Abstract
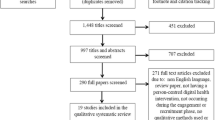
The use of nudges, i.e., design changes in the way choices are presented to steer users towards predetermined choices, has dramatically increased over the last few years. These interventions have moved online to become digital and are present across many fields from politics to healthcare. As the use of these mechanisms in healthcare has grown exponentially recently, it is crucial to understand the opportunities they offer and the risks they pose. However, at this stage, such an analysis is lacking. This chapter specifically addresses this issue by (1) analyzing how digital nudges can be applied in the continuum of care and (2) mapping the current empirical research landscape on the topic. To do so, this chapter presents a scoping review of the literature by searching relevant research in the electronic database of JMIR (Journal of Medical Internet Research). The search yielded 150 unique articles, of which 19 articles satisfied the criteria for inclusion in this study. The results indicate that feedback and reminders are the most commonly used digital nudges for behavior change in digital health. Moreover, the results show that most digital nudges research focuses on prevention and the post-acute phase of the continuum of care, with none of the studies investigating nudges for the acute phase. Finally, the results indicate that current empirical research on digital nudging in healthcare rarely discusses ethical considerations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åberg F, Helenius-Hietala J, Puukka P, Jula A. Binge drinking and the risk of liver events: a population-based cohort study. Liver Int. 2017;37(9):1373–81.
Angellotti E, Wong JB, Pierce A, Hescott B, Pittas AG. Combining wireless technology and behavioral economics to engage patients (WiBEEP) with cardiometabolic disease: a pilot study. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2019;5(1):1–6.
Arigo D, Suls JM. Smartphone apps providing social comparison for health behavior change: a need for better tailoring to person and context. Mhealth. 2018;4:46.
Bakker EA, van Bakel BM, Aengevaeren WR, Meindersma EP, Snoek JA, Waskowsky WM, van Kuijk AA, Jacobs MM, Hopman MT, Thijssen DH, et al. Sedentary behaviour in cardiovascular disease patients: risk group identification and the impact of cardiac rehabilitation. Int J Cardiol. 2021;326:194–201.
Boillat T, Grantcharov P, Rivas H. Increasing completion rate and benefits of checklists: prospective evaluation of surgical safety checklists with smart glasses. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019;7(4):e13447.
Caraban A, Karapanos E, Gonçalves D, Campos P. 23 ways to nudge: a review of technology-mediated nudging in human-computer interaction. In: Proceedings of the 2019 CHI conference on human factors in computing systems; 2019. p. 1–15.
Chokshi NP, Adusumalli S, Small DS, Morris A, Feingold J, Ha YP, Lynch MD, Rareshide CA, Hilbert V, Patel MS. Loss-framed financial incentives and personalized goal-setting to increase physical activity among ischemic heart disease patients using wearable devices: the active reward randomized trial. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(12):e009173.
Clayton N, Rodriguez LM, Rinker DV, Gonzales RG, Agana M, Tackett JL, Foster DW. Efficacy of personalized normative feedback as a brief intervention for college student gambling: a randomized controlled trial. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2015;83(3):500.
Cohen AB, Dorsey E, Mathews SC, Bates DW, Safavi K. A digital health industry cohort across the health continuum. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3(1):1–10.
Cortés-Pérez I, Nieto-Escamez FA, Obrero-Gaitán E. Immersive virtual reality in stroke patients as a new approach for reducing postural disabilities and falls risk: a case series. Brain Sci. 2020;10(5):296.
Ensaff H, Homer M, Sahota P, Braybrook D, Coan S, McLeod H. Food choice architecture: an intervention in a secondary school and its impact on students’ plant-based food choices. Nutrients. 2015;7(6):4426–37.
Ford AL, Bergh C, Södersten P, Sabin MA, Hollinghurst S, Hunt LP, Shield JP. Treatment of childhood obesity by retraining eating behaviour: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2010;340:b5388.
Forwood SE, Ahern AL, Marteau TM, Jebb SA. Offering within-category food swaps to reduce energy density of food purchases: a study using an experimental online supermarket. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2015;12(1):1–10.
Free C, Knight R, Robertson S, Whittaker R, Edwards P, Zhou W, Rodgers A, Cairns J, Kenward MG, Roberts I. Smoking cessation support delivered via mobile phone text messaging (txt2stop): a single-blind, randomised trial. Lancet. 2011;378(9785):49–55.
Gold N, Lin Y, Ashcroft R, Osman M. ‘Better off, as judged by themselves’: do people support nudges as a method to change their own behavior? Behav Public Policy. 2020:1–30.
Horne BD, Muhlestein JB, Lappé DL, May HT, Le VT, Bair TL, Babcock D, Bride D, Knowlton KU, Anderson JL. Behavioral nudges as patient decision support for medication adherence: the encourage randomized controlled trial. Am Heart J. 2022;244:125–34.
Intille SS, Kukla C, Farzanfar R, Bakr W. Just-in-time technology to encourage incremental, dietary behavior change. In: AMIA annual symposium proceedings, 2003. American Medical Informatics Association; 2003. p. 874.
Jesse M, Jannach D. Digital nudging with recommender systems: survey and future directions. Comput Hum Behav Rep. 2021;3:100052.
Karlsen R, Andersen A. Recommendations with a nudge. Technologies. 2019;7(2):45.
Kelly JA. Behavior changes & disease prevention: MCW research shows effectiveness of HIV/AIDS risk reduction interventions. Medical College of Wisconsin. WMJ. 2000;99(1):41–3.
Krakauer JW, Cortés JC. A non-task-oriented approach based on high-dose playful movement exploration for rehabilitation of the upper limb early after stroke: a proposal. NeuroRehabilitation. 2018;43(1):31–40.
Lehmann BA, Chapman GB, Franssen FME, Kok G, Ruiter RAC. Changing the default to promote influenza vaccination among health care workers. Vaccine. 2016;34(11):1389–92.
Levy N. Nudges in a post-truth world. J Med Ethics. 2017;43(8):495–500.
Marucci S, De Iaco G, Lisco G, Mariano F, Giagulli VA, Guastamacchia E, De Pergola G, Triggiani V Eating disorders and type 1 diabetes: a perspective. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2021. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871530321666211109152353
Milkman KL, Patel MS, Gandhi L, Graci HN, Gromet DM, Ho H, Kay JS, Lee TW, Akinola M, Beshears J, et al. A megastudy of text-based nudges encouraging patients to get vaccinated at an upcoming doctor’s appointment. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2021;118(20):e2101165118.
Neto OL, Haenni S, Phuka J, Ozella L, Paolotti D, Cattuto C, Robles D, Lichand G. Combining wearable devices and mobile surveys to study child and youth development in Malawi: implementation study of a multimodal approach. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2021;7(3):e23154.
Ockene JK, Ma Y, Zapka JG, Pbert LA, Goins KV, Stoddard AM. Spontaneous cessation of smoking and alcohol use among low-income pregnant women. Am J Prev Med. 2002;23(3):150–9.
Okeke F, Sobolev M, Estrin D. Towards a framework for mobile behavior change research. In: Proceedings of the technology, mind, and society; 2018. p. 1–6.
Perez-Marcos D, Chevalley O, Schmidlin T, Garipelli G, Serino A, Vuadens P, Tadi T, Blanke O, Millán JDR. Increasing upper limb training intensity in chronic stroke using embodied virtual reality: a pilot study. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2017;14(1):1–14.
Purohit AK, Holzer A. Functional digital nudges: identifying optimal timing for effective behavior change. In: Extended abstracts of the 2019 CHI conference on human factors in computing systems; 2019. p. 1–6.
Purohit AK, Holzer A. Unhooked by design: scrolling mindfully on social media by automating digital nudges; 2021.
Reijula S, Hertwig R. Self-nudging and the citizen choice architect. Behav Public Policy. 2022;6(1):119–49.
Sasco AJ, Secretan MB, Straif K. Tobacco smoking and cancer: a brief review of recent epidemiological evidence. Lung Cancer. 2004;45:S3–9.
Shah N, Adusumalli S. Nudges and the meaningful adoption of digital health. Pers Med. 2020;17:429.
Spring K, Gouze N, Galvin P, Gramatica F, Weltring KM. A model for a life-long personalised continuum of integrated care revolutionising healthcare delivery: description of technological impact. Berlin: Institute for Innovation and Technology; 2020.
Stallones RA. The association between tobacco smoking and coronary heart disease. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(3):735–43.
Stuart Mills. Nudge/sludge symmetry: on the relationship between nudge and sludge and the resulting ontological, normative and transparency implications. Behav Public Policy. 2020:1–24.
Sunstein CR, Thaler RH. Nudge: improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press; 2008.
Suzuki Y, Sukegawa A, Ueda Y, Sekine M, Enomoto T, Miyagi E, et al. Effect of a brief web-based educational intervention on willingness to consider human papillomavirus vaccination for children in Japan: randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(9):e28355.
Thaler RH. Nudge, not sludge. Science. 2018;361(6401):431.
Thaler RH, Sunstein CR, Balz JP. Choice architecture. In: The behavioral foundations of public policy. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press; 2014.
Tversky A, Kahneman D. The framing of decisions and the psychology of choice. In: Behavioral decision making. Boston, MA: Springer; 1985. p. 25–41.
Valle CG, Nezami BT, Tate DF. Designing in-app messages to nudge behavior change: lessons learned from a weight management app for young adults. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process. 2020;161:95–101.
Van Dalen HP, Henkens K. Comparing the effects of defaults in organ donation systems. Soc Sci Med. 2014;106:137–42.
Wang YC, Chou MY, Liang CK, Peng LN, Chen LK, Loh CH. Post-acute care as a key component in a healthcare system for older adults. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2019;23(2):54.
Wang Z, Luo Y, Yang S, Zou K, Pei R, He J, Deng Y, Zhou M, Zhao L, Guo H. Premature deaths caused by smoking in Sichuan, Southwest China, 2015–2030. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1–8.
Weinmann M, Schneider C, Vom Brocke J. Digital nudging. Bus Inf Syst Eng. 2016;58(6):433–6.
Wyse R, Delaney T, Stacey F, Lecathelinais C, Ball K, Zoetemeyer R, Lamont H, Sutherland R, Nathan N, Wiggers JH, et al. Long-term effectiveness of a multistrategy behavioral intervention to increase the nutritional quality of primary school students’ online lunch orders: 18-month follow-up of the click & crunch cluster randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. 2021a;23(11):e31734.
Wyse R, Delaney T, Stacey F, Zoetemeyer R, Lecathelinais C, Lamont H, Ball K, Campbell K, Rissel C, Attia J, et al. Effectiveness of a multistrategy behavioral intervention to increase the nutritional quality of primary school students’ web-based canteen lunch orders (click & crunch): cluster randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. 2021b;23(9):e26054.
Xu Z, Geng J, Zhang S, Zhang K, Yang L, Li J, Li J, et al. A mobile-based intervention for dietary behavior and physical activity change in individuals at high risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus: randomized controlled trial. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020;8(11):e19869.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the help of Satyam V Purohit for his assistance with screening of the research papers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Purohit, A.K., Schöbel, S., Bill, O., Holzer, A. (2023). Nudging to Change, the Role of Digital Health . In: Rivas, H., Boillat, T. (eds) Digital Health. Health Informatics. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17666-1_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17666-1_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-17665-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-17666-1
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)