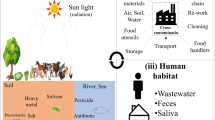
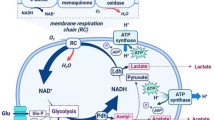
Abstract
Foodborne pathogenic bacteria encounter various environmental stressors along the food production chain, including production, processing, storage, distribution, and preparation. Bacteria are able to initiate a sophisticated regulatory network and alter the expression of proteins and genes to respond to external stressors. This can help bacteria survive under harsh conditions, which may lead to bacterial residue in foods. Furthermore, the development of a bacterial stress response might induce cross protection against other stresses and enhance pathogenicity, which could pose potential risks to food safety and public health. Therefore, a comprehensive and adequate understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the stress response of foodborne pathogens is important for the development and rational design of effective sterilization processing to ensure food safety with maximum preservation of food quality.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari A, Bary A, Cogger C et al (2016) Thermal and starvation stress response of Escherichia coli O157:H7 isolates selected from agricultural environments. J Food Protect 79(10):1673–1679
Agbaje M, Begum RH, Oyekunle MA et al (2011) Evolution of Salmonella nomenclature: a critical note. Folia Microbiol 56(6):497–503
Ágoston R, Soni K, Jesudhasan PR et al (2009) Differential expression of proteins in Listeria monocytogenes under thermotolerance-inducing, heat shock, and prolonged heat shock conditions. Foodborne Pathog Dis 6(9):1133–1140
Alreshidi MM, Dunstan RH, Macdonald MM et al (2015) Metabolomic and proteomic responses of Staphylococcus aureus to prolonged cold stress. J Proteome 121:44–55
Álvarez-Ordóñez A, Fernández A, Bernardo A et al (2009a) Comparison of acids on the induction of an acid tolerance response in Salmonella Typhimurium, consequences for food safety. Meat Sci 81(1):65–70
Álvarez-Ordóñez A, Fernández A, Bernardo A et al (2009b) A comparative study of thermal and acid inactivation kinetics in fruit juices of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and Salmonella enterica serovar Senftenberg grown at acidic conditions. Foodborne Pathog Dis 6:1147–1155
Álvarez-Ordóñez A, Begley M, Prieto M et al (2011) Salmonella spp. survival strategies within the host gastrointestinal tract. Microbiology 157(12):3268–3281
Álvarez-Ordóñez A, Prieto M, Bernardo A et al (2012) The acid tolerance response of Salmonella spp.: an adaptive strategy to survive in stressful environments prevailing in foods and the host. Food Res Int 45(2):482–492
Alves N, Rui M, Brando T et al (2020) Impact of exposure to cold and cold-osmotic stresses on virulence-associated characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes strains. Food Microbiol 87:103351
Anastasiadou M, Michailidis G (2016) Cytokine activation during embryonic development and in hen ovary and vagina during reproductive age and Salmonella infection. Res Vet Sci 109:86–93
Andersen JB, Roldgaard BB, Christensen BB et al (2007) Oxygen restriction increases the infective potential of Listeria monocytogenes in vitro in Caco-2 cells and in vivo in guinea pigs. BMC Microbiol 7:55
Anderson KL, Roberts C, Disz T et al (2006) Characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus heat shock, cold shock, stringent, and SOS responses and their effects on log-phase mRNA turnover. J Bacteriol 188(19):6739–6756
Apel D, Ellermeier J, Pryjma M et al (2012) Characterization of Campylobacter jejuni RacRS reveals roles in the heat shock response, motility, and maintenance of cell length homogeneity. J Bacteriol 194(9):2342
Arcari T, Feger ML, Guerreiro DN et al (2020) Comparative review of the responses of Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli to low pH stress. Genes 11(11):1330
Asao T, Kumeda Y, Kawai T et al (2003) An extensive outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning due to low-fat milk in Japan: estimation of enterotoxin A in the incriminated milk and powdered skim milk. Epidemiol Infect 130(1):33
Askoura M, Youns M, Hegazy WAH (2020) Investigating the influence of iron on Campylobacter jejuni transcriptome in response to acid stress. Microb Pathog 138:103777
Ávila ARAD, Marques SC, Piccolli RH et al (2013) Sensitivity to organic acids in vitro and in situ of Salmonella spp. And Escherichia coli isolated from fresh pork sausages. J Food Qual 36(3):155–163
Azizoglu RO, Drake M (2007) Impact of antibiotic stress on acid and heat tolerance and virulence factor expression of Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Food Prot 70(1):194–199
Bae YM, Lee SY (2017) Effect of salt addition on acid resistance response of Escherichia coli O157:H7 against acetic acid. Food Microbiol 65:74–82
Baek KT, Vegge CS, Skórko-Glonek J et al (2011) Different contributions of HtrA protease and chaperone activities to Campylobacter jejuni stress tolerance and physiology. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(1):57–66
Balaji B, O'connor K, Lucas JR et al (2005) Timing of induction of osmotically controlled genes in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, determined with quantitative real-time reverse transcription-PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8273–8283
Barrero-Tobon AM, Hendrixson DR (2012) Identification and analysis of flagellar coexpressed determinants (feds) of Campylobacter jejuni involved in colonization. Mol Microbiol 84:352–369
Beeby M, Ribardo DA, Brennan CA et al (2016) Diverse hightorque bacterial flagellar motors assemble wider stator rings using a conserved protein scaffold. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:E1917–E1926
Begley M, Hill C (2015) Stress adaptation in foodborne pathogens. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 6(1):191–210
Bera A, Biswas R, Herbert S et al (2007) Influence of wall teichoic acid on lysozyme resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 189(1):280–283
Beuchat LR, Worthington RE (1976) Relationships between heat resistance and phospholipid fatty acid composition of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol 31(3):389–394
Blaser MJ, Sazie E, Williams LP (1987) The influence of immunity on raw milk-associated Campylobacter infection. JAMA 257(1):43–46
Boehm M, Hoy B, Rohde M et al (2012) Rapid paracellular transmigration of Campylobacter jejuni across polarized epithelial cells without affecting TER: role of proteolytic-active HtrA cleaving E-cadherin but not fibronectin. Gut Pathog 4:3
Boehm M, Lind J, Backert S et al (2015) Campylobacter jejuni serine protease HtrA plays an important role in heat tolerance, oxygen resistance, host cell adhesion, invasion, and transmigration. Eur J Microbiol Immunol 5(1):68–80
Bore E, Langsrud S, Langsrud Ø et al (2007) Acid-shock responses in Staphylococcus aureus investigated by global gene expression analysis. Microbiology 153(7):2289–2303
Broberg CA, Calder TJ, Orth K (2011) Vibrio parahaemolyticus cell biology and pathogenicity determinants. Microbes Infect 13(12–13):992–1001
Brøndsted L, Andersen MT, Parker M et al (2005) The HtrA protease of Campylobacter jejuni is required for heat and oxygen tolerance and for optimal interaction with human epithelial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(6):3205–3212
Buchanan RL, Edelson SG (1999) pH-dependent stationary-phase acid resistance response of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in the presence of various acidulants. J Food Prot 62(3):211–218
Cameron A, Frirdich E, Huynh S et al (2012) Hyperosmotic stress response of Campylobacter jejuni. J Bacteriol 194(22):6116–6130
Caron E, Crepin VF, Simpson N et al (2006) Subversion of actin dynamics by EPEC and EHEC. Curr Opin Microbiol 9(1):40–45
CDC (2011) Estimated annual number of episodes of illnesses caused by 31 pathogens transmitted commonly by food, United States. https://www.cdc.gov/foodborneburden/pdfs/scallan-estimated-illnesses-foodborne-pathogens.pdf. Accessed 08 Mar 2021
CDC (2019) Campylobacter (Campylobacteriosis). https://www.cdc.gov/campylobacter/outbreaks/outbreaks.html. Accessed 08 Mar 2021
CDC (2021a) Listeria (Listeriosis). https://www.cdc.gov/listeria/. Accessed 08 Mar 2021
CDC (2021b) Vibrio species causing Vibriosis. https://www.cdc.gov/vibrio/faq.html. Accessed 08 Mar 2021
CDC (2021c). Prevent illness from C. perfringens. https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/diseases/clostridium-perfringens.html Accessed 08 Mar 2021
Cebrián G, Condón S, Maas P (2009) Heat-adaptation induced thermotolerance in Staphylococcus aureus: influence of the alternative factor σ B. Int J Food Microbiol 135(3):274–280
Cebrián G, Arroyo C, Condón S et al (2015) Osmotolerance provided by the alternative sigma factors σB and rpoS to Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli is solute dependent and does not result in an increased growth fitness in NaCl containing media. Int J Food Microbiol 214:83– 90
Chaibenjawong P, Foster SJ (2011) Desiccation tolerance in Staphylococcus aureus. Arch Microbiol 193(2):125–135
Chan YC, Hu Y, Chaturongakul S et al (2008) Contributions of two-component regulatory systems, alternative σ factors, and negative regulators to Listeria monocytogenes cold adaptation and cold growth. J Food Prot 71(2):420–425
Charlebois A, Jacques M, Boulianne M et al (2017) Tolerance of Clostridium perfringens biofilms to disinfectants commonly used in the food industry. Food Microbiol 62:32–38
Chen S, Cui S, McDermott PF et al (2007) Contribution of target gene mutations and efflux to decreased susceptibility of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium to fluoroquinolones and other antimicrobials. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51(2):535–542
Chiang ML, Yu RC, Chou CC (2005) Fatty acid composition, cell morphology and responses to challenge by organic acid and sodium chloride of heat-shocked Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Int J Food Microbiol 104(2):179–187
Chiang ML, Ho WL, Chou CC (2006) Response of Vibrio parahaemolyticus to ethanol shock. Food Microbiol 23(5):461–467
Collazo CM, Galán JE (1997) The invasion-associated type III system of Salmonella Typhimurium directs the translocation of sip proteins into the host cell. Mol Microbiol 24(4):747–756
Conte M, Petrone G, Di Biase A et al (2000) Acid tolerance in Listeria monocytogenes influences invasiveness of enterocyte-like cells and macrophage-like cells. Microb Pathogenesis 29(3):137–144
Cooper KK, Songer JG (2009) Necrotic enteritis in chickens: a paradigm of enteric infection by Clostridium perfringens type A. Anaerobe 15(1–2):55–60
Cossart P (2011) Illuminating the landscape of host-pathogen interactions with the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(49):19484–19491
Cróinín TÓ, Backert S (2012) Host epithelial cell invasion by Campylobacter jejuni: trigger or zipper mechanism? Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2:25
Dai X, Zhu M (2018) High osmolarity modulates bacterial cell size through reducing initiation volume in Escherichia coli. mSphere 3(5):e00430–e00418
Dallmier AW, Martin SE (1988) Catalase and superoxide dismutase activities after heat injury of Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 54(2):581–582
Darveau RP, Hancock RE (1983) Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella Typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol 155(2):831–838
de Jong HK, Parry CM, van der Poll T et al (2012) Host-pathogen interaction in invasive salmonellosis. PLoS Pathog 8(10):e1002933
ECDC (2019) Salmonella the most common cause of foodborne outbreaks in the European Union. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/salmonella-most-common-cause-foodborne-outbreaks-european-union. Accessed 08 Mar 2021
EFSA (2018) The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2017. EFSA J 16(12):e05500
Eglezos S, Dykes GA, Huang B, Turner MS, Seale R (2013) Genetic characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolates from food processing facilities before and after Postcook chiller heat treatment. J Food Prot 76(8):1466–1470
Elvira FA, Pardío-Sedas VT, Herrera DM, Castro RQ, Elvira KR (2020) Comparative survival and the cold-induced gene expression of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus from tropical eastern oysters during cold storage. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(6):1836
Endo Y, Tsurugi K, Yutsudo T et al (1988) Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes: RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur J Biochem 171(1–2):45–50
Fàbrega A, Vila J (2013) Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium skills to succeed in the host: virulence and regulation. Clin Microbiol Rev 26(2):308–341
Finn S, Rogers L, Händler K, McClure P, Amézquita A, Hinton JC et al (2015) Exposure of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium to three humectants used in the food industry induces different osmoadaptation systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(19):6800–6811
Fisher CW, Lee D, Dodge BA et al (2000) Influence of catalase and superoxide dismutase on ozone inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(4):1405–1409
Foster TJ (2017) Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol Rev 41(3):430–449
Frossard SM, Khan AA, Warrick EC, Gately JM, Hanson AD, Oldham ML et al (2012) Identification of a third osmoprotectant transport system, the osmU system, in Salmonella enterica. J Bacteriol 194(15):3861–3871
Futoma-Kołoch B, Bugla-Płskońska G, Dudek B et al (2019) Outer membrane proteins of Salmonella as potential markers of resistance to serum, antibiotics and biocides. Curr Med Chem 26(11):1960–1978
Fu Y, Galán JE (1998) The Salmonella Typhimurium tyrosine phosphatase SptP is translocated into host cells and disrupts the actin cytoskeleton. Mol Microbiol 27(2):359–368
García S, Heredia N (2011) Clostridium perfringens: a dynamic foodborne pathogen. Food Bioprocess Technol 4:624–630
Garcia J, Beingesser J, Fisher D, Sayeed S, McClane B, Posthaus H et al (2012) The effect of Clostridium perfringens type C strain CN3685 and its isogenic beta toxin null mutant in goats. Vet Microbiol 157(3–4):412–419
Gaupp R, Ledala N, Somerville GA (2012) Staphylococcal response to oxidative stress. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2:33
Gayán E, Cambré A, Michiels CW et al (2016) Stress-induced evolution of heat resistance and resuscitation speed in Escherichia coli O157:H7 ATCC 43888. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:6656–6663
Goossens E, Valgaeren BR, Pardon B et al (2017) Rethinking the role of alpha toxin in Clostridium perfringens-associated enteric diseases: a review on bovine necro-haemorrhagic enteritis. Vet Res 48(1):1–17
Graham JE, Wilkinson BJ (1992) Staphylococcus aureu Rethinking the role of alpha toxin in Clostridium perfringens-associated enteric diseases: a review on bovine necro-haemorrhagic enteritis osmoregulation: roles for choline, glycine betaine, proline, and taurine. J Bacteriol, 174(8), 2711–2716
Grant C, Konkel M, Cieplak W, Tompkins L (1993) Role of flagella in adherence, internalization, and translocation of Campylobacter jejuni in nonpolarized and polarized epithelial cell cultures. Infect Immun 61(5):1764–1771
Griffin PM, Tauxe RV (1991) The epidemiology of infections caused by Escherichia coli O157: H7, other enterohemorrhagic E. coli, and the associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Epidemiol Rev 13(1):60–98
Guibourdenche M, Roggentin P, Mikoleit M et al (2010) Supplement 2003-2007 (no. 47) to the white-Kauffmann-Le minor scheme. Res Microbiol 161(1):26–29
Haraga A, Ohlson MB, Miller SI (2008) Salmonellae interplay with host cells. Nat Rev Microbiol 6(1):53–66
Harrer A, Bucker R, Boehm M et al (2019) Campylobacter jejuni enters gut epithelial cells and impairs intestinal barrier function through cleavage of occludin by serine protease HtrA. Gut Pathog 11:4
Harris SM, Yue WF, Olsen SA et al (2012) Salt at concentrations relevant to meat processing enhances Shiga toxin 2 production in Escherichia coli O157:H7. Int J Food Microbiol 159(3):186–192
He S, Cui Y, Qin X et al (2018) Influence of ethanol adaptation on Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis survival in acidic environments and expression of acid tolerance-related genes. Food Microbiol 72:193–198
He S, Qin X, Wong CW et al (2019) Ethanol adaptation strategies in Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis revealed by global proteomic and mutagenic analyses. Appl Environ Microbiol 85:e01107–e01119
Hejair HM, Zhu Y, Ma J et al (2017) Functional role of ompF and ompC porins in pathogenesis of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Microb Pathogenesis 107:29–37
Heras A, Cain RJ, Bielecka MK et al (2011) Regulation of listeria virulence: PrfA master and commander. Curr Opin Microbiol 14(2):118–127
Heredia N, Labbe R, Garcia-Alvarado J (1998) Alteration in sporulation, enterotoxin production, and protein synthesis by Clostridium perfringens type A following heat shock. J Food Prot 61(9):1143–1147
Heredia N, Ybarra P, Hernández C et al (2009) Extracellular protectants produced by Clostridium perfringens cells at elevated temperatures. Lett Appl Microbiol 48(1):133–139
Horn N, Bhunia AK (2018) Food-associated stress primes foodborne pathogens for the gastrointestinal phase of infection. Front Microbiol 9:1962
Huang YJ, Tsai TY, Pan TM (2007) Physiological response and protein expression under acid stress of Escherichia coli O157:H7 TWC01 isolated from Taiwan. J Agric Food Chem 55(17):7182
Hughes RA, Hallett K, Cogan T et al (2009) The response of Campylobacter jejuni to low temperature differs from that of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(19):6292–6298
Jin S, Joe A, Lynett J et al (2001) JlpA, a novel surface-exposed lipoprotein specific to Campylobacter jejuni, mediates adherence to host epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol 39:1225–1236
Jin S, Song YC, Emili A, Sherman PM, Chan VL (2003) JlpA of Campylobacter jejuni interacts with surface-exposed heat shock protein 90α and triggers signalling pathways leading to the activation of NF-κB and p38 MAP kinase in epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol 5(3):165–174
Johler S, Layer F, Stephan R (2011) Comparison of virulence and antibiotic resistance genes of food poisoning outbreak isolates of Staphylococcus aureus with isolates obtained from bovine mastitis milk and pig carcasses. J Food Prot 74(11):1852–1859
Johnson MD, Bell J, Clarke K et al (2014) Characterization of mutations in the PAS domain of the EvgS sensor kinase selected by laboratory evolution for acid resistance in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 93(5):911
Jones TH, Murray A, Johns M et al (2006) Differential expression of proteins in cold-adapted log-phase cultures of Escherichia coli incubated at 8, 6 or 2°C. Int J Food Microbiol 107(1):12–19
Katzif S, Danavall D, Bowers S et al (2003) The major cold shock gene, cspA, is involved in the susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus to an antimicrobial peptide of human Cathepsin G. Infect Immun 71(8):4304–4312
Kenney LJ (2019) The role of acid stress in salmonella pathogenesis. Curr Opin Microbiol 47:45–51
Khaitsa M, Oloya J, Doetkott D et al (2008) Antimicrobial resistance and association with class 1 integrons in Escherichia coli isolated from Turkey meat products. J Food Prot 71(8):1679–1684
Kim HY, Kim CJ, Han SG et al (2014) Gastric fluid and heat stress response of Listeria monocytogenes inoculated on frankfurters formulated with 10%, 20%, and 30% fat content. Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour 34(1):20–25
Kim GH, Fratamico P, Breidt F et al (2016) Survival and expression of acid resistance genes in Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli acid adapted in pineapple juice and exposed to synthetic gastric fluid. J Appl Microbiol 121(5):1416–1426
Knudsen GM, Ng Y, Gram L (2013) Survival of bactericidal antibiotic treatment by a persister subpopulation of Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:7390–7397
Konkel ME, Kim BJ, Klena JD et al (1998) Characterization of the thermal stress response of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun 66(8):3666–3672
Kovač J, Šimunović K, Wu Z et al (2015) Antibiotic resistance modulation and modes of action of (-)-α-pinene in Campylobacter jejuni. PLoS One 10(4):e0122871
Krause-Gruszczynska M, van Alphen LB, Oyarzabal OA et al (2007) Expression patterns and role of the CadF protein in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 274(1):9–16
Kubori T, Sukhan A, Aizawa S-I et al (2000) Molecular characterization and assembly of the needle complex of the Salmonella Typhimurium type III protein secretion system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(18):10225–10230
Kuhle V, Hensel M (2002) SseF and SseG are translocated effectors of the type III secretion system of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 that modulate aggregation of endosomal compartments. Cell Microbiol 4(12):813–824
Kwon Y, Park S, Birkhold S et al (2000) Induction of resistance of Salmonella Typhimurium to environmental stresses by exposure to short-chain fatty acids. J Food Sci 65(6):1037–1040
Lara-Tejero M, Galán JE (2001) CdtA, CdtB, and CdtC form a tripartite complex that is required for cytolethal distending toxin activity. Infect Immunity 69:4358–4365
Lebrun M, Mainil J, Linden A (2010) Cattle enterotoxaemia and Clostridium perfringens: description, diagnosis and prophylaxis. Vet Rec 167(1):13–22
Lee H, Ma R, Grimm MC et al (2014) Examination of the anaerobic growth of Campylobacter concisus strains. Int J Microbiol 2014:476047
Leenanon B, Elhanafi D, Drake MA (2003) Acid adaptation and starvation effects on Shiga toxin production by Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Food Prot 66(6):970–977
Leyer G, Johnson E (1992) Acid adaptation promotes survival of Salmonella spp. in cheese. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(6):2075–2080
Li Y, Zhou D, Hu S et al (2018) Transcriptomic analysis by RNA-seq of Escherichia coli O157:H7 response to prolonged cold stress. LWT 97:17–24
Liang Z, Ke B, Deng X et al (2015) Serotypes, seasonal trends, and antibiotic resistance of non-typhoidal Salmonella from human patients in Guangdong Province, China, 2009-2012. BMC Infect Dis 15(1):53
Limón J, Heredia N, Solís-Soto L et al (2011) Cold tolerance of Clostridium perfringens induced by food additives at neutral pH. Acta Aliment Hung 40(1):87–94
Liu J, Zhai L, Lu W et al (2017) Amino acid decarboxylase-dependent acid tolerance, selected phenotypic, and virulence gene expression responses of Salmonella enterica serovar Heidelberg. Food Res Int 92:33–39
Loepfe C, Raimann E, Stephan R et al (2010) Reduced host cell invasiveness and oxidative stress tolerance in double and triple csp gene family deletion mutants of Listeria monocytogenes. Foodborne Pathog Dis 7(7):775
Lorentzen G, Mennen S, Olsen RL, Skjerdal T (2011) Invasiveness of Listeria monocytogenes strains of Caco-2 cells in response to a period of extreme salt stress reflecting salt-curing and rehydration of cod (Gadus morhua L.). Food Control 22(7):1040–1045
Lowy FD (2003) Antimicrobial resistance: the example of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest 111(9):1265–1273
Lu X, Liu Q, Wu D et al (2011) Using of infrared spectroscopy to study the survival and injury of Escherichia coli O157: H7, Campylobacter jejuni and Pseudomonas aeruginosa under cold stress in low nutrient media. Food Microbiol 28(3):537–546
Marcus SL, Brumell JH, Pfeifer CG et al (2000) Salmonella pathogenicity islands: big virulence in small packages. Microbes Infect 2(2):145–156
Mattick KL, Jørgensen F, Legan JD et al (2000) Survival and filamentation of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis pt4 and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium dt104 at low water activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(4):1274–1279
Mellin JR, Cossart P (2012) The non-coding RNA world of the bacterial pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. RNA Biol 9(4):372–378
Mihoub F, Mistou MY, Guillot A et al (2003) Cold adaptation of Escherichia coli: microbiological and proteomic approaches. Int J Food Microbiol 89(2–3):171–184
Minami J, Katayama S, Matsushita O et al (1997) Lambda-toxin of Clostridium perfringens activates the precursor of epsilon-toxin by releasing its N- and C-terminal peptides. Microbiol Immunol 41:527–535
Montanari C, Serrazanetti DI, Felis G et al (2015) New insights in thermal resistance of staphylococcal strains belonging to the species Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus lugdunensis and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 50:605–612
Montet MP, Christieans S, Thevenot D et al (2009) Fate of acid-resistant and non-acid resistant Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains in experimentally contaminated French fermented raw meat sausages. Int J Food Microbiol 129(3):264–270
Muchaamba F, Eshwar AK, Stevens MJA et al (2019) Variable carbon source utilization, stress resistance, and virulence profiles among Listeria monocytogenes strains responsible for listeriosis outbreaks in Switzerland. Front Microbiol 10:957
Mueller-Herbst S, Wustner S, Muhlig A et al (2014) Identification of genes essential for anaerobic growth of Listeria monocytogenes. Microbiology 160:752–765
Murray R (2005) Recognition and management of Staphylococcus aureus toxin-mediated disease. Intern Med J 35:S106–S119
Müsken A, Bielaszewska M, Greune L et al (2008) Anaerobic conditions promote expression of Sfp fimbriae and adherence of sorbitol-fermenting enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:NM to human intestinal epithelial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1087–1093
Nachamkin IRVING, Yang XH, Stern NJ (1993) Role of Campylobacter jejuni flagella as colonization factors for three-day-old chicks: analysis with flagellar mutants. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(5):1269
Naughton LM, Blumerman SL, Carlberg M et al (2009) Osmoadaptation among Vibrio species and unique genomic features and physiological responses of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(9):2802–2810
Navarro MA, McClane BA, Uzal FA (2018) Mechanisms of action and cell death associated with Clostridium perfringens toxins. Toxins 10(5):212
Neal-McKinney J, Konkel M (2012) The Campylobacter jejuni CiaC virulence protein is secreted from the flagellum and delivered to the cytosol of host cells. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2:31
Newell DG, Koopmans M, Verhoef L et al (2010) Food-borne diseases-the challenges of 20 years ago still persist while new ones continue to emerge. Int J Food Microbiol 139:S3–S15
Nikolaus T, Deiwick J, Rappl C et al (2001) SseBCD proteins are secreted by the type III secretion system of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 and function as a translocon. J Bacteriol 183(20):6036–6045
Novak JS, Tunick MH, Juneja VK (2001) Heat treatment adaptations in Clostridium perfringens vegetative cells. J Food Prot 64(10):1527–1534
Oh E, Andrews KJ, McMullen LM et al (2019) Tolerance to stress conditions associated with food safety in Campylobacter jejuni strains isolated from retail raw chicken. Sci Rep UK 9(1):1–9
Olesen I, Jespersen L (2010) Relative gene transcription and pathogenicity of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli after long-term adaptation to acid and salt stress. Int J Food Microbiol 141(3):248–253
Oliver HF, Orsi RH, Wiedmann M et al (2013) σ(B) plays a limited role in the ability of Listeria monocytogenes strain F2365 to survive oxidative and acid stress and in its virulence characteristics. J Food Prot 76(12):2079–2086
Ollinger J, Wiedmann M, Boor KJ (2008) σB-and PrfA-dependent transcription of genes previously classified as putative constituents of the Listeria monocytogenes PrfA regulon. Foodborne Pathog Dis 5(3):281–293
Orihuel A, Terán L, Renaut J et al (2019) Physiological and proteomic response of Escherichia coli O157: H7 to a bioprotective lactic acid bacterium in a meat environment. Food Res Int 125:108622
Pereira BMP, Wang X, Tagkopoulos I (2020) Short-and long-term transcriptomic responses of Escherichia coli to biocides: a systems analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 86(14):e00708–e00720
Perez KJ, Ceccon RV, Malheiros PS et al (2010) Influence of acid adaptation on the survival of Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Typhimurium in simulated gastric fluid and in Rattus norvegicus intestine infection. J Food Saf 30:398–414
Petit L, Gibert M, Popoff MR (1999) Clostridium perfringens: toxinotype and genotype. Trends Microbiol 7(3):104–110
PHAC (2021) Surveillance of Clostridium perfringens infection. https://www.canada.ca/en/publichealth/services/diseases/clostridium-perfringens/surveillance.html#number-of-cases-of-clostridium-perfringens-infection-incanada. Accessed 08 Mar 2021
Pickett CL, Whitehouse CA (1999) The cytolethal distending toxin family. Trends Microbiol 7(7):292–297
Pinner RW, Schuchatn A, Swaminathan B et al (1992) Role of foods in sporadic Listeriosis: II. Microbilogic and epidemiologic investigation. JAMA 267(15):2046–2050
Pöntinen A, Aalto-Araneda M, Lindström M, Korkeala H (2017a) Heat resistance mediated by pLM58 plasmid-borne ClpL in Listeria monocytogenes. mSphere 2(6):e00364–e00317
Pöntinen A, Lindström M, Skurnik M, Korkeala H (2017b) Screening of the two-component-system histidine kinases of Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e. LiaS is needed for growth under heat, acid, alkali, osmotic, ethanol and oxidative stresses. Food Microbiol 65:36–43
Qiao J, Zhu M, Lu Z et al (2020) The antibiotics resistance mechanism and pathogenicity of cold stressed Staphylococcus aureus. LWT 126:109274
Radoshevich L, Cossart P (2018) Listeria monocytogenes: towards a complete picture of its physiology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 16(1):32–46
Raju D, Setlow P, Sarker MR (2007) Antisense-RNA-mediated decreased synthesis of small, acid-soluble spore proteins leads to decreased resistance of Clostridium perfringens spores to moist heat and UV radiation. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(7):2048–2053
Reid AN, Pandey R, Palyada K et al (2008) Identification of Campylobacter jejuni genes involved in the response to acidic pH and stomach transit. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(5):1583–1597
Ren J, Wang X, Wu X, Wang R (2019) Epidemiological characteristics of food poisoning in China, July-September, 2018. Disease Surveillance 34(8):741–745
Ricke SC, Dawoud TM, Kim SA et al (2018) Salmonella cold stress response: mechanisms and occurrence in foods. Adv Appl Microbiol 104:1–38
Ringus DL, Ivy RA, Wiedmann M et al (2012) Salt stress-induced transcription of σB-and CtsR-regulated genes in persistent and non-persistent Listeria monocytogenes strains from food processing plants. Foodborne Pathog Dis 9(3):198–206
Sánchez B, Cabo ML, Margolles A et al (2010) A proteomic approach to cold acclimation of Staphylococcus aureus CECT 976 grown at room and human body temperatures. Int J Food Microbiol 144(1):160–168
Savva CG, Clark AR, Naylor CE et al (2019) The pore structure of Clostridium perfringens epsilon toxin. Nat Commun 10(1):1–10
Sawires YS, Songer JG (2006) Clostridium perfringens: insight into virulence evolution and population structure. Anaerobe 12(1):23–43
Scallan E, Hoekstra RM, Angulo FJ et al (2011) Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—major pathogens. Emerg Infect Dis 17(1):7
Schnupf P, Portnoy DA (2007) Listeriolysin O: a phagosome-specific lysin. Microbes Infect 9(10):1176–1187
Schuppler M (2014) How the interaction of Listeria monocytogenes and Acanthamoeba spp. affects growth and distribution of the food borne pathogen. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(7):2907–2916
Schuster CF, Wiedemann DM, Kirsebom FC et al (2020) High-throughput transposon sequencing highlights the cell wall as an important barrier for osmotic stress in methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and underlines a tailored response to different osmotic stressors. Mol Microbiol 113(4):699–717
Seo SW, Kim D, O’Brien EJ et al (2015) Decoding genome-wide GadEWX-transcriptional regulatory networks reveals multifaceted cellular responses to acid stress in Escherichia coli. Nat Commun 6:7970
Sergelidis D, Abrahim A (2009) Adaptive response of Listeria monocytogenes to heat and its impact on food safety. Food Control 20(1):1–10
Shah J, Desai PT, Chen D et al (2013) Preadaptation to cold stress in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium increases survival during subsequent acid stress exposure. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(23):7281–7289
Shen HW, Yu RC, Chou CC (2007) Acid adaptation affects the viability of Salmonella Typhimurium during the lactic fermentation of skim milk and product storage. Int J Food Microbiol 114(3):380–385
Shen C, Geornaras I, Belk KE et al (2011) Thermal inactivation of acid, cold, heat, starvation, and desiccation stress-adapted Escherichia coli O157:H7 in moisture-enhanced nonintact beef. J Food Prot 74(4):531–538
Shrihari RY, Singh NP (2012) Multiplex reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction to study the expression of virulence and stress response genes in Staphylococcus aureus. J Food Sci 77(2):M95–M101
Slanec T, Schmidt H (2011) Specific expression of adherence-related genes in Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain EDL933 after heat treatment in ground beef. J Food Prot 74(9):1434–1440
Sleator RD, Wouters J, Gahan CGM et al (2001) Analysis of the role of OpuC, an osmolyte transport system, in salt tolerance and virulence potential of Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2692–2698
Songer JG (1996) Clostridial enteric diseases of domestic animals. Clin Microbiol Rev 9(2):216
Soufi L, Abbassi MS, Sáenz Y et al (2009) Prevalence and diversity of integrons and associated resistance genes in Escherichia coli isolates from poultry meat in Tunisia. Foodborne Pathog Dis 6(9):1067–1073
Spaulding AR, Salgado-Pabón W, Kohler PL et al (2013) Staphylococcal and streptococcal superantigen exotoxins. Clin Microbiol Rev 26(3):422–447
Spector MP, Kenyon WJ (2012) Resistance and survival strategies of Salmonella enterica to environmental stresses. Food Res Int 45(2):455–481
Su YC, Liu C (2007) Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a concern of seafood safety. Food Microbiol 24(6):549–558
Sun Y, Reid B, Ferreira F et al (2019) Infection-generated electric field in gut epithelium drives bidirectional migration of macrophages. PLoS Biol 17(4):e3000044
Swaminathan B, Gerner-Smidt P (2007) The epidemiology of human listeriosis. Microbes Infect 9(10):1236–1243
Tack DM, Ray L, Griffin PM et al (2020) Preliminary incidence and trends of infections with pathogens transmitted commonly through food-foodborne diseases active surveillance network, 10 US sites, 2016–2019. MMWR Morbid Mortal Wkly Rep 69(17):509
Tang J, Jia J, Chen Y et al (2018) Proteomic analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus under cold stress. Curr Microbiol 75(1):20–26
Tsai YW, Ingham SC (1997) Survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella spp. in acidic condiments. J Food Prot 60:751–755
Urmersbach S, Aho T, Alter T et al (2015) Changes in global gene expression of Vibrio parahaemolyticus induced by cold-and heat-stress. BMC Microbiol 15(1):1–13
Verbrugghe E, Van Parys A, Leyman B et al (2015) Heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli promotes intestinal colonization of Salmonella enterica. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 43:1–7
Vidovic S, Mangalappalli-Illathu AK, Korber DR (2011) Prolonged cold stress response of Escherichia coli O157 and the role of rpoS. Int J Food Microbiol 146(2):163–169
Vidovic S, Mangalappalli-Illathu AK, Xiong H et al (2012) Heat acclimation and the role of RpoS in prolonged heat shock of Escherichia coli O157. Food Microbiol 30(2):457–464
Wang H, Wang X, Yu L et al (2020) Resistance of biofilm formation and formed-biofilm of Escherichia coli O157: H7 exposed to acid stress. LWT 118:108787
Wattinger L, Stephan R, Layer F et al (2012) Comparison of Staphylococcus aureus isolates associated with food intoxication with isolates from human nasal carriers and human infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol 31(4):455–464
Whiteley AT, Ruhland BR, Edrozo MB et al (2017) A redoxresponsive transcription factor is critical for pathogenesis and aerobic growth of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun 85:e00978–e00916
Wiseman GM (1975) The hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus. Bacteriol Rev 39(4):317
Wong H, Peng PY, Han JM et al (1998) Effect of mild acid treatment on the survival, enteropathogenicity, and protein production in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun 66(7):3066–3071
Wong HC, Liao R, Hsu P et al (2018) Molecular response of Vibrio parahaemolyticus to the sanitizer peracetic acid. Int J Food Microbiol 286:139–147
Wood A, Irving SE, Bennison DJ et al (2019) The (p) ppGpp-binding GTPase era promotes rRNA processing and cold adaptation in Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS Genet 15(8):e1008346
World Health Organization (2015) WHO estimates of the global burden of foodborne diseases: foodborne disease burden epidemiology reference group 2007–2015
Wu YL, Lee LH, Rollins DM et al (1994) Heat shock- and alkaline pH-induced proteins of Campylobacter jejuni: characterization and immunological properties. Infect Immun 62(10):4256
Wu S, Yu PL, Flint S (2017) Persister cell formation of Listeria monocytogenes in response to natural antimicrobial agent nisin. Food Control 77:243–250
Xu J, Li T, Gao Y et al (2019) MgrB affects the acid stress response of Escherichia coli by modulating the expression of iraM. FEMS Microbiol Lett 366(11):fnz123
Xu Y, Zhao Z, Tong WH et al (2020) An acid-tolerance response system protecting exponentially growing Escherichia coli. Nat Commun 11(1):1496
Yaashikaa P, Saravanan A, Kumar PS (2016) Isolation and identification of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus from prawn (Penaeus monodon) seafood: preservation strategies. Microb Pathogenesis 99:5–13
Yang J, Tang CB, Xiao J et al (2018) Influences of epigallocatechin gallate and citric acid on Escherichia coli O157:H7 toxin gene expression and virulence-associated stress response. Lett Appl Microbiol 67(5):435–441
Yeung PS, Boor KJ (2004) Effects of acid stress on Vibrio parahaemolyticus survival and cytotoxicity. J Food Prot 67(7):1328
Zarzecka U, Grinzato A, Kandiah E et al (2020) Functional analysis and cryo-electronmicroscopy of Campylobacter jejuni serine protease HtrA. Gut Microbes 12(1):1810532
Zhou C, Fey PD (2020) The acid response network of Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Opin Microbiol 55:67–73
Zorraquino V, Kim M, Rai N et al (2017) The genetic and transcriptional basis of short and long term adaptation across multiple stresses in Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Evol 34(3):707–717
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ding, T., Liao, X., Feng, J. (2022). The Importance of Understanding the Stress Response in Foodborne Pathogens Along the Food Production Chain. In: Ding, T., Liao, X., Feng, J. (eds) Stress Responses of Foodborne Pathogens. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90578-1_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90578-1_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-90577-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-90578-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)