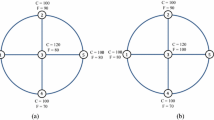
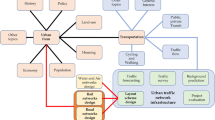
Abstract
Traffic congestion is a growing concern in the world's most populated metropolitan areas. Over the past decades, several approaches have been developed to better understand and control urban traffic management, such as artificial intelligence, video streaming, fuzzy logic, and complex networks. In this study, we apply a combination of fuzzy logic and complex network analysis to better understand the dynamic structure of urban traffic networks. When studying the dynamic processes of transportation networks, the exploration of the critical entities plays a crucial role in exploring and analyzing the resilience and management of urban traffic systems. Therefore, we propose measures of flow and travel time variability as well as dynamic road saturation factors to develop fuzzy measures of dynamic centrality. Also, the fuzzy temporal spectral centrality is also considered for this purpose. Our proposal is a fundamental building component for intelligent traffic monitoring and provides real support for the resilience of urban networks.
This work was partially funded by the Digital Development Agency (ADD) and the National Center for Scientific and Technical Research (CNRST) in partnership with the Ministry of Industry, Commerce and Green and Digital Economy (MICEVN) and the Ministry of National Education, Professional Training, Higher Education and Scientific Research (MENFPESRC) # AL KHAWARIZMI Program #Intelligent & Resilient Urban Network Defender: A distributed real-time reactive intelligent transportation system for urban traffic congestion symbolic control and monitoring.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agryzkov, T., Oliver, J.L., Tortosa, L., Vicent, J.: A new betweenness centrality measure based on an algorithm for ranking the nodes of a network. Appl. Math. Comput. 244, 467–478 (2014)
Agryzkov, T., Oliver, J.L., Tortosa, L., Vicent, J.F.: An algorithm for ranking the nodes of an urban network based on the concept of PageRank vector. Appl. Math. Comput. 219(4), 2186–2193 (2012)
Agryzkov, T., Tortosa, L., Vicent, J.F.: New highlights and a new centrality measure based on the Adapted PageRank Algorithm for urban networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 291, 14–29 (2016)
Agryzkov, T., Tortosa, L., Vicent, J.F., Wilson, R.: A centrality measure for urban networks based on the eigenvector centrality concept. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 46(4), 668–689 (2019)
Atanassov, K.T.: Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets: Theory and Applications (Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing), vol. 35. Physica-Verlag, Heidelberg (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7908-1870-3
Boulmakoul, A., Karim, L., Nahri, M.: Un système distribué et temps réel pour l’analyse de la centralité spectrale dynamique des réseaux urbains (2017)
Henry, E., Bonnetain, L., Furno, A., El Faouzi, N.E., Zimeo, E.: Spatio-temporal correlations of betweenness centrality and traffic metrics. In: 6th International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS), pp. 1–10. IEEE (2019)
Hu, R.J., Li, Q., Zhang, G.Y., Ma, W.C.: Centrality measures in directed fuzzy social networks. Fuzzy Inf. Eng. 7(1), 115–128 (2015)
Hu, R.-J., Zhang, G., Liao, L.-P.: The closeness centrality analysis of fuzzy social network based on inversely attenuation factor. In: Cao, B.-Y., Nasseri, H. (eds.) Fuzzy Information & Engineering and Operations Research & Management. AISC, vol. 211, pp. 457–465. Springer, Heidelberg (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38667-1_46
Karim, L., Boulmakoul, A., Cherradi, G., Lbath, A.: Fuzzy centrality analysis for smart city trajectories. In: Kahraman, C., Cevik Onar, S., Oztaysi, B., Sari, I.U., Cebi, S., Tolga, A.C. (eds.) INFUS 2020. AISC, vol. 1197, pp. 933–940. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51156-2_108
Liao, L.P., Hu, R.J., Zhang, G.Y.: The centrality analysis of fuzzy social networks. Fuzzy Syst. Math. 27(2), 169–173 (2012)
Parand, F.A., Rahimi, H., Gorzin, M.: Combining fuzzy logic and eigenvector centrality measure in social network analysis. Phys. A 459, 24–31 (2016)
Rosenfeld, A.: Fuzzy Graphs, Fuzzy Sets and Their Applications. In: Zadeh, L.A., Fu, K.S., Shimura, M. (eds.), pp. 77–95 (1975)
Zadeh, A.S.M., Rajabi, M.A.: Analyzing the effect of the street network configuration on the efficiency of an urban transportation system. Cities 31, 285–297 (2013)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. In: Fuzzy Sets, Fuzzy Logic, and Fuzzy Systems: Selected Papers by Lotfi A Zadeh, pp. 394–432 (1996)
Lordan, O., Sallan, J.M.: Dynamic measures for transportation networks. PLoS ONE 15(12), e0242875 (2020)
Katz, L.: A new status index derived from sociometric analysis. Psychometrika 18(1), 39–43 (1953)
Bonacich, P., Lloyd, P.: Eigenvector-like measures of centrality for asymmetric relations. Soc. Netw. 23(3), 191–201 (2001)
Page, L., Brin, S., Motwani, R., Winograd, T.: The PageRank Citation Ranking: Bringing Order to the Web. Stanford InfoLab (1999)
Boulmakoul, A., Laarabi, M.H., Sacile, R., Garbolino, E.: An original approach to ranking fuzzy numbers by inclusion index and Bitset Encoding. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Making 16(1), 23–49 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-016-9237-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Boulmakoul, A., Badaoui, Fe., Karim, L., Lbath, A., Oulad Haj Thami, R. (2022). Fuzzy Spatiotemporal Centrality for Urban Resilience. In: Kahraman, C., Cebi, S., Cevik Onar, S., Oztaysi, B., Tolga, A.C., Sari, I.U. (eds) Intelligent and Fuzzy Techniques for Emerging Conditions and Digital Transformation. INFUS 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 307. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85626-7_92
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85626-7_92
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-85625-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-85626-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)