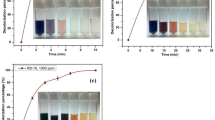
Abstract
Water is the primary necessity of every living being. But for better livelihood, human beings doing numerous activities such as industrialization, urbanization, etc. lead to polluting surface water sources. The wastewater contains various pollutants like dye, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, surfactants, etc. (Garcia-Segura et al., 2016). A dye is a common pollutant that is harmful, toxic and carcinogenic in nature coming in the effluents of various industries like textile, paper, paint, food, leather, hair colouring cosmetics and printing industries. Eosin yellow (EY) is one of the synthetic dyes based on disodium salt (Rani et al., 2020). Discharge of effluent carrying EY dye will create environmental issues by increasing chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) in the water source. Also, coloured water inhibits the penetration of sunlight into the water body, so it affects the photosynthesis process of aquatic plants. This phenomenon results in a decrease in dissolved oxygen (DO) level in the water body which also affects the respiration process of aquatic animals (Kumar and Ghosh, 2019; Tarkwa et al., 2019). Being carcinogenic and mutagenic in nature, it also affects human health. So, there is a strong need for treatment before it is released into any surface water stream.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babuponnusami, A. and Muthukumar, K. (2014). A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2: 557–572.
Bokare, A.D. and Choi, W. (2014). Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes. J. Hazard. Mater., 275: 121–135.
Garcia-Segura, S., Bellotindos, L.M., Huang, Y.H., Brillas, E. and Lu, M.C. (2016). Fluidized-bed Fenton process as alternative wastewater treatment technology-A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 67: 211–225.
Hasnath, K. and Akhilnath, G. (2017). COD removal from synthetic wastewater containing azithromycin using fluidized bed Fenton process. IJARIIE, 2: 51–59.
Kumar, V. and Ghosh, P. (2019). Performance evaluation of modified black clay as a heterogeneous Fenton catalyst on decolourization of azure B dye: Kinetic study and cost evaluation. Trans. Tianjin Univ., 25: 527–539.
Mesquita, I., Matos, L.C., Duarte, F., Maldonado-Hódar, F.J., Mendes, A. and Madeira, L.M. (2012). Treatment of azo dye-containing wastewater by a Fenton-like process in a continuous packed-bed reactor filled with activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater., 237: 30–37.
Rani Rosaline, D., Inbanathan, S.S., Suganthi, A., Rajarajan, M., Kavitha, G., Srinivasan, R., Hegazy, H.H., Umar, A., Algarni, H. and Manikandan, E. (2020). Visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of eosin yellow (EY) dye based on NiO-WO3 nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotech., 20: 924–933.
Tarkwa, J.B., Oturan, N., Acayanka, E., Laminsi, S. and Oturan, M.A. (2019). Photo-fenton oxidation of Orange G azo dye: Process optimization and mineralization mechanism. Environ. Chem. Lett., 17: 473–479.
Tsai, W.C., de Luna, M.D., Bermillo-Arriesgado, H.L., Futalan, C.M., Colades, J.I. and Wan, M.W. (2016). Competitive fixed-bed adsorption of Pb (II), Cu (II), and Ni (II) from aqueous solution using chitosan-coated bentonite. Int. J. Polym. Sci., 2016: 1–11.
Vu, A.T., Xuan, T.N. and Lee, C.H. (2019). Preparation of mesoporous Fe2O3· SiO2 composite from rice husk as an efficient heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst for degradation of organic dyes. J. Water. Process. Eng., 28: 169–180.
Wang, X., Yang, L., Zhang, J., Wang, C. and Li, Q. (2014). Preparation and characterization of chitosan–poly (vinyl alcohol)/bentonite nanocomposites for adsorption of Hg (II) ions. Chem. Eng. J., 251: 404–412.
Yazdanbakhsh, A.R., Mohammadi, A.S., Sardar, M., Godini, H. and Almasian, M. (2014). COD removal from synthetic wastewater containing azithromycin using combined coagulation and a Fenton-like process. Environ. Eng. Manage. J., 13(12): 2929–2936.
Zhao, Y., Kang, S., Qin, L., Wang, W., Zhang, T., Song, S. and Komarneni, S. (2020). Self-assembled gels of Fe-chitosan/montmorillonite nanosheets: Dye degradation by the synergistic effect of adsorption and photo-Fenton reaction. Chem. Eng. J., 379: 122322.
Zheng, H., Pan, Y. and Xiang, X. (2007). Oxidation of acidic dye Eosin Y by the solar photo-Fenton processes. J. Hazard. Mater., 141: 457–464.
Zhou, L., Hu, J., Zhong, H. and Li, X. (2012). Study of phenol removal using fluidized-bed Fenton process. Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 90: 377–382.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mohapatra, T., Ghosh, P. (2022). Degradation of Eosin Yellow Dye Solution by using Nanosized Copper Based Heterogenous Fenton-like Catalyst in a Fluidised Bed Reactor. In: Haq, I., Kalamdhad, A.S., Dash, S. (eds) Environmental Degradation: Monitoring, Assessment and Treatment Technologies. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-94148-2_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-94148-2_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-94147-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-94148-2
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)