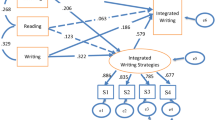
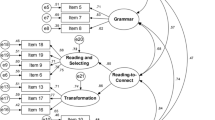
Abstract
Although integrated writing tasks have received increasing attention in language testing research over the past two decades, the processes related to how students use source material in integrated tasks remain largely unknown. The present study probed into the volume and the patterns of source use, if any, across three integrated writing tasks, namely reading–writing, listening–writing, and reading–listening–writing. Source material use variations among students by proficiency levels were also examined. The results showed that although both the more and the less proficient students used source material in their writing, their source use frequency and source type differed in terms of comprehension, the borrowing of ideas, and gaining language and organizational support. From this, implications for the design of and further inquiries into integrated tasks were drawn.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bereiter, C., & Scardamalia, M. (1987). The psychology of written composition. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Chan, S. (2017). Using keystroke logging to understand writers’ processes on a reading-into-writing test. Language Testing in Asia, 7(10), 1–27.
Chan, S. (2018). Defining integrated reading-into-writing constructs: Evidence at the B2 C1 interface (English profile series studies 08). Cambridge University Press.
Cheong, C. M., Zhu, X., & Liao, X. (2018). Differences between the relationship of l1 learners’ performance in integrated writing with both independent listening and independent reading cognitive skills. Reading & Writing, 31, 779–811.
Cumming, A., Kantor, R., Baba, K., Erdosy, U., Eouanzoui, K., & James, M. (2005). Differences in written discourse in independent and integrated prototype tasks for next generation of TOEFL. Assessing Writing, 10(1), 5–43.
Flower, L. S., & Hayes, J. R. (1984). A cognitive process theory of writing. College Composition and Communication, 4, 365–387.
Gebril, A., & Plakans, L. (2009). Investigating source use, discourse features, and process in integrated writing tests. Spaan Working Papers in Second or Foreign Language Assessment, 7, 47–84.
He, L. Z., & Sun, Y. X. (2015). Investigating the effects of prompt characteristics on Chinese test-takers’ integrated writing performance. Foreign Language Teaching and Research, 47(2), 237–250.
Homayounzadeh, M., Saadat, M., & Ahmadi, A. (2019). Investigating the effect of source characteristics on task comparability in integrated writing tasks. Assessing Writing, 41(1), 25–46.
Liu, F. L., & Stapleton, P. (2018). Connecting writing assessment with critical thinking: an exploratory study of alternative rhetorical functions and objects of enquiry in writing prompts. Assessing Writing, 38(1), 10–20.
Michel, M., Révész, A., Lu, X., Kourtali, N., & Borges, L. (2020). Investigating L2 writing processes across independent and integrated tasks: A mixed-methods study. Second Language Research, 36(3), 1–28.
Ohta, R., Plakans, L., & Gebril, A. (2018). Integrated writing scores based on holistic and multi-trait scales: A generalizability analysis. Assessing Writing, 38(1), 21–36.
Plakans, L. (2008). Comparing composing processes in writing-only and reading-to-write test tasks. Assessing Writing, 13(2), 111–129.
Plakans, L. (2015). Integrated second language writing assessment: Why? What? How? Language and Linguistics Compass, 9(4), 159–167.
Plakans, L., & Gebril, A. (2012). A close investigation into source use in integrated second language writing tasks. Assessing Writing, 17(1), 18–34.
Plakans, L., & Gebril, A. (2013). Using multiple texts in an integrated writing assessment: Source text use as a predictor of score. Journal of Second Language Writing, 22(3), 217–230.
Plakans, L., & Gebril, A. (2017). Exploring the relationship of organization and connection with scores in integrated writing assessment. Assessing Writing, 31(1), 98–112.
Ruiz-Funes, M. (2015). Exploring the potential of second/foreign language writing for language learning: The effects of task factors and learner variables. Journal of Second Language Writing, 28, 1–19.
Rukthong, A., & Brunfaut, T. (2020). Is anybody listening? The nature of second language listening in integrated listening-to-summarize tasks. Language Testing, 37(1), 31–53.
Serviss, H. R., & Rodrigue, T. K. (2010). Writing from sources, writing from sentences. Writing & Pedagogy, 2(2), 177–192.
Wang, J., Engelhard, G., Raczynski, K., Song, T., & Wolfe, E. W. (2017). Evaluating rater accuracy and perception for integrated writing assessments using a mixed-methods approach. Assessing Writing, 33(1), 36–47.
Weigle, S. C. (2004). Integrating reading and writing in a competency test for non-native speakers of English. Assessing Writing, 9(1), 27–55.
Weigle, S. C., & Parker, K. (2012). Source text borrowing in an integrated reading/writing assessment. Journal of Second Language Writing, 21(2), 118–133.
Wu, Y. (2014). Explore test-takers’ source use strategies in an EFL reading-to-write integrated task. Computer-assisted Foreign Language Education, 159, 63–69.
Xu, H., & Gao, C. F. (2007). An empirical study on integrating reading with writing in EFL teaching. Modern Foreign Languages, 30(2), 184–190; 220.
Yang, H. C. (2009). Exploring the complexity of second language writers’ strategy use and performance on an integrated writing test through structural equation modeling and qualitative approaches. Unpublished doctoral dissertation. The University of Texas.
Yang, H. C., & Plakans, L. (2012). Second language writers’ strategy use and performance on an integrated reading-listening-writing task. TESOL Quarterly, 46(1), 80–103.
Ye, W., & Ren, W. (2019). Source use in the story continuation writing task. Assessing Writing, 39(1), 39–49.
Zhang, X. L., & Zhou, Y. (2014). The effect of task type on Chinese EFL learners’ writing performance. Modern Foreign Language, 37(4), 548–558.
Zhang, X. L., & Zhou, Y. (2016). The influence of task type on different levels of Chinese EFL learners’ English writing process. Journal of PLA University of Foreign Languages, 39(1), 87–95.
Zhang, X. L., Zhou, Y., & Zhang, S. Y. (2015). Chinese EFL learners’ writing strategy use in reading-to-write and reading-listening-writing tasks. TESOL International Journal, 10(2), 97–109.
Zhou, D. D. (2004). Effects of task frequency on story retelling. Journal of PLA University of Foreign Languages, 27(5), 41–45.
Zhu, X., Li, X., Yu, G., Cheong, C. M., & Liao, X. (2016). Exploring the relationships between independent listening and listening-reading writing tasks in Chinese language testing: Toward a better understanding of the construct underlying integrated writing tasks. Language Assessment Quarterly, 13(3), 167–185.
Funding
This research was funded by Project of Educational Commission of Guangdong Province of China (2017WQNCX017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zhou, Y., Bin, K. (2022). How Chinese College EFL Learners Use Source Material Across Different Integrated Writing Tasks: A Comparative Study. In: Hamp-Lyons, L., Jin, Y. (eds) Assessing the English Language Writing of Chinese Learners of English. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92762-2_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92762-2_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-92761-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-92762-2
eBook Packages: EducationEducation (R0)