temporal action proposal generation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2019)
Lin, T., Zhao, X., Shou, Z.: Single shot temporal action detection. In: Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia (2017)
Lin, T., Zhao, X., Su, H., Wang, C., Yang, M.: BSN: boundary sensitive network for temporal action proposal generation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11208, pp. 3–21. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01225-0_1
Liu, J., Kuipers, B., Savarese, S.: Recognizing human actions by attributes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2011)
Liu, Y., Albanie, S., Nagrani, A., Zisserman, A.: Use what you have: video retrieval using representations from collaborative experts. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (2019)
Loshchilov, I., Hutter, F.: Decoupled weight decay regularization. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (2019)
Luo, H., et al.: CLIP4Clip: an empirical study of clip for end to end video clip retrieval. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.08860 (2021)
Mettes, P., Thong, W., Snoek, C.G.M.: Object priors for classifying and localizing unseen actions. Int. J. Comput. Vision 129, 1954–1971 (2021)
Miech, A., Alayrac, J.B., Smaira, L., Laptev, I., Sivic, J., Zisserman, A.: End-to-end learning of visual representations from uncurated instructional videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2020)
Miech, A., Laptev, I., Sivic, J.: Learning a text-video embedding from incomplete and heterogeneous data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02516 (2018)
Mishra, A., Pandey, A., Murthy, H.A.: Zero-shot learning for action recognition using synthesized features. Neurocomputing 390, 117–130 (2020)
Monfort, M., et al.: Spoken moments: learning joint audio-visual representations from video descriptions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2021)
Monfort, M., et al.: Multi-moments in time: Learning and interpreting models for multi-action video understanding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 1 (2021)
Mori, Y., Takahashi, H., Oka, R.: Image-to-word transformation based on dividing and vector quantizing images with words. In: First International Workshop on Multimedia Intelligent Storage and Retrieval Management (ACM Multimedia Conference) (1999)
Nawhal, M., Mori, G.: Activity graph transformer for temporal action localization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.08540 (2021)
Perrett, T., Masullo, A., Burghardt, T., Mirmehdi, M., Damen, D.: Temporal relational cross transformers for few-shot action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2021)
Radford, A., et al.: Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (2021)
Rohrbach, A., et al.: Movie description. Int. J. Comput. Vision 123, 94–120 (2017)
Schick, T., Schütze, H.: Exploiting cloze questions for few shot text classification and natural language inference. In: Proceedings of the Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (2021)
Shin, T., Razeghi, Y., IV, R.L.L., Wallace, E., Singh, S.: AutoPrompt: eliciting knowledge from language models with automatically generated prompts. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (2020)
Shou, Z., Chan, J., Zareian, A., Miyazawa, K., Chang, S.F.: CDC: convolutional-de-convolutional networks for precise temporal action localization in untrimmed videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2017)
Shou, Z., Wang, D., Chang, S.F.: Temporal action localization in untrimmed videos via multi-stage CNNs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2014)
Soomro, K., Zamir, A.R., Shah, M.: UCF101: a dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. arXiv preprint arXiv:1212.0402 (2012)
Su, H., Gan, W., Wu, W., Qiao, Y., Yan, J.: BSN++: complementary boundary regressor with scale-balanced relation modeling for temporal action proposal generation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2021)
Tan, J., Tang, J., Wang, L., Wu, G.: Relaxed transformer decoders for direct action proposal generation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2021)
Tran, D., Wang, H., Torresani, L., Ray, J., LeCun, Y., Paluri, M.: A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2018)
Wang, L., et al.: Temporal segment networks: towards good practices for deep action recognition. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9912, pp. 20–36. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_2
Wang, M., Xing, J., Liu, Y.: ActionCLIP: a new paradigm for video action recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.08472 (2021)
Wang, Q., Zhang, Y., Zheng, Y., Pan, P.: RCL: recurrent continuous localization for temporal action detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2022)
Wang, X., Girshick, R., Gupta, A., He, K.: Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2018)
Weston, J., Bengio, S., Usunier, N.: WSABIE: scaling up to large vocabulary image annotation. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2011)
Xie, S., Sun, C., Huang, J., Tu, Z., Murphy, K.: Rethinking spatiotemporal feature learning: speed-accuracy trade-offs in video classification. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11219, pp. 318–335. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01267-0_19
Xu, H., Das, A., Saenko, K.: R-C3D: region convolutional 3d network for temporal activity detection. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2017)
Xu, J., Mei, T., Yao, T., Rui, Y.: MSR-VTT: a large video description dataset for bridging video and language. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Xu, M., Zhao, C., Rojas, D.S., Thabet, A., Ghanem, B.: G-TAD: sub-graph localization for temporal action detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2020)
Yang, L., Peng, H., Zhang, D., Fu, J., Han, J.: Revisiting anchor mechanisms for temporal action localization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 8535–8548 (2020)
Yao, L., et al.: FILIP: fine-grained interactive language-image pre-training. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (2022)
Yeung, S., Russakovsky, O., Mori, G., Fei-Fei, L.: End-to-end learning of action detection from frame glimpses in videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Yu, Y., Kim, J., Kim, G.: A joint sequence fusion model for video question answering and retrieval. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 487–503. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_29
Zhang, C., Wu, J., Li, Y.: ActionFormer: localizing moments of actions with transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.07925 (2022)
Zhang, H., Zhang, L., Qi, X., Li, H., Torr, P.H.S., Koniusz, P.: Few-shot action recognition with permutation-invariant attention. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12350, pp. 525–542. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58558-7_31
Zhang, R., et al.: Tip-adapter: training-free clip-adapter for better vision-language modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.03930 (2021)
Zhao, P., Xie, L., Ju, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Tian, Q.: Bottom-up temporal action localization with mutual regularization. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12353, pp. 539–555. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58598-3_32
Zhao, Y., Xiong, Y., Wang, L., Wu, Z., Tang, X., Lin, D.: Temporal action detection with structured segment networks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (2017)
Zhou, K., Yang, J., Loy, C.C., Liu, Z.: Learning to prompt for vision-language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.01134 (2021)
Zhou, K., Yang, J., Loy, C.C., Liu, Z.: Conditional prompt learning for vision-language models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2022)
Zhu, L., Yang, Y.: Compound memory networks for few-shot video classification. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11211, pp. 782–797. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_46
Zhu, L., Yang, Y.: Label independent memory for semi-supervised few-shot video classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44, 273–285 (2020)
Zhu, X., Toisoul, A., Perez-Rua, J.M., Zhang, L., Martinez, B., Xiang, T.: Few-shot action recognition with prototype-centered attentive learning. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (2021)
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2020YFB1406801), 111 plan (No. BP0719010), STCSM (No. 18DZ2270700), State Key Laboratory of UHD Video and Audio Production and Presentation, the UK EPSRC Programme Grant Visual AI (EP/T028572/1), and a Google-DeepMind Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ju, C., Han, T., Zheng, K., Zhang, Y., Xie, W. (2022). Prompting Visual-Language Models for Efficient Video Understanding. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13695. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19833-5_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19833-5_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-19832-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-19833-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)