Abstract
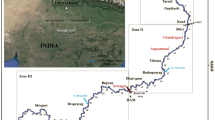
Dams are built on rivers for diverse purposes, where the most are associated with Multi-purpose river valley projects. The river water is blocked to use it for domestic purposes, irrigation, industries, navigation, and hydroelectricity. Above all, most of these projects set a common “welfare” target of managing soil erosion. However, the effort of stagnating the natural flow of alluvial channels sets ample examples where adjustment of upstream channels and consequent lateral shifting exacerbates massive threats of riverbank erosion. This chapter discusses this particular phenomenon experienced in the different parts of Indian landmasses in its first part. The latter part is specific instead. The study has been carried out to examine the channel adjustment of river Ganga upstream of Farakka Barrage up to Sahebganj with the spatial extension between 24° 45′ N and 25° 30′ N latitudes and 87° 30′ E—88° 30′ E longitudes. River Ganga, the principal stream of the great Ganga basin at the Himalayan foreland, carries a substantial sedimentary load to the lower deltaic plain in Bengal. Near Rajmahal Hills, after crossing Sahebganj, the natural downstream adjustment in terms of channel slope, channel planform, and cross-section morphology of the river exhibits a drastic change in response to the modification of the channel gradient as a consequence of the human-induced changes in hydrology and sedimentary modification as well as a degree of base-level modification with the construction of the Farakka Barrage in Malda. The plateau basalt province of lower Cretaceous to the Jurassic age at the western margin and the old alluvium Barind tract in the eastern margin of the Ganga valley has a typical role. The tectonic tilting and geological settings of Rajmahal traps, which have long been a potential force of a rapid eastbound shift of the channel, are further stimulated by the Farakka Barrage. The geostrategic decision to select sites for a large Dam overrides the geomorphic and geologic realities that crave out the left bank erosion of the river Ganga in the Malda District, bringing a massive threat to human life and resources.
The content of this chapter are based on the paper entitled ‘Channel Adjustment of River Ganga in Response to Human-induced Changes: Some Observations at Upstream of Farakka Barrage’, presented by the authors in Two Day International Seminar on “Fluvial Processes and Anthropogenic Footprint” on 11–16 March 2016, organized by the Department of Geography, University of Gour Banga, Malda in West Bengal, India.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Inquisitive readers might be interested to witness the grimed scenario of the bank erosion through the photographs by Tanmoy Bhaduri, in his photography blog ‘MONGABAY’ with the theme entitled ‘Erosion along Ganga’s riverbanks in West Bengal finds new victims’ (See here: https://india.mongabay.com/2020/11/photos-erosion-along-gangas-riverbanks-in-west-bengal-finds-new-victims/).
References
Ahmed AA, Fawzi A (2009) Meandering and bank erosion of the River Nile and its environmental impact on the area between Sohag and El-Minia, Egypt. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-009-0048-y
JC Aitchison JR Ali AM Davis 2007 When and where did India and Asia collide? J Geophys Res 112 1 19 https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JB004706
ED Andrews 1986 Downstream effects of flaming gorge reservoir on the green river, Colorado and Utah Geol Soc Am Bull 97 1012 1023
S Arroyo 1925 Channel improvements of Rio Grande and El Paso Eng News-Rec 95 374 376
Asokan A, Anitha J (2019) Change detection techniques for remote sensing applications: a survey. Earth Sci Inform 12:143–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-019-00380-5
AA Assani E Stichelbout AG Roy F Petit 2006 Comparison of impacts of dams on the annual maximum flow characteristics in the three regulated hydrological regimes in Québec Hydrol Process 20 3485 3501
AK Baksi 1995 Petrogenesis and timing of volcanism in the Rajmahal flood basalt province, Northeastern India Chem Geol 121 73 90
AK Baksi T Barman D Paul E Farrar 1987 Widespread early cretaceous flood basalt volcanism in eastern India: geochemical data from the Rajmahal–Bengal–Sylhet Traps Chem Geol 63 133 141
Ball V (1877) Geology of the Rajmahal hills. Memories GSI 13(II):155–248
Barbarossaa V, Rafael JP, Schmittc, Mark AJH, Christiane Z, Henry K, Aafke MS (2020) PNAS 117(7):3648. https://www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1912776117
A Benke 1990 Perspective on America’s vanishing streams J N Am Benthol Soc 9 77 88
W Bian T Yang Y Ma J Jin F Gao S Wang W Peng S Zhang H Wu H Li L Cao Y Shi 2019 Paleomagnetic and geochronological results from the Zhela and Weimei Formations lava flows of the eastern Tethyan Himalaya: new insights into the breakup of eastern Gondwana J Geophys Res Solid Earth 124 44 64 https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JB016403.
Biswas B (1963) Results of exploration for Petroleum in the western part of the Bengal Basin, India. In: Proceedings of the 2nd symposium on the development of petroleum resources, economic commission for Asia and far east, mineral resources development series,18. New York: United Nations, pp 241–250.
SA Brandt 2000 Classification of geomorphological effects downstream of dams CATENA 40 375 401
AP Brooks GJ Brierley 1997 Geomorphic responses of the Lower Bega River to catchment disturbance, 1851–1926 Geomorphology 1 291 304
C Camporeale P Perona A Porporato L Ridolfi 2005 On thelong-term behavior of meandering rivers Water Resour Res 41 W12403 https://doi.org/10.1029/2005WR004109
PA Carling 1988 Channel change and sediment transport in regulated U. K. Rivers. Regulated Rivers 2 369 388
HH Chang 1988 On the cause of river meandering WR White Eds International conference on River Regime Wiley New York 83 93
Chatterjee G (2016) Farakka barrage: floods and water wars imminent, but political compulsions dictate CM behaviour. Firstpost. Retrieved from https://www.firstpost.com/politics/farakka-barrage-floods-and-water-wars-imminent-but-political-compulsions-dictate-cm-behaviour-2982440.html
ZY Chen ZH Wang B Finlayson J Chen DW Yin 2010 Implications of flow control by the Three Gorges Dam on sediment and channel dynamics of the middle Yangtze (Changjiang) River China Geology 38 1043 1046
N Chien 1985 Changes in river regime after the construction of upstream reservoirs Earth Surf Proc Land 10 143 159
MF Coffin MS Pringle RA Duncan TP Gladczenko M Storey RD Muller LA Gahagan 2002 Kerguelen hotspot Magma output since 130 Ma J Petrology 43 7 1121 1137 https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/43.7.1121
V Courtillot 1999 Evolutionary catastrophes: the science of mass extinctions Press p, Camb Uni 95
P Dandekar 2014 Lessons from Farakka as government plans more barrages on Ganga SANDRP 12 10–11 8 15
Davies HL, Sun SS, Frey FA, Gautier I, McCulloch MT, Price RC, Bassias Y, Klootwijk CT, Leclaire L (1989) Basalt basement from the Kerguelen Plateau and the trail of a DUPAL plume. Contrib Mineral Petrol 103:457–469
BW Davy TRH Davies 1979 Entropy concepts in fluvial geomorphology—re-evaluation Water Resour Res 15 1 103 106
Eng J (2014) ROC analysis: web-based calculator for ROC curves. Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore (updated 2014 Mar 19). www.jrocfit.org
JE Evans JM Huxley RK Vincent 2007 Upstream channel changes following dam construction and removal using a GIS/Remote Sensing approach J Am Water Resour Assoc 43 3. 10.1111⁄j.1752-1688.2007.00055.x
Fisher W (1995) Toward sustainable development? Struggling Over India's Narmada River. M. E. Sharpe. p 161. ISBN 978-1-56324-341-7
FA Frey MF Coffin PJ Wallace D Weis X Zhao SW Wise Jr V Wahnert DAH Teagle PJ Saccocia DN Reusch MS Pringle KE Nicolaysen CR Neal RD Muller CL Moore JJ Mahoney L Keszthelyi H Inokuchi RA Duncan H Delius JE Damuth D Damasceno HK Coxall MK Borre F Boehm J Barling NT Arndt M Antretter 2000 Origin and evolution of a submarine large igneous province: the Kerguelen Plateau and Broken Ridge, southern Indian Ocean Earth Planet Sci Lett 176 73 89
B Fu BF Wu YH Lu ZH Xu JH Cao D Niu GS Yang YM Zhou 2010 Three gorges project: efforts and challenges for the environment Prog Phys Geogr 34 741 754
C Gaina RD Muller B Brown T Ishihara 2007 Breakup and early seafloor spreading between India and Antarctica Geophys J Int 170 151 169
A Ghatak AR Basu 2013 Isotopic and trace element geochemistry of alkalic–maficultramafic-carbonatitic complexes and flood basalts in NE India: Origin in a heterogeneous Kerguelen Plume Geochim Cosmochim Acta 115 46 72
NC Ghose N Chatterjee BF Windley 2017 Subaqueous early eruptive phase of the Late Aptian Rajmahal volcanism, India: evidence from volcaniclastic rocks, bentonite, black shales, and oolite Geosci Front 8 809 822
WL Graf 1999 Dam nation: a geographic census of American dams and their large-scale hydrologic impacts Water Resour Res 35 1305 1311
EA Greathouse CM Pringle WH McDowell JG Holmquist 2006 Indirect upstream effects of dams: consequences of migratory consumer extirpation in Puerto Rico Ecol Appl 16 1 339 352
KJ Gregory C Park (1974) Adjustment of river channel capacity downstream from a reservoir Water Resour Res 10 870 873
KJ Gregory 1987 Environmental effects of river channel change Regulated Rivers 1 358 363
Hobson GV (1929) General report. Geol. Surv. India Records of the Geol. Surv India. LXII(1):145–146
Hossain M, Khan M, Chowdhury K, Rashed A (2019) Synthesis of the tectonic and structural elements of the Bengal Basin and its surroundings. In: Mukherjee S (ed) Tectonics and structural geology: Indian context. Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2019, pp 135–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99341-6_6
H Huang HH Chang GC Nanson 2004 Minimum energy as the general form of critical flow and maximum flow efficiency and for explaining variations in river channel pattern Water Resour Res 40 4 W04502 https://doi.org/10.1029/2003wr002539
S Ingle D Weis JS Scoates FA Frey 2002 Relationship between the early Kerguelen plume and continental flood basalts of the paleo-Eastern Gondwana margins Earth Planet Sci Lett 197 35 50
S Ishizaka 2006 The Anti Tehri Dam movement as a new social movement and Gandhism J Jpn Assoc S Asian Stud 18 2006
James GA (2014) Ecology is permanent economy: the activism and environmental philosophy of Sunderlal Bahuguna. State University of New York Press, Albany. ISBN 978-1-4384-4673-8
Jenks George F (1967) The data model concept in statistical mapping. Int Yearb Cartography 7:186–190
Kapawar MR, Mamilla V (2020) Paleomagnetism and rock magnetism of early Cretaceous Rajmahal basalts, NE India: implications for paleogeography of the Indian subcontinent and migration of the Kerguelen hotspot. J Asian Earth Sci 201(2020):104517. ISSN 1367-9120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104517
R Kent 1991 Lithospheric uplift in eastern Gondwana: evidence for long-lived mantle plume system? Geology 19 19 23
RW Kent MS Pringle R Dietmar Müller AD Saunders NC Ghose 2002 40Ar/39Ar Geochronology of the Rajmahal Basalts, India, and Their Relationship to the Kerguelen Plateau J Petrol 43 1141 1153 https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/43.7.1141
RW Kent AD Saunders PD Kempton NC Ghose 1997 Rajmahal Basalts, Eastern India: mantel sources and melts distribution at a volcanic rifted margin Am Geophys Union Geophys Monogr 100 145 182
Kishwar M (1995) A Himalayan catastrophe: the controversial Tehri Dam in the Himalayas. Manushi 91 (Nov-Dec 1995), pp 5–16
CT Klootwijk 1971 Palaeomagnetism of the Upper Gondwana Rajmahal Traps, Northeast India Tectonophysics 12 449 467
TM Koel RE Sparks 2002 Historical patterns of river stage and fish communities as criteria for operations of dams on the Illinois River River Res Appl 18 3 19
GM Kondolf 1997 Hungry water: effects of dams and gravel mining on rivers channels Environ Manage 21 533 551
F Lajoie AA Assani AG Roy M Mesfioui 2007 Impacts of dams on monthly flow characteristics. The influence of watershed size and seasons J Hydrol 334 423 439
Langbein WB, Leopold LB (1966) River meanders—theory of minimum variance. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 422-H. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Lawson JM (1925) Effect of Rio Grande storage on river erosion and deposition. Eng News Record 327–334
FK Ligon WE Dietrich WJ Trush 1995 Downstream ecological effects of dams Bioscience 45 183 192
HY Madukwe 2016 Granulometric Analysis of the Sandstone Facies of the Ise Formation, Southwestern Nigeria J Multi Eng Sci Technol (JMEST) 3 3909 3919
FJ Magilligan KH Nislow 2001 Long-term changes in regional hydrologic regime following impoundment in a humid-climate watershed J Am Water Resour Assoc 37 1551 1569
FJ Magilligan KH Nislow 2005 Changes in hydrologic regime by dams Geomorphology 71 61 78
FJ Magilligan HJ Haynie KH Nislow 2008 Channel adjustments to dams in the Connecticut River basin: implications for forested mesic watersheds Ann Assoc Am Geogr 98 267 284
FJ Magilligan KH Nislow BE Graber 2003 A scale-independent assessment of discharge reduction and riparian disconnectivity following flow regulation by dams Geology 31 569 572
JJ Mahoney JD McDougall GW Lugmair K Gopalan 1983 Kerguelen hotspot source for Rajmahal Traps and Ninetyeast Ridge? Nature 303 385 389
Malhotra SL (1951) Effects of barrages and weirs on the regime of rivers. In: Proceedings of international association of hydraulic research, 4th Meeting, pp 335–347
S Mandal 2017 Assessing the instability and shifting character of the river bank Ganga in Manikchak Diara of Malda District, West Bengal using Bank Erosion Hazard Index (BEHI), RS & GIS Eur J Geogr 8 4 6 25
W Marsh J Dozier 1981 Landscape: an introduction to physical geography Addison-Wesley Reading, MA
MG Mehta 2010 A river of no dissent: Narmada Movement and coercive Gujarati nativism South Asian Hist Cult 1 4 509 528
S Misra 2006 Precambrian chronostratigraphic growth of Singhbhum-Orissa Craton, Eastern Indian shield: an alternative model J Geol Soc India 67 356 378
WK Mohanty AK Mohapatra AK Verma KF Tiampo K Kislay 2014 Earthquake forecasting and its verification in northeast India Geomat Nat Haz Risk 7 194 214
RJ Moiola D Weiser 1968 Textural parameters: an evaluation J Sediment Petrol 38 45 53 https://doi.org/10.1306/74D718C5-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Nandy P (1992) The Old Man and the River. In: Rigzin T (ed. 1997), Fire in the heart, firewood on the back: writings on and by Himalayan Crusader Sunderlal Bahuguna, Silyara, Tehri Garhwal: Parvatiya Navjeevan Mandal, pp 9–13
GC Nanson HQ Huang 2008 Least action principle, equili brium states, iterative adjustment and the stability of alluvial channels Earth Surf Proc Land 33 6 923 942
Narula S (2008) The story of Narmada Bachao Andolan: Human Rights in the global economy and the struggle against the World Bank. New York University School of Law, p 5
NRLD (2018) National Register of Large Dams 2018, Central Water Commission, Govt of India. http://cwc.gov.in/national-register-large-dams
HKH Olierook F Jourdan RE Merle NE Timms N Kusznir J Muhling 2016 Bunbury Basalt: Gondwana breakup products or earliest vestiges of the Kerguelen mantle plume? Earth Planet Sci Lett 440 20 32 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2016.02.008
C Paola 2000 Quantitative models of sedimentary basin filling Sedimentology 47 Suppl. 1 121 178
E Pascoe 1959 A manual of Geology of India and Burma Gov 3 485 1343
Perona P, Porporato A, Ridolfi L (2002) River dynamics after cutoff: a discussion of different approaches, In: Bousmar D, Zech Y (eds) Proceedings of the River flow 2002 international conference on fluvial hydraulics. International Association for Hydro-Environment Engineering and Research, Spain, pp 715–721
GE Petts AM Gurnell 2005 Dams and geomorphology: research progress and future directions Geomorphology 71 27 47
Petts GE (1980) Morphological changes of river channels consequent upon headwater impoundment. J Inst Water Eng Sci 34:374–382
JD Phillips 2003 Toledo Bend reservoir and geomorphic response in the lower Sabine River River Res Appl 19 137 159
NL Poff JD Allan MB Bain JR Karr BD Richter RE Sparks JC Stromberg 1997 The natural flow regime Bioscience 47 769 784
NL Poff BP Bledsoe CO Cuhaciyan 2006 Hydrologic variation with land use across the contiguous United States: geomorphic and ecological consequences for stream ecosystems Geomorphology 9 264 285
ME Power WE Dietrich JC Finlay 1996a Dams and downstream aquatic biodiversity: potential food web consequences of hydrologic and geomorphic change Environ Manage 20 887 895
ME Power WE Dietrich JC Finlay 1996b Dams and downstream biodiversity: potential food web consequences of hydrologic and geomorphic change Environ Manage 20 887 895
B Prasad BS Pundir 2017 Gondwana biostratigraphy of the Purnea Basin (Eastern Bihar, India), and its correlation with Rajmahal and Bengal Gondwana Basins J Geol Soc India 90 405 427
CM Pringle 1997 Exploring how disturbance is trans-mitted upstream: going against the flow J N Am Benthol Soc 16 425 438
Ray Chowdhury PE (1965) Bihar District gazetteers Santahal Pargana. Secretariat Press, Patna, pp 7-9 and p 36
Rhoads BL (2020) River dynamics: geomorphology to support management. Cambridge University Press.https://doi.org/10.1017/9781108164108
BD Richter JV Baumgartner J Powell DP Braun 1996 A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems Conserv Biol 10 1163 1174
SB Rood JM Mahoney 1990 Collapse of riparian poplar forests downstream from dams in Western Prairies: probable causes and prospects for mitigation Envrion Manage 14 451 464
AB Roy 2014 Indian subcontinent, reference module in earth systems and environmental sciences Elsevier
AB Roy A Chatterjee 2015 Tectonic framework and evolutionary history of the Bengal Basin in the Indian subcontinent Curr Sci 109 271 279
Rudra K (2006) Shifting of the Ganga and land erosion in West Bengal/A socio-ecological viewpoint. CDEP Occasional Paper-8. Indian Institute of Management, Calcutta, pp 1–43
Rudra K (2008) Banglar nadikatha. Kolkata, Sahitya Samsad, pp 11–19
Rudra K (2009) Re-flooding the Kosi. Himal S Asian 22(3):50–51
Rudra K (2018) The dynamic Ganga. In: Rivers of the Ganga-Brahmaputra-Meghna Delta. Geography of the physical environment. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-76544-0_4
Sarif MN, Siddiqui L, Islam MS, Parveen N, Saha M (2021) Evolution of river course and morphometric features of the River Ganga: a case study of up and downstream of Farakka Barrage. Int Soil Water Conserv Res. ISSN 2095-6339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2021.01.006
Shrevastava RN, Shah SC (1966) Ginko digitata brong: from the Rajmahal hills, Santhgal Parganas (Bihar). Records GSI 96(2):309–312
Shulits S (1934) Experience with bed degradation below dams on European rivers. Eng News Record 838–839
M Siegmund-Schultze 2018 The legacy of large dams and their effects on the water-land nexus Reg Environ Change 18 1883 1888 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-018-1414-7
MB Singer (2007a) The influence of major dams on hydrology through the drainage network of the Sacramento Valley, California River Res Appl 23 55 72
MB Singer 2008 Downstream patterns of bed-material grain size in a large, lowland alluvial river subject to low sediment supply Water Resour Res 44 W12202 https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR007183
MB Singer 2010 Transient response in longitudinal grain size to reduced gravel supply in a large river Geophys Res Lett 37 L18403 https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL044381
MB Singer (2007b) The influence of major dams on hydrology through the drainage network of the Sacramento River Basin, California, River Res Applic 23 55 72
AP Singh N Kumar B Singh 2004 Magmatic underplating beneath the Rajmahal Traps: gravity signature and derived 3-D configuration J Earth Syst Sci 113 759 769
Singh A (2019) Farakka barrage: one historic stupidity that made Bihar a target of both floods and famine. Retrieved from https://tfipost.com/2019/10/farakka-barrage-one-historic-stupidity-that-made-bihar-a-target-of-both-floods-and-famine/
A Singh K Bhushan C Singh MS Steckler SH Akhter L Seeber W-Y Kim AK Tiwari R Biswas 2016 Crustal structure and tectonics of Bangladesh: new constraints from inversion of receiver functions Tectonophysics 680 99 112
A Singh C Singh BLN Kennett 2015 A review of crust and upper mantle structure beneath the Indian subcontinent Tectonophysics 644–645 1 21
A Sinha S Rais 2019 Granulometric Analysis of Rajmahal Inter-Trappen sedimentary rocks (early cretaceous), Eastern India, implications for depositional history Int J Geosci 10 238 253 https://doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2019.103015
R Sinha S Ghosh 2012 Understanding dynamics of large rivers aided by satellite remote sensing: a case study from Lower Ganga plains India Geocarto Int 27 3 207 219 https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2011.620180
Storey M, Kent RW, Saunders AD, Salters VJ, Hergt J, Whitechurch H, Sevigny JH, Thirlwall MF, Leat P, Ghose NC, Gifford M, Schlich R et al (1992) Lower cretaceous volcanic rocks on continental margins and their relationship to the Kerguelen Plateau, In: Proceedings of the Ocean drilling program. Sci Results 120:33–53. https://doi.org/10.2973/odp.proc.sr.120.118.1992
S Tiwari GS Jassal (2003) Origin and evolution of the Garo-Rajmahal Gap J Geol Soc India 57 389 403
DJ Topping DM Rubin JLE Vierra (2000) Colorado River sediment transport 1. Natural sediment supply limitation and the influence of Glen Canyon Dam Water Resour Res 36 515 542
Williams GP, Wolman MG (1984) Downstream effects of Dams on Alluvial Rivers. U. S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1286. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC. 83 pp
Willis CM, Griggs GB (2003) Reductions in fluvial sediment discharge by coastal dams in California and implications for beach sustainability. J Geol 111
JX Xu 1990 An experimental study of complex response in river channel adjustment downstream from a reservoir Earth Surf Proc Land 15 43 53
CT Yang 1971 On river meanders J Hydrol 13 231 253
A Yin CS Dubey AAG Webb TK Kelty M Grove GE Gehrels WP Burgess 2010 Geologic correlation of the Himalayan orogen and Indian craton: Part 1. Structural geology, U-Pb zircon geochronology, and tectonic evolution of the Shillong Plateau and its neighboring regions in NE India Geol Soc Am Bull 122 336 359
Y Zahar A GhoRbel G Albergel 2008 Impacts of large dams on downstream flow conditions of rivers: Aggradation and reduction of the Medjerda channel capacity downstream of the Sidi Salem dam (Tunisia) J Hydrol 351 318 330
C Zarfl AE Lumsdon J Berlekamp L Tydecks K Tockner 2015 A global boom in hydropower dam construction Aquat Sci 77 1 161 170 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-014-0377-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sarkar, T., Mishra, M. (2022). Large Dams, Upstream Responses, and Riverbank Erosion: Experience from the Farakka Barrage Operation in India. In: Mandal, S., Maiti, R., Nones, M., Beckedahl, H.R. (eds) Applied Geomorphology and Contemporary Issues. Geography of the Physical Environment. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04532-5_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04532-5_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-04531-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-04532-5
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)