Abstract
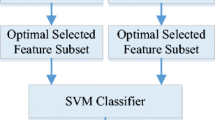
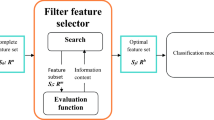
Today’s most significant healthcare problem that is prevailing is the chronic kidney disease (CKD). The disease integrates well-defined patho-physiological process that will be experimental for determining irregular kidney functions and the glomerular filtration rates. To forecast the disease, different data mining techniques are used to discover the connections between various elements, which can be utilized to determine the progress and status of CKD. Data is obtained from the patient’s healthcare records. The main purpose of this research is to avail the Hybrid Filter Wrapper Embedded-Based Feature Selection (HFWE-FS), which will be utilized to select CKD datasets from potential feature subsets. HFWE-FS algorithm integrates the process of filtering, wrapping and embedding algorithms. The filter algorithms are integrated with reference on certain metrics: Gini index, gain ratio, One R and Relief. The wrapper algorithms via enhanced bat algorithms are purposed to select the analytical features from wide-range CKD sets of data. The embedded algorithms are underpinned, and this depends on the support vector machine (SVM)-t statistic, which selects the analytical features out of the wide-range CKD dataset. The results of the feature selection algorithms are integrated and identified as the HFWE-FS algorithm. The SVM algorithm for the CKD prediction is proposed as a final stage. The database used is taken from ‘CKD’ implemented on the MATLAB. The results perceived that the SVM classifier along with HFWE algorithm gets high classification rate when contrasted with other categorization algorithms: Naïve Bayes (NB), artificial neural networks (ANNs) and support vector machine (SVM) in CKD completion.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J., Glynn, L.G.: Definition of chronic kidney disease and measurement of kidney function in original research papers: a review of the literature. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 26(9), 2793–2798 (2011)
Chen, Z., Zhang, X., Zhang, Z.: Clinical risk assessment of patients with chronic kidney disease by using clinical data and multivariate models. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 48(12), 2069–2075 (2016)
Cho, B.H., Yu, H., Kim, K.W., Kim, T.H., Kim, I.Y., Kim, S.I.: Application of irregular and unbalanced data to predict diabetic nephropathy using visualization and feature selection methods. Artif. Intell. Med. 42(1), 37–53 (2008)
Di Noia, T., Ostuni, V.C., Pesce, F., Binetti, G., Naso, D., Schena, F.P., Di Sciascio, E.: An end stage kidney disease predictor based on an artificial neural networks ensemble. Expert Syst. Appl. 40(11), 4438–4445 (2013)
Go, A.S., Chertow, G.M., Fan, D., McCulloch, C.E., Hsu, C.Y.: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 351(13), 1296–1305 (2004)
Holte, R.C.: Very simple classification rules perform well on most commonly used datasets. Mach. Learn. 11(1), 63–90 (1993)
Huang, M.J., Chen, M.Y., Lee, S.C.: Integrating data mining with case-based reasoning for chronic diseases prognosis and diagnosis. Expert Syst. Appl. 32, 856–867 (2007)
Karegowda, A.G., Jayaram, M.A., Manjunath, A.S.: Feature subset selection problem using wrapper approach in supervised learning. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 1(7), 13–17 (2010)
Kathuria, P., Wedro, B.: Chronic kidney disease quick overview. IOP Publishing emedicine health, http://www.Emedicinehealth.com/chronic_kidney_disease/page2_em.htm#chronic_kidney_disease_quick_overview, 2016
Komarasamy, G., Wahi, A.: An optimized K-means clustering technique using bat algorithm. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 84(2), 263–273 (2012)
Kumar, M.: Prediction of chronic kidney disease using random Forest machine learning algorithm. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Mob. Comput. 5(2), 24–33 (2016)
Ladha, L., Deepa, T.: Feature selection methods and algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 3(5), 1787–1797 (2011)
Norouzi, J., Yadollahpour, A., Mirbagheri, S.A., Mazdeh, M.M., Hosseini, S.A.: Predicting renal failure progression in chronic kidney disease using integrated intelligent fuzzy expert system. Comput. Math. Methods Med, 1–9 (2016)
O’Seaghdha, C.M., Lyass, A., Massaro, J.M., Meigs, J.B., Coresh, J., D’Agostino, R.B., Astor, B.C., Fox, C.S.: Risks score for chronic kidney disease in the general population. Am. J. Med. 125(3), 270–277 (2012)
Salekin, A., dStankovic, J.: Detection of chronic kidney disease and selecting important predictive attributes, IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), pp. 262–270, 2016
Priscila, S.S., Hemalatha, M.: Diagnosis of heart disease with particle bee-neural network. Biomed. Res. Spec. Issue, S40–S46 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kalaiselvi, K., V. J. Sara, S.B. (2022). A Hybrid Filter Wrapper Embedded-Based Feature Selection for Selecting Important Attributes and Prediction of Chronic Kidney Disease. In: Ramu, A., Chee Onn, C., Sumithra, M. (eds) International Conference on Computing, Communication, Electrical and Biomedical Systems. EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86165-0_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86165-0_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-86164-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-86165-0
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)