Abstract
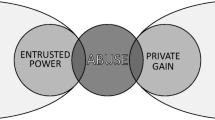
This chapter will address the philosophical and ethical perspective that corruption, in its many forms, is embedded in most societies’ fabrics as well as justified and rationalised. The chapter will examine corruption and its negative influence on societies by allowing for ethical pluralisms, i.e. Aristoteles and Confucian thought. We will attempt to discuss this from a global ethics overview that tries to avoid imposing a Greek and western lens and that should conjoin shared norms while simultaneously preserving the irreducible differences between cultures and peoples. We have three main objectives for this chapter. Firstly, we will explore the argument that in any culture, corruption in its many forms, may it be guanxi, bribes, political favours, bribes, are covered by the traditional understanding of some types of ethical/philosophical judgement. Secondly, we critically analyse how corruption may have positive effects under some circumstances. Thirdly, we attempt to help the reader better comprehend the diversity in legislation and approaches by governments and the inherent conflicts for both multinationals and companies that are internationalising. Thus, we discuss the impact of globalisation on corporate governance and the current anti-corruption measures many nations are trying to both implement and superimpose globally through their home-based multinationals.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arjoon, Surendra. 2017. “Virtues, Compliance, and Integrity: A Corporate Governance Perspective”. In International Handbooks in Business Ethics, 995–1002. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands.
Barcham, Manuhuia. 2012. “Rule by Natural Reason: Late Medieval and Early Renaissance Conceptions of Political Corruption”. In Corruption: Expanding the Focus. ANU Press.
Basu, Kaushik, and Tito Cordella, eds. 2018. Institutions, Governance and the Control of Corruption. 1st ed. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing.
Begu, L.S., S.A. Apostu, and A.O. Enache. 2019. “Corruption Perceptions Index and Economic Development of the Country”. Proceedings of the International Conference on Applied Statistics (Sciendo) 1 (1): 115–22.
Belfort, Jordan. 2011. Catching the Wolf of Wall Street: More Incredible True Stories of Fortunes, Schemes, Parties, and Prison. New York, NY, USA: Bantam Books.
Botton, Alain de. 2008. The Consolations of Philosophy. Harlow: Penguin Books.
Buckley, Peter J., and Mark Casson. 1976. “The Multinational Enterprise in the World Economy”. In The Future of the Multinational Enterprise, 1–31. London: Palgrave Macmillan UK.
Coates, A. J. 1997. The Ethics of War. Manchester: Manchester University Press.
Cole, P. 2007. “Human Rights and the National Interest: Migrants, Healthcare and Social Justice”. Journal of Medical Ethics 33 (5): 269–272.
Corporate Political Engagement Index 2018. 2021. Org.Uk. Accessed June 16. https://www.transparency.org.uk/cpei/.
Dearmon, J., and R. Grier. 2011. “Trust and the Accumulation of Physical and Human Capital”. European Journal of Political Economy 27 (3): 507–519.
Denoon, Donald. 2009. A Trading Network and Its South African Node—Networks of Empire: Forced Migration in the Dutch East India Company, Xv+340. By Kerry Ward. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Hardback (ISBN 978-0-521-88586-7). Journal of African History 50 (3): 457–58.
Dimanti, Eugen, and Guglielmo Tosato. 2018. “Causes and Effects of Corruption: What Has Past Decade’s Empirical Research Taught Us? A Survey: Causes and Effects of Corruption”. Journal of Economic Surveys 32 (2): 335–56.
Duiker, William J., and Jackson J. Spielvogel. 2010. The Essential World History: V. 1. Belmont, CA, USA: Wadsworth Publishing.
Duiker, William J. Duiker, and Jackson J. Spielvogel. 1994. World History, Volume I to 1800. Wadsworth Publishing Company.
Dunning, John H. 2003. “Some Antecedents of Internalization Theory”. Journal of International Business Studies 34 (2): 108–15.
Elson, Peter R., Jean-Marc Fontan, Sylvain Lefèvre, and James Stauch. 2018. “Foundations in Canada: A Comparative Perspective”. The American Behavioral Scientist 62 (13): 1777–1802.
Gaustad, Edwin S., and John T. Noonan Join. 1988. “The Believer and the Powers That Are: Cases, History, and Other Data Bearing on the Relation of Religion and Government”. Journal of American History (Bloomington, Ind.) 75 (1): 226.
Gustafson, Andrew. 2013. “In Defense of a Utilitarian Business Ethic: Business and Society Review”. Business and Society Review 118 (3): 325–60.
Hammurabi. 2018. The Code of Hammurabi: (Annotated)(Illustrated). Edited by Jan Oliveira. Translated by Robert Francis Harper. Independently Published.
Hauser, Marc, and Peter Singer. 2005. “Morality Without Religion”. Free Inquiry 26: 18–19.
Heeks, Richard, and Harald Mathisen. 2012. “Understanding Success and Failure of Anti-Corruption Initiatives”. Crime, Law, and Social Change 58 (5): 533–49.
Hess, David, and Thomas W. Dunfee. 2000. “Fighting Corruption: A Principled Approach: The C Principles (Combating Corruption)”. Cornell International Law Journal 33 (3): 593–626.
Hitka, Miloš, Milota Vetráková, Žaneta Balážová, and Zuzana Danihelová. 2015. “Corporate Culture as a Tool for Competitiveness Improvement”. Procedia Economics and Finance 34: 27–34.
Hodder, Ian. 2012. Entangled: An Archaeology of the Relationships Between Humans and Things. 1st ed. Chichester: Wiley.
Huttenback, Robert A. 2003. Kashmir and the British Raj 1847–1947. Karachi, Pakistan: OUP.
Imran, Syed Muhammad, Hafeez Ur Rehman, and Rana Ejaz Ali Khan. 2019. “Determinants of Corruption and Its Impact on Firm Performance: Global Evidence”. Pakistan Journal of Commerce and Social Sciences 13 (4): 1017–28.
Jacques, Scott, and Richard Wright. 2010. “Right or Wrong? Toward a Theory of IRBs’ (Dis)Approval of Research”. Journal of Criminal Justice Education 21 (1): 42–59.
Johnson, Noel D., William Ruger, Jason Sorens, and Steven Yamarik. 2014. “Corruption, Regulation, and Growth: An Empirical Study of the United States”. Economics of Governance 15 (1): 51–69.
Jurkiewicz, Carole L. 2020. “The Ethinomics of Corruption”. In Global Corruption and Ethics Management: Translating Theory into Action. Rowman & Littlefield. https://rowman.com/ISBN/9781538117415/Global-Corruption-and-Ethics-Management-Translating-Theory-into-Action.
Keefer, Bradley S. 2013. Conflicting Memories on the “River of Death”: The Chickamauga Battlefield and the Spanish-American War, 1863–1933. Kent, OH: Kent State University Press.
Kurer, Oskar. 1993. “Clientelism, Corruption, and the Allocation of Resources”. Public Choice 77 (2): 259–73.
Leff, Nathaniel H. 1964. “Economic Development Through Bureaucratic Corruption”. The American Behavioral Scientist 8 (3): 8–14.
Lewis, N., 1954. “On Official Corruption in Roman Egypt: The Edict of Vergilius Capito”. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 98 (2): 153–58.
Leys, Colin. 1965. “What Is The Problem About Corruption?” The Journal of Modern African Studies 3 (2): 215–30.
Luo, Yadong. 2008. “The Changing Chinese Culture and Business Behavior: The Perspective of Intertwinement Between Guanxi and Corruption”. International Business Review (Oxford, England) 17 (2): 188–93.
Martins, Lurdes, Jorge Cerdeira, and Aurora Teixeira. 2020. “Does Corruption Boost or Harm Firms’ Performance in Developing and Emerging Economies? A Firm‐Level Study”. World Economy 43 (8): 2119–52.
Méon, Pierre-Guillaume, and Laurent Weill. 2010. “Is Corruption an Efficient Grease?” World Development 38 (3): 244–59.
Michael, Michael L. 2006. “Business Ethics: The Law of Rules”. Business Ethics Quarterly: The Journal of the Society for Business Ethics 16 (4): 475–504.
Mill, John Stuart. 1998. Utilitarianism. London: Oxford University Press.
Morse, John. 1999. “The Missing Link Between Virtue Theory and Business Ethics”. Journal of Applied Philosophy 16 (1): 47–58.
Mulgan, Richard. 2012. “Aristotle on Legality and Corruption”. In Corruption: Expanding the Focus. ANU Press.
Napal, Geetanee. 2001. Disclosing Corruption: A Move Towards Transparency in Mauritius. Editions Le Printemps.
Nicholas. 1963. Al-Farabi’s Short Commentary on Aristotle’s Prior Analytics. Pittsburgh, PA, USA: University of Pittsburgh Press.
Ninkovich, Frank A. 1999. “Cuba, the Philippines, and the Hundred Years’ War”. Reviews in American History 27 (3): 444–51.
Pierre-Guillaume, Meon and Khalid, Sekkat. 2005. “Does Corruption Grease or Sand the Wheels of Growth?”. Public Choice 122 (1): 69–97.
Plato. 1979. The Laws of Plato. Balgowlah, NSW, Australia: Beaufort Books.
Plato. 2012. Statesman. Edited by Eva Brann, Peter Kalkavage, and Eric Salem. Newburyport, MA, USA: Focus Publishing/R Pullins.
Redding, Gordon. 2003. “Guanxi and Business. Yadong Luo”. China Journal (Canberra, A.C.T.) 49: 172–74.
Rock, Michael T., and Heidi Bonnett. 2004. “The Comparative Politics of Corruption: Accounting for the East Asian Paradox in Empirical Studies of Corruption, Growth and Investment”. World Development 32 (6): 999–1017.
Roman, Ronald M., Sefa Hayibor, and Bradley R. Agle. 1999. “The Relationship Between Social and Financial Performance: Repainting a Portrait”. Business and Society 38 (1): 109–25.
Rose-Ackerman, Susan. 1997. Corruption: A Study in Political Economy. San Diego, CA, USA: Academic Press.
Rose-Ackerman, Susan. 2002. “‘Grand’ Corruption and the Ethics of Global Business”. Journal of Banking & Finance 26 (9): 1889–1918.
Sandel, Michael J. 2009. Justice: What’s the Right Thing to Do? Farrar Straus Giroux.
Smialek, Jeanna. 2020. “Trump Tried to Kill Anti-Bribery Rule He Deemed “Unfair,” New Book Alleges”. The New York Times, January 15. https://www.nytimes.com/2020/01/15/business/economy/trump-bribery-law.html.
Spence, Lewis. 2017. The Popul Vuh. Pinnacle Press.
Stefes, Christoph H. 2006. Understanding Post-Soviet Transitions: Corruption, Collusion and Clientelism. 2006th ed. Gordonsville, VA, USA: Palgrave Macmillan.
Strunk, Thomas. 2016. History After Liberty: Tacitus on Tyrants, Sycophants, and Republicans. Ann Arbor, MI, USA: University of Michigan Press.
Tanzi, Vito, and Hamid Davoodi. 1997. “Corruption, Public Investment, and Growth”. https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/wp/wp97139.pdf.
Trautmann, Thomas R. 2016. Arthashastra: The Science of Wealth. New Delhi, India: Portfolio.
Urbina, Dante A. 2020. “The Consequences of a Grabbing Hand: Five Selected Ways in Which Corruption Affects the Economy”. Economia (Pontificia Universidad Catolica Del Peru. Departamento de Economia) 43 (85): 65–88.
Vahlne, Jan-Erik, and Jan Johanson. 2013. “The Uppsala Model on Evolution of the Multinational Business Enterprise—From Internalization to Coordination of Networks”. International Marketing Review 30 (3): 189–210.
Verbeke, Alain, M. Amin Zargarzadeh, and Oleksiy Osiyevskyy. 2014. “Internalization Theory, Entrepreneurship and International New Ventures”. Multinational Business Review 22 (3): 246–69.
Wang, Tangjia. 2014. “Is Confucianism a Source of Corruption in Chinese Society? A New Round of Debate in Mainland China”. Dao 13 (1): 111–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Gerardou, F.S., Moran, B.V.G., Meriton, R., Brown, A. (2022). The Cancer of Corruption: A Philosophical and Ethical Perspective. In: Faldetta, G., Mollona, E., Pellegrini, M.M. (eds) Philosophy and Business Ethics. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97106-9_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97106-9_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-97105-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-97106-9
eBook Packages: Business and ManagementBusiness and Management (R0)