Abstract
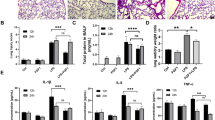
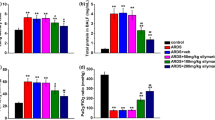
Taurine has the function of immune regulation, relieving acute and chronic inflammation caused by various agents, and maintaining cell homeostasis. This investigation focused on the protective functions of taurine targeting acute lung injury (ALI) induced by LPS. Sixty male SD rats aged 6−7 weeks were segregated at random: blank control group (C group), taurine control group (T group), ALI model group (LPS group), and taurine prevention groups (LPST1, LPST, LPST3 Groups). C group and LPS group were given normal drinking water, while T group and LPST group were given 2% taurine in drinking water. LPST1 group was given 1% taurine in drinking water while. LPST3 group was given 3% taurine in drinking water. On the 14th and 28th day, LPS group and LPST1, LPST, and LPST3 groups were subjected to injection of LPS (25 mg/kg) into the trachea of rats. Serum, peripheral blood, lung tissue, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were collected at 6 h post-LPS injection. The wet/dry ratio (W/D) of lung was measured by hot drying method. The population of white blood cells and the abundance of inflammatory-related cells within peripheral blood were counted by an automatic blood cell analyzer. The population of white blood cells within BALF was counted by a white blood cell counting plate combined with Swiss Giemsa staining, while the proportion of related white blood cells was calculated. BCA reagent was used to determine the protein concentration in BALF. The levels of pro-inflammatory factors (IL-1 β, IL-6, IL-18, TNF - α), anti-inflammation factors (IL-10, IL-4), and taurine within serum and lung tissue were detected by ELISA. Lung structural tissue alterations were observed through HE staining techniques. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activities within lung tissue were detected through colorimetry. Protein expression levels of TLR4, MyD88, NF-κ Bp65, NF-κ Bp-p65, MCP-1, together with CD68 within lung tissue, were analyzed by Western blot (WB) and immunohistochemistry (IHC). The taurine pretreatment group contained significantly reduced W/D, MPO activity, and the number of inflammatory cells in BALF induced by LPS. In addition, compared with ALI model group, the taurine pretreatment group contained significantly reduced levels of pro-inflammatory factors in lung tissue, increased levels of anti-inflammatory factors, and decreased expression levels of key proteins in TLR-4/NF-κ B pathway. Taurine can protect rats from ALI by inhibiting the activation of neutrophils, macrophages, and TLR-4/NF-κ B signaling pathway.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALI:
-
acute lung injury
- ARDS:
-
acute respiratory distress syndrome
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
References
Ajuebor MN, Flower RJ, Hannon R et al (1998) Endogenous monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 recruits monocytes in the zymosan peritonitis model. J Leukoc Biol 63:108–116
Aratani Y (2018) Myeloperoxidase: its role for host defense, inflammation, and neutrophil function. Arch Biochem Biophys 640:47–52
Blazquez-Prieto J, Lopez-Alonso I, Huidobro C et al (2018) The emerging role of neutrophils in repair after acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 59:289–294
Cavaillon JM (2018) xotoxins and endotoxins: inducers of inflammatory cytokines-sciencedirect toxicon
Chen Y, Guo L, Lang H et al (2018) Effect of a stellate ganglion block on acute lung injury in septic rats. Inflammation 41:1601–1609
Chesney RW (1985) Taurine: its biological role and clinical implications. Adv Pediatr Infect Dis 32:1–42
Danielson C, Benjamin RJ, Mangano MM et al (2010) Pulmonary pathology of rapidly fatal transfusion-related acute lung injury reveals minimal evidence of diffuse alveolar damage or alveolar granulocyte infiltration. Transfusion 48:2401–2408
De Boever S, Croubels S, Meyer E, Sys S, Beyaert R, Ducatelle R, De Backer P (2009) Characterization of an intravenous lipopolysaccharide inflammation model in broiler chickens. Avian Pathol 38:403–411
Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S et al (2009) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): an overview. J Interf Cytokine Res 29:313–326
Fei YX, Zhao B, Yin QY, et al (2019) Ma Xing Shi Gan decoction attenuates PM2.5 induced lung injury via inhibiting 10:1361
Grommes J, Soehnlein O (2011) Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury. Mol Med 17:293–307
Hamesch K, Borkham-Kamphorst E, Strnad P et al (2015) Lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory liver injury in mice. Lab Anim 49:37–46
Hofford JM, Milakofsky L, Pell S, Vogel W (1996) A profile of amino acid and catecholamine levels during endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in sheep: searching for potential markers of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Lab Clin Med 128:545–551
Hsieh YH, Deng JS, Chang YS, et al (2018) Ginsenoside Rh2 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating the TLR 4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways in mice nutrients 10:1208
Huxtable RJ (1992) Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev 72:101–163
Jain S, Darveau RP (2000) Contribution of Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide to periodontitis. Periodontol 54:53–70
Jakaria M, Azam S, Haque ME et al (2019) Taurine and its analogs in neurological disorders: focus on therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms. Redox Biol 24:101223
Jerala R (2007) Structural biology of the LPS recognition. Int J Med Microbiol 297:353–363
Jia X, Cao B, An Y et al (2019) Rapamycin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting IL-1beta and IL-18 production. Int Immunopharmacol 67:211–221
Ju M, Liu B, He H et al (2018) MicroRNA-27a alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via inhibiting in fl ammation and apoptosis through modulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathway. Cell Cycle 17:2001–2018
Kraus D, Winter J, Jepsen S et al (2012) Interactions of adiponectin and lipopolysaccharide from Porphyromonas gingivalis on human oral epithelial cells. PLoS One 7:e30716
Li W, Huang H, Niu X, Fan T, Hu H, Li Y, Yao H, Li H, Mu Q (2014) Tetrahydrocoptisine protects rats from LPS-induced acute lung injury. Inflammation 37:2106–2115
Li N, Song Y, Zhao W, Han T, Lin S, Ramirez O, Liang L (2016a) Small interfering RNA targeting NF-κB attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. BMC Physiol 16:7
Li N, Song Y, Zhao W et al (2016b) Small interfering RNA targeting NF-kappaB attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. BMC Physiol 16:7
Lomaga MA, Yeh WC, Sarosi I et al (1999) TRAF6 deficiency results in osteopetrosis and defective interleukin-1, CD40, and LPS signaling. Genes Dev 13:1015–1024
Lou J, Hu Y, Wu MD et al (2018) Endothelial cell-specific anticoagulation reduces inflammation in a mouse model of acute lung injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40:769–780
Lu HL, Huang XY, Luo YF et al (2018) Activation of M1 macrophages plays a critical role in the initiation of acute lung injury. Biosci Rep 38:BSR20171555
Mokra D, Kosutova P (2015) Biomarkers in acute lung injury. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 209:52–58
Niu F, Xu X, Zhang R et al (2019) Ursodeoxycholic acid stimulates alveolar fluid clearance in LPS-induced pulmonary edema via ALX/cAMP/PI3K pathway. J Cell Physiol 234:20057–20065
Ribeiro A, Almeida VI, Costola-De-Souza C et al (2015) Cannabidiol improves lung function and inflammation in mice submitted to LPS-induced acute lung injury. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 37:35–41
Shah D, Romero F, Stafstrom W et al (2014) Extracellular ATP mediates the late phase of neutrophil recruitment to the lung in murine models of acute lung injury. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 306:L152–L161
Shie PH, Huang SS, Deng JS et al (2015) Spiranthes sinensis suppresses production of pro-inflammatory mediators by down-regulating the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and up-regulating HO-1/Nrf2 ANTI-OXidant protein. Am J Chin Med 43:969–989
Szymanski K, Winiarska K (2008) Taurine and its potential therapeutic application. Postepy Hig Med Dosw 62:75–86
Takeda K, Akira S (2004) TLR signaling pathways. Semin Immunol 16:3–9
Wu XN, Yang Y, Zhang HH et al (2020) Robustaflavone-4’-dimethyl ether from Selaginella uncinata attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting FLT3-mediated neutrophil activation[J]. Int Immunopharmacol 82:106338
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. (31872440, 31872441).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zhao, D. et al. (2022). Taurine Alleviates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Suppressing TLR-4/NF-κB Pathway. In: Schaffer, S.W., El Idrissi, A., Murakami, S. (eds) Taurine 12. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1370. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93337-1_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93337-1_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-93336-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-93337-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)