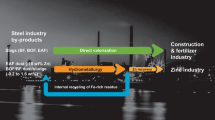
Abstract
Like other industrial processes, hot-dip galvanizing of steel generates some by-products and wastes. Secondary materials contain a relatively high percentage of zinc being valuable sources of the metal. Solid by-products like zinc ash, bottom dross, and top dross are currently sold to pyrometallurgical recycling plants, although zinc ash consisting of easy leachable components is suitable for hydrometallurgical treatment. In turn, flux skimming is deposited in landfills for hazardous wastes, but it could be leached for zinc recovery. Waste aqueous solutions from pretreatment steps, such as spent baths from pickling, stripping, and fluxing, or washing waters can be also regenerated by hydrometallurgical methods instead of going to landfills. This chapter presents the characteristics of main secondary raw materials originating from hot-dip galvanizing lines and reviews hydrometallurgical methods developed for their recycling or regeneration.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EPT:
-
Emulsion pertraction technology
- Mt:
-
Million ton
- NDSX:
-
Non-dispersive solvent extraction
- ppm:
-
Part per million
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- S/L:
-
Solid to liquid ratio
- ΔGfo:
-
Standard Gibbs free energy of formation (25 °C)
- ΔGro:
-
Standard free energy change of reaction (25 °C)
References
Abbey CE, Jin W, Moats MS (2018) Manganese-chloride interactions on Pb–Ag anode behaviour in synthetic sulfuric acid electrolytes. In B. Davis et al. (eds) Extraction 2018, the minerals, metals & materials society, pp 1521–1533
Abd El-Rahman MK, Abdel Kahlek MA, Werther J (2005) Physical treatment of zinc skimmed from the galvanized process using fluidized bed up-stream column. Eur J Miner Process Environ Prot 5(2):163–173
AGA (2010) Performance of hot-dip galvanized steel products in the atmosphere, soil, water, concrete, and more. American Galvanizers Association
Arguillarena A, Margallo M, Arruti-Fernández A, Pinedo J, Gómez P, Urtiaga A (2020) Scale-up of membrane-based zinc recovery from spent pickling acids of hot-dip galvanizing, Membranes 10:444
Baik DS, Fray DJ (2001) Electrodeposition of zinc from high acid zinc chloride solutions. J Appl Electrochem 31:1141–1147
Barakat MA (2003) The pyrometallurgical processing of galvanizing zinc ash and flue dust. JOM 55(8):26–29
Barakat MA, Mahmoud MHH, Shehata M (2006) Hydrometallurgical recovery of zinc from a fine blend of galvanization processes. Sep Sci Technol 41:1757–1772
Bright MA, Deem NJ, Fryatt J (2007) The advantages of recycling metallic zinc from the processing wastes of industrial molten zinc applications. Light Metals 2007. Miner Metals Mater Soc
Carrillo-Abad J, Garcia-Gabaldon M, Perez-Herranz V (2014) Study of the zinc recovery from spent pickling baths by means of an electrochemical membrane reactor using a cation-exchange membrane under galvanostatic control. Sep Pur Technol 132:479–486
Chen TT, Cabri LJ (1986) Mineralogical overview of iron control in hydrometallurgical processing. In: Dutrizac JE, Monhemius AJ (eds) Iron control in hydrometallurgy. Ellis Horwood Ltd., Chichester, pp 19–55
Cierpiszewski R, Miesiąc I, Regel-Rosocka M, Sastre AM, Szymanowski J (2002) Removal of zinc(II) from spent hydrochloric acid solutions from zinc hot galvanizing plants. Ind Eng Chem Res 41:598–603
Csicsovszki G, Kékesi T, Török TI (2005) Selective recovery of Zn and Fe from spent pickling solutions by the combination of anion exchange and membrane electrowinning techniques. Hydrometallurgy 77:19–28
Dakhili N, Razavizadeh H, Salehi MT, Seyedein SH (2011) Recovery of zinc from the final slag of steel’s galvanizing process. Adv Mater Res 264–265:592–596
Dvořák P, Jandová J (2005) Hydrometallurgical recovery of zinc from hot-dip galvanizing ash. Hydrometallurgy 77:29–33
EC (2010) Guidance on classification of waste according to EWC-Stat categories. Supplement to the manual for the implementation of the regulation (EC) No 2150/2002 on Waste Statistics. Commission of the European Communities Eurostat
Fleitlikh IY, Pashkov GL, Grigorieva NA, Logutenko OA, Kopanyov AM (2014) Zinc extraction from sulfate–chloride solutions with mixtures of trialkyl amine and organic acids. Hydrometallurgy 149:110–117
Ghare NY, Wani KS, Patil VS (2013) A review on methods of recovery of acid(s) from spent pickle liquor of steel industry. J Environ Sci Eng 55(2):253–266
Gordon RB, Graedel TE, Bertram M, Fuse K, Lifset R, Rechberger H, Spatari S (2003) The characterization of technological zinc cycles. Resour Conserv Recycl 39:107–135
Gostu S, Mishra D, Sahu KK, Agrawal A (2014) Precipitation and characterization of zinc borates from hydrometallurgical processing of zinc ash. Mater Lett 134:198–201
Grenville HW (1929) Recovery of zinc, U.S. Patent 1,719,056
Guo H, Lu J, Dreisinger D, Kuha LL, Steyl J, Smith J (2010) Zinc electrowinning of from acidic chloride solutions. In: Lead-Zinc 2010 symposium, Vancouver, Canada, pp 685–699
Güresin N, Topkaya YA (1998) Dechlorination of zinc dross. Hydrometallurgy 49:179–187
Hagemann S (2012) Entwicklung eines thermodynamischen Modells für Zink, Blei und Cadmium in salinaren Lösungen, GRS-219, 283 (in German)
Haines AK, Tunley TH, Te Riele WAM, Cloete FLD, Sampson TD, Econ B (1973) The recovery of zinc from pickle liquors by ion exchange. J South Afr Inst Min Metall 74(4):149–157
Hewaidy IF, Sabr HO, Nassi EH (1979) Characteristics of electrolytic zinc powder produced from zinc dross. Powder Technol 24(2):245–250
Ismael MRC, Carvalho JMR (2003) Iron recovery from sulfate leach liquors in zinc hydrometallurgy. Min Eng 16:31–39
Jha MK, Kumar V, Singh RJ (2001) Review of hydrometallurgical recovery of zinc from industrial wastes. Res Conserv Recycl 33:1–22
Jha MK, Kumar V, Singh RJ (2002) Solvent extraction of zinc from chloride solutions. Solv Extr Ion Exch 20(3):389–405
Kelsall GH, Guerra E, Li G, Bestetti M (2000) Effects of manganese(II) and chloride ions in zinc electrowinning reactors. In: Woods R, Doyle FM (eds) Electrochemistry in mineral and metal processing V, proceedings of the international symposium 2000–14, Electrochemical Society, pp 350–361
Kerney U (1994) Treatment of spent pickling acids from hot-dip galvanizing. Res Conserv Recycl 10:145–151
Kołodziej B (1996) Elektrowydzielanie metali—procesy hydrometalurgiczne. Physicochem Probl Miner 30:233–247 (in Polish)
Kong G, White R (2010) Toward cleaner production of hot-dip galvanizing in China. J Clean Prod 18(10–11):1092–1099
Kuklik V, Kudlaček J (2016) Hot-dip galvanizing of steel structures. Elsevier, Oxford-Cambridge
Laso J, García V, Bringas E, Urtiaga A, Ortiz I (2015) Selective recovery of zinc over iron from spent pickling wastes by different membrane-based solvent extraction process configurations. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:3218–3224
Lawson GJ (1975) Solvent extraction of metals from chloride solutions. J Appl Chem Biotechnol 25:949–957
Luo G, Wang Y, Zeng J, He H, Yan J, He C, Zhang R, Li S (2014) Study on the formation of bottom dross in hot-dip Zn-0.1%Ni alloy. Adv Mater Res 881–883:1572–1575
Lupa L, Negrea P, Iovi A, Ciopec M, Mosoarca G (2006) Zinc recover from zinc ash by extraction with clorhidric acid solutions. Chem Bull Politeh Univ (Timisoara) 51(1–2):71–74
Mackinnon DJ, Brannen JM (1991) Effect of manganese, magnesium, sodium and potassium sulphates on zinc electrowinning from synthetic acid sulphate electrolytes. Hydrometallurgy 27:99–111
Mackinnon DJ, Brannen JM, Morrison RM (1982) Zinc electrowinning from aqueous chloride electrolyte. J Appl Electrochem 12:39–53
Marañón E, Fernández Y, Súarez FJ, Alonso FJ, Sastre H (2000) Treatment of zinc pickling baths by means of anionic resins. Ind Eng Chem Res 39:3370–3376
Marder AR (2000) The metallurgy of zinc-coated steel. Prog Mater Sci 45:191–271
Mass P, Peissker P (2011) Handbook of hot-dip galvanization. Wiley, Weinheim
Miesiąc I (2003) Utilization methods of spent hydrochloric acid from hot-dip zinc galvanizing. Pol J Chem Technol 5(4):34–36
Muresan L, Maurin G, Oniciu L, Gaga D (1996) Influence of metallic impurities on zinc electrowinning from sulphate electrolyte. Hydrometall 43:345–354
Muthu N, Faieza AA, Rosnah RBM (2013) Minimization of spent acid waste from the galvanizing plant in Malaysia. Glob J Res Eng E 13(6):15–24
Najiba, S., 2010. Recovery of zinc from the ash of galvanizing plant by hydrometallurgical route, PhD. Thesis, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology.
Nicol M, Akilan C, Tjandrawan V, Gonzalez JA (2017) The effects of halides in the electrowinning of zinc. I. Oxidation of Chloride on Lead-Silver Anodes. Hydrometallurgy 173:125–133
Nirdosh I, Kalia RK, Muthuswami SV (1988) Bench-scale investigations on the electrolytic recovery of zinc powder from Galvanizer’s ash. Hydrometallurgy 20(2):203–217
Parus A, Olszanowski A, Wieszczycka K (2011) Solvent extraction of iron(III) from chloride solutions in the presence of copper(II) and zinc(II) using hydrophobic pyridyl ketoximes. Sep Sci Technol 46(1):87–93
Pirošková J, Trpčevská J, Laubertová M, Holková B, Sminčaková E (2014) Acid leaching of top dross generated during wet batch hot-dip galvanizing process. Metall 7–8:248–252
Pirošková J, Trpčevská J, Laubertová M, Sminčaková E (2015) The influence of hydrochloric acid on the zinc extraction from flux skimming. Acta Metall Slovac 21(2):127–134
Pirošková J, Trpčevská J, Orač D, Laubertová M, Horvathová H, Holková B (2018) Production of zinc oxide from hazardous waste—sal ammoniac skimming. J Min Metall Sect B-Metall 54(3), B, 377–384
Pirošková J, Trpčevská J, Sminčaková E, Holková B (2016) Kinetic study of zinc leaching from flux skimming. Metall 1–2:514–518
Rabah MA, El-Sayed AS (1995) Recovery of zinc and some of its valuable salts from secondary resources and wastes. Hydrometallurgy 37:23–32
Rahman MM, Qadir MR, Neger AJMT, Kurny ASW (2013) Studies on the preparation of zinc oxide from galvanizing plant waste. Am J Mater Eng Technol 1(4):59–64
Ramachandran P, Nandakumar V, Sathaiyan N (2004) Electrolytic recovery of zinc from zinc ash using a catalytic anode. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 79:578–583
Regel-Rosocka M (2010) A review on methods of regeneration of spent pickling solutions from steel processing. J Hazard Mater 177:57–69
Regel-Rosocka M, Cieszyńska A, Wiśniewski M (2007) Methods of regeneration of spent pickling solutions from steel treatment plants. Pol J Chem Technol 9(2):42–45
Rudnik E (2019a) Recovery of zinc from zinc ash by leaching in sulphuric acid and electrowinning. Hydrometallurgy 188:256–263
Rudnik E (2019b) Investigation of industrial waste materials for hydrometallurgical recovery of zinc. Min Eng 139:105871
Rudnik E (2020) Hydrometallurgical recovery of zinc from industrial hot dipping top ash. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 30:2239–2255
Rudnik E, Włoch G, Szatan L (2018a) Hydrometallurgical treatment of zinc ash from hot-dip galvanizing process. Min Metall Process 35(2):69–76
Rudnik E, Włoch G, Szatan L (2018b) Preliminary investigation on leaching behaviour of zinc ash. Arch Metall Mater 63(2):801–807
Şahin FC, Derin B, Yücel O (2000) Chloride removal from zinc ash. Scand J Metall 29:224–230
Sahu KK, Agarwal A, Pandey BD (2004) Recent trends and current practices for secondary processing of zinc and lead. Part II: zinc recovery from secondary sources. Waste Manage Res 22:248–254
Saramak D, Krawczykowski D, Gawenda T (2018) Investigations of zinc recovery from metallurgical waste. IOP conference series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 427:012017
Schmitz D, Friedrich B (2007) In-house recycling of hard zinc and zinc ash by liquid metal centrifugation. In: Proceedings of EMC 2007, 1–20 pp
Sinha S, Choudhari R, Mishra D, Shekhar S, Agrawal A, Sahu KK (2020) Valorisation of waste galvanizing dross: emphasis on the recovery of zinc with zero effluent strategy. J Environ Manage 256:109985
Stokes F (1990) Chemical reactions in fluxes for hot-dip galvanizing. Anti-Corr Met Mater 37(4):12–14
Sminčaková E, Trpčevská J, Pirošková J (2017) Kinetic aspects of leaching zinc from waste galvanizing zinc by using hydrochloric acid solutions. JOM 69(10):1869–1875
Stocks C, Wood J, Guy S (2005) Minimisation and recycling of spent acid wastes from galvanizing plants. Res Conserv Recycl 44:153–166
Subbaiah T, Mallick SC, Bhattacharya IN, Anand S, Das RP (2004) Preparation and characterisation of ferrite grade zinc oxide from zinc ash. Eur J Min Process Environ Prot 4(3):236–242
Takácová Z, Hluchánová B, Trpcevská J (2010) Leaching of zinc from zinc ash originating from hot dip galvanizing. Metall 64(12):517–519
Tang B, Su W, Wang J, Fu F, Yu G, Zhang J (2012) Minimizing the creation of spent pickling liquors in a pickling process with high-concentration hydrochloric acid solutions: mechanism and evaluation method. J Environ Manage 98:147–154
Tjandrawan V, Nicol MJ (2013) Electrochemical oxidation of iron(II) ions on lead alloy anodes. Hydrometallurgy 131–132:81–88
Trpčevská J, Hlucháňova B, Vindt T, Zorawski W, Jakubéczyová D (2010) Characterization of the bottom dross formed during batch hot-dip galvanizing and its refining. Acta Metall Slovac 16(3):151–156
Trpčevská J, Hoĺková B, Briančin J, Korálová K, Pirošková J (2015) The pyrometallurgical recovery of zinc from the coarse-grained fraction of zinc ash by centrifugal force. Int J Min Process 143:25–33
Trpčevská J, Rudnik E, Holková B, Laubertová M (2018) Leaching of zinc ash with hydrochloric acid solutions. Pol J Environ Stud 27(4):1765–1771
Wang Z, Gao J, Shi A, Meng L, Guo Z (2018) Recovery of zinc from galvanizing dross by a method of super-gravity separation. J All Comp 735:1997–2008
Wojciechowska A, Wieszczycka K, Wojciechowska I, Olszanowski A (2017) Lead(II) extraction from aqueous solutions by pyridine extractants. Sep Pur Technol 177:239–248
Worrell E, Reuter MA (eds) (2014) Handbook of recycling: state-of-the-art for practitioners, analysts, and scientists. Elsevier
Vourlias G, Pistofidis N, Stergioudis G, Polychroniadis EK (2005) A negative effect of the insoluble particles of dross on the quality of the galvanized coatings. Solid State Sci 7(4):465–474
Vourialis G, Pistofidis N, Pavlidou E, Stergioudis G, Polychroniadis EK (2007) Study of the structure of hot-dip galvanizing byproducts. J Optoel Adv Mater 9(9):2937–2942
Xiao H-F, Chen Q, Cheng H, Min L-X, Qin W-M, Chen B-S, Xiao D, Zhang W-M (2017) Selective removal of halides from spent zinc sulfate electrolyte by diffusion dialysis. J Membr Sci 537:111–118
Zhang W-S, Cheng C-Y (2007) Manganese metallurgy review. Part III: Manganese Control in Zinc and Copper Electrolytes. Hydrometallurgy 89:178–188
Zhang QB, Hua Y (2009) Effect of Mn2+ ions on the electrodeposition of zinc from acidic sulphate solutions. Hydrometallurgy 99(3–4):249–254
Zhao Y, Zhang C (2017) Pollution control and resource reuse for alkaline hydrometallurgy of amphoteric metal hazardous wastes. Springer International Publishing AG, pp 13–38
Zueva SB, Ferella F, Innocenzi V, De Michelis I, Corradini V, Ippolito NM, Vegliò F (2021) Recovery of zinc from the treatment of spent acid solutions from the pickling stage of galvanizing plants. Sustainab 13:407
Websites
https://ippc.mos.gov.pl/ippc/?id=39: Reference document for best available techniques in iron and steel processing (in Polish; Accessed on 12 Jul 2021)
https://www.statista.com. Accessed on 17 Jun 2021
YouTube (2018) Taejong Galva Benjamin, Hot dip galvanizing line in South Korea, designed and installed by Taejong, 3 Aug 2018, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k3cisbnQdu4. Accessed on 17 Jun 2021
YouTube (2019a) James Tai, Zinc dross remover, 25 Nov 2019, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T2etPXIgOV4. Accessed on 17 Jun 2021
YouTube (2019b) Graeme Turnbull, Trailer Hot Dip Galvanizing, 29 Apr 2019b, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5nG_MYhicT4. Accessed on 17 Jun 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Rudnik, E. (2023). Hydrometallurgical Recovery of Zinc from By-Products and Waste Materials of Hot-Dip Galvanizing Process. In: Kaya, M. (eds) Recycling Technologies for Secondary Zn-Pb Resources. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-14685-5_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-14685-5_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-14684-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-14685-5
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)