Abstract
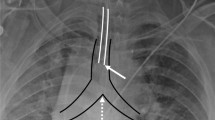
The accurate localization of inserted medical tubes and parts of human anatomy is a common problem when analyzing chest radiographs and something deep neural networks could potentially automate. However, many foreign objects like tubes and various anatomical structures are small in comparison to the entire chest X-ray, which leads to severely unbalanced data and makes training deep neural networks difficult. In this paper, we present a simple yet effective ‘Only-One-Object-Exists’ (OOOE) assumption to improve the deep network’s ability to localize small landmarks in chest radiographs. The OOOE enables us to recast the localization problem as a classification problem and we can replace commonly used continuous regression techniques with a multi-class discrete objective. We validate our approach using a large scale proprietary dataset of over 100K radiographs as well as publicly available RANZCR-CLiP Kaggle Challenge dataset and show that our method consistently outperforms commonly used regression-based detection models as well as commonly used pixel-wise classification methods. Additionally, we find that the method using the OOOE assumption generalizes to multiple detection problems in chest X-rays and the resulting model shows state-of-the-art performance on detecting various tube tips inserted to the patient as well as patient anatomy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Unfortunately, we are not in the position to disclose this data at this time.
References
Babenko, B., Yang, M.H., Belongie, S.: Robust object tracking with online multiple instance learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33, 1619–1632 (2010)
Bustos, A., Pertusa, A., Salinas, J.M., de la Iglesia-Vayá, M.: Padchest: a large chest x-ray image dataset with multi-label annotated reports. Med. Image Anal. 66, 101797 (2020)
Chen, C., Liu, M.-Y., Tuzel, O., Xiao, J.: R-CNN for small object detection. In: Lai, S.-H., Lepetit, V., Nishino, K., Sato, Y. (eds.) ACCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 10115, pp. 214–230. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54193-8_14
Frid-Adar, M., Amer, R., Greenspan, H.: Endotracheal tube detection and segmentation in chest radiographs using synthetic data. In: Shen, D., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11769, pp. 784–792. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32226-7_87
Girshick, R.: Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (2015)
Godoy, M.C., Leitman, B.S., De Groot, P.M., Vlahos, I., Naidich, D.P.: Chest radiography in the ICU: Part 1, evaluation of airway, enteric, and pleural tubes. Am. J. Roentgenolo. 198, 536–571 (2012)
Godoy, M.C., Leitman, B.S., De Groot, P.M., Vlahos, I., Naidich, D.P.: Chest radiography in the ICU: Part 2, evaluation of cardiovascular lines and other devices. Am. J. Roentgenol. 198, 572–581 (2012)
Gupta, P.K., Gupta, K., Jain, M., Garg, T.: Postprocedural chest radiograph: impact on the management in critical care unit. Anesth. Essays Res. 8, 139 (2014)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Henriques, J.F., Caseiro, R., Martins, P., Batista, J.: Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. In: Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Perona, P., Sato, Y., Schmid, C. (eds.) ECCV 2012. LNCS, vol. 7575, pp. 702–715. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33765-9_50
Irvin, J., et al.: Chexpert: a large chest radiograph dataset with uncertainty labels and expert comparison. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2019)
Jakab, T., Gupta, A., Bilen, H., Vedaldi, A.: Unsupervised learning of object landmarks through conditional image generation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 31 (2018)
Jeon, S., Nam, S., Oh, S.W., Kim, S.J.: Cross-identity motion transfer for arbitrary objects through pose-attentive video reassembling. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12369, pp. 292–308. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58586-0_18
Johnson, A.E., et al.: MIMIC-CXR, a de-identified publicly available database of chest radiographs with free-text reports. Sci. Data 6, 1–8 (2019)
Kara, S., Akers, J.Y., Chang, P.D.: Identification and localization of endotracheal tube on chest radiographs using a cascaded convolutional neural network approach. J. Digit. Imaging 34, 898–904 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-021-00463-0
Kónya, S.: 5k trachea bifurcation on chest xray. https://www.kaggle.com/sandorkonya/5k-trachea-bifurcation-on-chest-xray (2021)
Law, M., et al.: Ranzcr-clip - catheter and line position challenge. https://www.kaggle.com/c/ranzcr-clip-catheter-line-classification (2021)
Lee, H., Mansouri, M., Tajmir, S.H., Lev, M.H., Do, S.: A deep-learning system for fully-automated peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) tip detection. J. Digit. Imaging 31, 393–402 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-017-0025-z
Li, C., Bai, J., Hager, G.D.: A unified framework for multi-view multi-class object pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2018)
Li, C., Zeeshan Zia, M., Tran, Q.H., Yu, X., Hager, G.D., Chandraker, M.: Deep supervision with shape concepts for occlusion-aware 3D object parsing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2017)
Lin, T.Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2017)
Lin, T.Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Dollár, P.: Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (2017)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2015)
Oh, S.W., Kim, S.J.: Approaching the computational color constancy as a classification problem through deep learning. Pattern Recognit. 61, 405–416 (2017)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 28 (2015)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9351, pp. 234–241. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Su, H., Qi, C.R., Li, Y., Guibas, L.J.: Render for CNN: viewpoint estimation in images using CNNs trained with rendered 3D model views. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2015)
Sullivan, R., Holste, G., Burkow, J., Alessio, A.: Deep learning methods for segmentation of lines in pediatric chest radiographs. In: Medical Imaging 2020: Computer-Aided Diagnosis (2020)
Tong, K., Wu, Y., Zhou, F.: Recent advances in small object detection based on deep learning: a review. Image Visi. Comput. 97, 103910 (2020)
Wang, X., Peng, Y., Lu, L., Lu, Z., Bagheri, M., Summers, R.: Hospital-scale chest x-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2017)
Wu, Y., Lim, J., Yang, M.H.: Online object tracking: a benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2013)
Çallı, E., Sogancioglu, E., van Ginneken, B., van Leeuwen, K.G., Murphy, K.: Deep learning for chest x-ray analysis: a survey. Med. Image Anal. 72, 102125 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nam, G., Kim, T., Lee, S., Kooi, T. (2022). OOOE: Only-One-Object-Exists Assumption to Find Very Small Objects in Chest Radiographs. In: Wu, S., Shabestari, B., Xing, L. (eds) Applications of Medical Artificial Intelligence. AMAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13540. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17721-7_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17721-7_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-17720-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-17721-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)