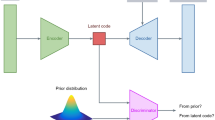
Abstract
Understanding pathological mechanisms for heterogeneous brain disorders is a difficult challenge. Normative modelling provides a statistical description of the ‘normal’ range that can be used at subject level to detect deviations, which relate to disease presence, disease severity or disease subtype. Here we trained a conditional Variational Autoencoder (cVAE) on structural MRI data from healthy controls to create a normative model conditioned on confounding variables such as age. The cVAE allows us to use deep learning to identify complex relationships that are independent of these confounds which might otherwise inflate pathological effects. We propose a latent deviation metric and use it to quantify deviations in individual subjects with neurological disorders and, in an independent Alzheimer’s disease dataset, subjects with varying degrees of pathological ageing. Our model is able to identify these disease cohorts as deviations from the normal brain in such a way that reflect disease severity.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Data used in preparation of this article were obtained from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database (adni.loni.usc.edu). As such, the investigators within the ADNI contributed to the design and implementation of ADNI and/or provided data but did not participate in analysis or writing of this report. A complete listing of ADNI investigators can be found at: http://adni.loni.usc.edu/wp-content/uploads/how_to_apply/ADNI_Acknowledgement_List.pdf.
References
Alemi, A.A., Fischer, I., Dillon, J.V., Murphy, K.: Deep variational information bottleneck. CoRR abs/1612.00410 (2016). http://arxiv.org/abs/1612.00410
Apostolova, L., et al.: Hippocampal atrophy and ventricular enlargement in normal aging, mild cognitive impairment (mci), and Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 26, 17–27 (2012)
Baron, J.C., et al.: In vivo mapping of gray matter loss with voxel-based morphometry in mild Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 14, 298–309 (2001)
Bojanowski, P., Joulin, A., Lopez-Paz, D., Szlam, A.: Optimizing the latent space of generative networks (2017)
Desikan, R.S., et al.: An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 31(3), 968–980 (2006)
Dincer, A.B., Janizek, J.D., Lee, S.I.: Adversarial deconfounding autoencoder for learning robust gene expression embeddings. Bioinformatics 36, 573–582 (2020)
Elad, D., et al.: Improving the predictive potential of diffusion MRI in schizophrenia using normative models-towards subject-level classification. Hum. Brain Mapp. 42, 4658–4670 (2021)
Erus, G., et al.: Imaging Patterns of Brain Development and their Relationship to Cognition. Cerebral Cortex 25(6), 1676–1684 (2014)
Johnson, W.E., Li, C., Rabinovic, A.: Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics 8(1), 118–127 (2006)
Kia, S.M., et al.: Hierarchical Bayesian regression for multi-site normative modeling of neuroimaging data. In: Martel, A.L., et al. (eds.) MICCAI 2020. LNCS, vol. 12267, pp. 699–709. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59728-3_68
Kingma, D., Welling, M.: Auto-encoding variational Bayes (12 2014)
Kirichenko, P., Izmailov, P., Wilson, A.G.: Why normalizing flows fail to detect out-of-distribution data (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2006.08545. https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.08545
Kostro, D., et al.: Correction of inter-scanner and within-subject variance in structural MRI based automated diagnosing. NeuroImage 98, 405–415 (2014)
Kumar, A., Sattigeri, P., Balakrishnan, A.: Variational inference of disentangled latent concepts from unlabeled observations. CoRR abs/1711.00848 (2017). http://arxiv.org/abs/1711.00848
Kumar, S.: Normvae: normative modeling on neuroimaging data using variational autoencoders. arXiv e-prints arXiv:2110.04903 (2021)
Marquand, A., Kia, S.M., Zabihi, M., Wolfers, T., Buitelaar, J., Beckmann, C.: Conceptualizing mental disorders as deviations from normative functioning. Mol. Psychiatry 24, 1415–1424 (2019)
Marquand, A.F., Rezek, I., Buitelaar, J., Beckmann, C.F.: Understanding heterogeneity in clinical cohorts using normative models: beyond case-control studies. Biol. Psychiat. 80(7), 552–561 (2016)
Mathieu, E., Rainforth, T., Siddharth, N., Teh, Y.W.: Disentangling disentanglement in variational autoencoders (2019)
Miller, M.I., et al.: Amygdala atrophy in symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease based on diffeomorphometry: the biocard cohort. Neurobiol. Aging 36, S3–S10 (2015)
Ordaz, S.J., Foran, W., Velanova, K., Luna, B.: Longitudinal growth curves of brain function underlying inhibitory control through adolescence. J. Neurosci. 33(46), 18109–18124 (2013)
Petersen, R., et al.: Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI): clinical characterization. Neurology 74(3), 201–209 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0b013e3181cb3e25,https://europepmc.org/articles/PMC2809036
Pinaya, W., et al.: Using normative modelling to detect disease progression in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease in a cross-sectional multi-cohort study. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–13 (2021)
Pinaya, W., Mechelli, A., Sato, J.: Using deep autoencoders to identify abnormal brain structural patterns in neuropsychiatric disorders: a large-scale multi-sample study. Hum. Brain Map. 40, 944–954 (2018)
Rao, A., Monteiro, J.M., Mourao-Miranda, J.: Predictive modelling using neuroimaging data in the presence of confounds. Neuroimage 150, 23–49 (2017)
Rolinek, M., Zietlow, D., Martius, G.: Variational autoencoders pursue PCA directions (by accident) (2019)
Sohn, K., Lee, H., Yan, X.: Learning structured output representation using deep conditional generative models. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 28. Curran Associates, Inc. (2015)
Sudlow, C., et al.: UK biobank: an open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 12, e1001779 (2015)
Trippe, B.L., Turner, R.E.: Conditional density estimation with Bayesian normalising flows (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.1802.04908, https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.04908
Wang, H., Wu, Z., Xing, E.P.: Removing confounding factors associated weights in deep neural networks improves the prediction accuracy for healthcare applications. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 24, 54–65 (2019)
Wolfers, T., Beckmann, C.F., Hoogman, M., Buitelaar, J.K., Franke, B., Marquand, A.F.: Individual differences v. the average patient: mapping the heterogeneity in ADHD using normative models. Psychol. Med. 50(2), 314–323 (2019)
Zhao, Q., Adeli, E., Pohl, K.: Training confounder-free deep learning models for medical applications. Nat. Commun. 11, 1–9 (2020)
Ziegler, G., Ridgway, G., Dahnke, R., Gaser, C.: Individualized gaussian process-based prediction and detection of local and global gray matter abnormalities in elderly subjects. NeuroImage 97, 1–9 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the EPSRC-funded UCL Centre for Doctoral Training in Intelligent, Integrated Imaging in Healthcare (i4health) and the Department of Health’s NIHR-funded Biomedical Research Centre at University College London Hospitals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lawry Aguila, A., Chapman, J., Janahi, M., Altmann, A. (2022). Conditional VAEs for Confound Removal and Normative Modelling of Neurodegenerative Diseases. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022. MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13431. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16431-6_41
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16431-6_41
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16430-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16431-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)