Abstract
For the given non-unary input alphabet \(\varSigma \), a maximal prefix code h mapping strings over \(\varSigma \) to binary strings, and an optimal deterministic finite automaton (DFA) \(\mathcal {A}\) with n states recognizing a language \(\mathcal {L}\) over \(\varSigma \), we consider the problem of how many states we need for an automaton \(\mathcal {A}'\) that decides membership in \(h(\mathcal {L})\), the binary coded version of \(\mathcal {L}\). Namely, \(\mathcal {A}'\) accepts binary inputs belonging to \(h(\mathcal {L})\) and rejects binary inputs belonging to \(h(\mathcal {L}^{\scriptscriptstyle \mathrm {C}})\), where \(\mathcal {L}^{\scriptscriptstyle \mathrm {C}}\) is the complement of \(\mathcal {L}\). The outcome on inputs that are not valid binary codes for any string in \(\varSigma ^{*}\) can be arbitrary: \(\mathcal {A}'\) may accept, reject, or halt in a “don’t care” state. We show that any optimal deterministic don’t care finite automaton (dcDFA) \(\mathcal {A}'\) solving this promise problem uses at most \((\Vert {\varSigma }\Vert -1){\cdot }n\) states but at least n states. We also show that, for each non-unary input alphabet \(\varSigma \), there exists a maximal binary prefix code h such that, for each \(n\ge 2\) and for each N in range from n to \((\Vert {\varSigma }\Vert -1){\cdot }n\), there exists a language \(\mathcal {L}\) over \(\varSigma \) such that the optimal DFA recognizing \(\mathcal {L}\) uses exactly n states and any optimal dcDFA for solving the above promise problem uses exactly N states. Thus, we have the complete state hierarchy for deciding membership in the binary coded version of \(\mathcal {L}\), with no magic numbers in between the lower and upper bounds.
Supported by the Slovak grant contract VEGA 1/0177/21.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
State complexity of homomorphisms depends on the length of the images of symbols and is somewhat difficult to define in the general case. Perhaps the only existing related result is the state complexity of projections (that is, homomorphisms mapping each symbol either to itself or to \(\varepsilon \)), which was determined to be \(3/4{\cdot }2^n-1\) in [12].
- 2.
Throughout the paper, \(\Vert {X}\Vert \) denotes the cardinality of the set X.
- 3.
This phenomenon can be seen in Fig. 2, where we have “3”\(\mathop {\longrightarrow }\limits ^{a_4}\)“5” for \(\mathcal {A}_{{\scriptscriptstyle \varSigma },n,g,k}\). Since \(h(a_4)=\) “00001”, this corresponds to
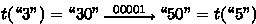 for \(\mathcal {A}'_{{\scriptscriptstyle \varSigma },n,g,k}\), passing twice through
for \(\mathcal {A}'_{{\scriptscriptstyle \varSigma },n,g,k}\), passing twice through
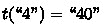 .
.
References
Berstel, J., Perrin, D., Reutenauer, C.: Codes and Automata. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Birget, J.-C.: Intersection and union of regular languages and state complexity. Inform. Process. Lett. 43, 185–190 (1992)
Bruyère, V.: Maximal codes with bounded deciphering delay. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 84, 53–76 (1991)
Čevorová, K.: Kleene star on unary regular languages. In: Jurgensen, H., Reis, R. (eds.) DCFS 2013. LNCS, vol. 8031, pp. 277–288. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39310-5_26
Geffert, V.: Magic numbers in the state hierarchy of finite automata. Inform. Comput. 205, 1652–1670 (2007)
Goldreich, O.: On promise problems: a survey. In: Goldreich, O., Rosenberg, A.L., Selman, A.L. (eds.) Theoretical Computer Science. LNCS, vol. 3895, pp. 254–290. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/11685654_12
Holzer, M., Rauch, C.: The range of state complexities of languages resulting from the cascade product—the unary case (extended abstract). In: Maneth, S. (ed.) CIAA 2021. LNCS, vol. 12803, pp. 90–101. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79121-6_8
Hopcroft, J., Motwani, R., Ullman, J.: Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and Computation. Addison-Wesley, Boston (2001)
Hricko, M., Jirásková, G., Szabari, A.: Union and intersection of regular languages and descriptional complexity. In: Proceedings of Descriptional Complexity of Formal Systems, pp. 170–181. IFIP & University, Milano (2005)
Iwama, K., Kambayashi, Y., Takaki, K.: Tight bounds on the number of states of DFA’s that are equivalent to \(n\)-state NFA’s. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 237, 485–494 (2000)
Jirásková, G.: Magic numbers and ternary alphabet. Internat. J. Found. Comput. Sci. 22, 331–344 (2011)
Jirásková, G., Masopust, T.: On a structural property in the state complexity of projected regular languages. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 449, 93–105 (2012)
Moreira, N., Pighizzini, G., Reis, R.: Optimal state reductions of automata with partially specified behaviors. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 658, 235–245 (2017)
Paull, M.C., Unger, S.H.: Minimizing the number of states in incompletely specified sequential switching functions. IRE Trans. Electron. Comput. 3, 356–367 (1959)
Pfleeger, C.P.: State reduction in incompletely specified finite-state machines. IEEE Trans. Comput. C–22, 1099–1102 (1973)
Rabin, M., Scott, D.: Finite automata and their decision problems. IBM J. Res. Develop. 3, 114–125 (1959)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Geffert, V., Pališínová, D., Szabari, A. (2022). State Complexity of Binary Coded Regular Languages. In: Han, YS., Vaszil, G. (eds) Descriptional Complexity of Formal Systems. DCFS 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13439. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13257-5_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13257-5_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-13256-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-13257-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


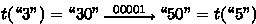 for
for 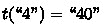 .
.