Abstract
Neutron stars are remarkable natural laboratories that allow us to investigate the fundamental constituents of matter and their interactions under extreme conditions that cannot be reproduced in terrestrial laboratories. This chapter gives a brief pedagogical introduction to the physics of matter at very high densities (i.e. up to several times the density of atomic nuclei) that hopefully could be useful to researchers in pulsars’ astrophysics and related areas.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Stellar masses will be given in unit of the mass of the Sun, M ⊙ = 1.988 × 1033g.
- 2.
The star may also contain species of identical bosons as in the case of negative pions (π −) or negative kaons (K −) condensation.
- 3.
- 4.
k B T = 1 MeV corresponds to T ≃ 1.134 × 1010 K.
- 5.
i.e. imagine for a moment to “switch off” the weak interaction.
- 6.
This is possible if the electron Fermi momentum satisfies
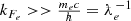 , thus for densities
, thus for densities 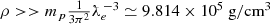 .
. - 7.
Neutrino are trapped in neutron star interior for a few tens of second after their birth [15].
- 8.
Including those considered in the present chapter.
- 9.
Notice that the presence of tiny charge-symmetry breaking (CSB) and charge-independence breaking (CIB) terms in the nuclear interaction (for a review, see e.g. [29]) could invalidate Eq. (9.23). For example a CSB component in the NN interaction produces a linear (and more generally odd-power) β-term in Eq. (9.23) [30]. However, it has been numerically demonstrated by various authors (e.g. [30] and [31]) that the effects on \({\widetilde E}(n, \beta )\) and on the nuclear symmetry energy of CSB and CIB terms in the nucleon-nucleon interaction are essentially negligible.
- 10.
Hadrons, i.e. particles subject to the strong interaction, can be classified in two groups: baryons if they have spin J = 1∕2, 3∕2, 5∕2, …, or mesons if they have spin J = 0, 1, 2, … . According to the hadrons’ quark model, baryons are colorless bound states of three quarks (q 1 q 2 q 3), and mesons are colorless quark–anti-quark \((q_1 \bar {q}_2\)) bound states.
- 11.
The strong interaction between quarks can be neglected due to the asymptotic freedom of QCD which, for the purpose of the present estimate, is a reasonable approximation at the high densities found in neutron stars cores.
- 12.
The actual mean-life time of the HS will depend on the mass accretion or on the spin-down rate which modifies the nucleation time τ via an explicit time dependence of the stellar central pressure.
- 13.
Since the nucleation time is extremely sensitive to the value of the stellar central pressure P c and thus to its corresponding gravitational mass M HS(P c) (see Fig. 4 and 5 in Ref. [106]), the critical mass value is not influenced by the particular choice τ = 1 yr.
- 14.
The SQM EoS used to calculate the QS configurations reported in Fig. 9.9 satisfies the strange matter hypothesis.
References
Abbott, B.P., et al.: LIGO scientific collaboration and Virgo collaboration. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 161101 (2017)
Abbott, B.P., et al.: LIGO scientific collaboration and Virgo collaboration. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 161101 (2018)
Abbott, B.P., et al.: LIGO scientific collaboration and Virgo collaboration. arXiv:2001.01761
Demorest, P.B., Pennucci, T., Ransom, S., Roberts, M., Hessels, J: Nature 467, 1081 (2010)
Antoniadis, J., et al.: Science 340, 1233232 (2013)
Cromartie, H.T., Fonseca, E., M Ransom, S., et al.: Nat. Astron. 4, 72 (2020)
Fetter, A.L., Walecka, J.D.: Quantum Theory of Many-Particle Systems. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York (1971)
Bhattacharyya, S.: Adv. Space Res. 45, 949 (2010)
Watts, A.L.: AIP Conference Proceedings 2127, 020008 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5117798
Miller, M.C.: Astrophysical constraints on dense matter in neutron stars. In: Belloni, T.M., Méndez, M., Zhang, C. (eds.) Timing Neutron Stars: Pulsations, Oscillations and Explosions. Astrophysics and Space Science Library, vol. 461. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-62110-3_1
Harrison, B.K., Wakano, M., Wheeler, J.A.: La Structure et l’Evolution de l’Univers. Stoops, Brussels (1958)
Harrison, B.K., Thorne, K.S., Wakano, M., Wheeler, J.A.: Gravitation Theory and Gravitational Collapse. University of Chicago Press, Chicago (1965)
Chamel, N., Haensel, P.: Living Rev. Relativ. 11, 10 (2008)
Glendenning, N.K.: Compact Stars: Nuclear Physics, Particle Physics, and General Relativity. Springer, New York (2000)
Prakash, M., Bombaci, I., Prakash, M., Ellis, J.P., Lattimer, J.M., Knorren, R.: Phys. Rep. 280, 1 (1997)
J. R. Oppenheimer, G. M. Volkoff, Phys. Rev 55, 374 (1939)
Brown, L.M., Rechenberg, H.: The Origin of the Concept of Nuclear Forces. Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol and Philadelphia (1996)
Bombaci, I., Lombardo, U.: Phys. Rev. C 44, 1892 (1991)
Zuo, W., Bombaci, I., Lombardo, U.: Eur. Phys. J. A 50, 12 (2014)
Lattimer, J.M.: Gen. Rel. Grav. 46, 1713 (2014)
Lattimer, J.M., Prakash, M.: Phys. Rep. 621, 127 (2016)
Kalantar-Nayestanaki, N., Epelbaum, E., Messchendorp, J.G., Nogga, A.: Rep. Prog. Phys. 75, 016301 (2012)
Hammer, H.W., Nogga, A., Schenk, A.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 197 (2013)
Wiringa, R.B., Fiks, V., Fabrocini, A.: Phys. Rev. C, 38, 1010 (1988)
Baldo, M., Bombaci, I., Burgio, G.F.: A&A 328, 274 (1997)
Akmal, A., Pandharipande, V.R., Ravenhall, D.G.: Phys. Rev. C 58, 1804 (1998)
Li, Z.H., Schulze, H.-J.: Phys. Rev. C 78, 028801 (2008)
Bombaci, I., Logoteta, D.: A&A 609, A128 (2018)
Miller, G.A., Opper, A.K., Stephenson, E.J.: Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 56, 253 (2006)
Haensel, P.: J. Phys. G 3, 373 (1997)
Müther, H., Polls, A., Machleidt, R.: Phys. Lett. B 445, 259 (1999)
Blaizot, J.P., Gogny, D., Grammaticos, B.: Nucl. Phys. A 265, 315 (1976)
Shlomo, S., Kolomietz, V.K. Colò, G.: Eur. Phys. J. A 30, 23 (2006)
Li, B.A., Han, X.: Phys. Lett. B 727, 276 (2013)
Kievsky, A., Viviani, M., Logoteta, D., Bombaci, I., Girlanda, L.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 072701 (2018)
Danielewicz, P., Lee, J.: Nucl. Phys. A 922, 1 (2014)
Roca-Maza, X., et al.: Phys. Rev. C 87, 034301 (2013)
Tolman, R.C.: Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA) 20, 169 (1934)
Gulminelli, F., Raduta, Ad.D.: Phys. Rev. C 92, 055803 (2015)
Bombaci, I., Logoteta, D.: EPJ Web of Conferences 117, 07005 (2016)
Bombaci, I.: JPS Conf. Proc. 17, 101002 (2017)
Wiringa, R.B., Stoks, V.G.J., Schiavilla, R.: Phys. Rev. C 51, 38 (1995)
Rijken, Th.A., Nagels, M.M., Yamamoto, Y.: Nucl. Phys. A 835, 160, (2010)
Baldo, M., Burgio, G.F., Schulze, H.-J.: Phys. Rev. C 61, 055801 (2000)
Vidaña, I., Polls, A., Ramos, A., Engvik, L., Hjorth-Jensen, M.: Phys. Rev. C 62, 035801 (2000)
Schulze, H.-J., Rijken, Th.A.: Phys. Rev. C 84, 035801 (2011)
Djapo, H., Schaefer, B.-J., Wambach, J.: Phys. Rev. C 81, 035803 (2010)
Hashimoto, O., Tamura, H.: Progr. Part. Nucl. Phys. 57, 564 (2006)
Millener, D.J.: Lect. Notes Phys. 724, 31 (2007)
Rappold, C., et al., HypHI Collaboration: Nucl. Phys. A 913, 170 (2013)
Feliciello, A., Nagae, T.: Rep. Progr. Phys. 78, 096301 (2015)
Tamura, H., et al.: Proceedings, 11th International Conference on Hypernuclear and Strange Particle Physics (HYP 2012): Barcelona, Spain, October 1–5, 2012. Nuclear Phys., vol. A914, p. 99 (2013)
Botta, E., Bressani, T., Garbarino, G.: Eur. Phys. J. A 48, 41 (2012)
Curceanu, C., et al.: Acta Phys. Pol. B 46, 203 (2015)
Gal, A., Hungerford, E.V., Millener, D.J.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 88, 035004 (2016)
Tolos, L., Fabbietti, L.: Progr. Part. Nucl. Phy. 112, 103770 (2020)
Petschauer, S., Haidenbauer, J., Kaiser, N., Meißner, U.-G., Weise, W.: Front. Phys. 8, 12 (2020)
Spitzer, R.: Phys. Rev. 110, 1190 (1958)
Bach, G.G.: Nuovo Cimento XI, 73 (1959)
Dalitz, R.H.: 9th Int. Ann. Conf. on High-Energy Physics. Academy of Sciences, USSR, vol. I, p. 587 (1960)
Bodmer, A., Sampanthar, S.: Nucl. Phys. 31, 251 (1962)
Conte, F., Iwao, S.: Nucl. Phys. 58, 291 (1964)
Bodmer, A.R., Murphy, J.W.: Nucl. Phys. 64, 593 (1965)
Gal, A.: Phys. Rev. 152, 975 (1966); Gal, A.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 18, 568 (1967)
Bhaduri, R.K., Losieau, B.A., Nogami, Y.: Ann. Phys. 44, 57 (1967)
Gal, A., Soper, J.M., Dalitz, R.H.: Ann. Phys. 63, 53 (1971)
Bodmer, A.R., Usmani, Q.N., Carlson, J.: Phys. Rev. C 29, 684 (1984)
Yamamoto, Y.: Phys. Rev. C 36, 2166 (1987)
Vidaña, I., Logoteta, D., Providencia, C., Polls, A., Bombaci, I.: Europhys. Lett. 94, 11002 (2011)
Yamamoto, Y., Furumoto, T., Yasutake, N., Rijken, Th.: Phys. Rev. C 90, 045805 (2014)
Lonardoni, D., Lovato, A., Gandolfi, S., Pederiva, F.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 092301 (2015)
Logoteta, D., Vidaña, I., Bombaci, I.: Eur. Phys. J. A 55, 207 (2019)
Gerstung, D., Kaiser, N., Weise, W.: Eur. Phys. J. A 56, 175 (2020)
Ivanenko, D., Kurdgelaidze, D.F.: Lett. Nuovo Cimento 2, 13 (1969)
Itho, N.: Prog. Teor. Phys. 44, 291 (1970)
Iachello, F., Langer, W.D., Lande, A.: Nucl. Phys. A 219, 612 (1974)
Collins, J.C., Perry, M.J.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 34, 1353 (1975)
Baym, G., Chin, S.A.: Phys. Lett. B 62, 241 (1976)
Keister, B.D., Kisslinger, L.S.: Phys. Lett. B 64, 117 (1976)
Lenzi, C.H., Lugones, G.: Astrophys. J. 759, 57 (2012)
Bonanno, L., Sedrakian, A.: A&A 539, A16 (2012)
Orsaria, M., Rodrigues, H., Weber, F., Contrera, G.A.: Phys. Rev. C 89, 015806 (2014)
Bombaci, I., Logoteta, D.: MNRAS 433, L79 (2013)
Whittenbury, D.L., Matevosyan, H.H., Thomas, A.W.: Phys. Rev. C 93, 035807 (2016)
Bodmer, A.R.: Phys. Rev. D 4, 1601 (1971)
Terazawa, H.: INS Rep. 336 (Univ. Tokyo, INS) (1979); J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 58, 3555 (1989); 58, 4388 (1989); 59, 1199 (1990)
Witten, E.: Phys. Rev. D 30, 272 (1984)
Farhi, E., Jaffe, R.L.: Phys. Rev. D 30, 2379 (1984)
Madsen, J.: Phys. Rev. D 50, 3328 (1994)
Mustafa, M.G., Ansari, A.: Phys. Rev. D 53, 5136 (1996)
Alcock, C., Farhi, E., Olinto, A.: Astrophys. J. 310, 261 (1986)
Dey, M., Bombaci, I., Dey, J., Ray, S., Samanta, B.C.: Phys. Lett. B 438, 123 (1998); Phys. Lett. B 447, 352 (1999); Phys. Lett. B 467, 303 (1999)
Li, X.-D., Bombaci, I., Dey, M., Dey, J., van den Heuvel, E.P.J.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 3776 (1999)
Li, X.-D., Ray, S., Dey, J., Dey, M., Bombaci, I.: Astrophys. J. 527, L51 (1999)
Xu, R.X., Qiao, G.J., Zhang, B.: Astrophys. J. 522, L109 (1999)
Casalbuoni, R., Nardulli, G.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 76, 263 (2004)
Alford, M.G., Schmitt, A., Rajagopal, K., Schafer, T.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 455 (2008).
Anglani, R., Casalbuoni, R., Ciminale, M., Ippolito, N., Gatto, R., Mannarelli, M., Ruggeri, M.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 86, 509 (2014)
Buballa, M., Carignano, S.: Progr. Part. Nucl. Phys. 81, 39 (2015)
Bhattacharyya, S., Bombaci, I., Bandyopadhyay, D., Thampan, A.V., Logoteta, D.: New Astron. 54, 61 (2017)
Bhattacharyya, S., Bombaci, I., Logoteta, D., Thampan, A.V.: MNRAS 457, 3101 (2016)
Lindblom, L.: Astrophys. J. 398, 569 (1992)
Riley, T.E., et al.: MNRAS 478, 1093 (2018)
Berezhiani, Z., Bombaci, I., Drago, A., Frontera, F., Lavagno, A.: Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 113, 268 (2002)
Berezhiani, Z., Bombaci, I., Drago, A., Frontera, F., Lavagno, A.: Astrophys. J. 586, 1250 (2003)
Bombaci, I., Parenti, I., Vidaña, I.: Astrophys. J. 614, 314 (2004)
Drago, A., Lavagno, A., Pagliara, G.: Eur. Phys. J. A 19, 197 (2004)
Lugones, G., Bombaci, I.: Phys. Rev. D 72, 065021 (2005)
Drago, A., Lavagno, A., Parenti, I.: Astrophys. J. 659, 1519 (2007)
Bombaci, I., Lugones, G., Vidaña, I.: A&A 462, 1017 (2007)
Bombaci, I., Panda, P.K., Providencia, C., Vidaña, I. : Phys. Rev. D 77, 083002 (2008)
Bombaci, I., Logoteta, D., Panda, P.K., Providencia, C., Vidaña, I.: Phys. Lett. B 680, 448 (2009)
Bombaci, I., Logoteta, D., Providencia, C., Vidaña, I.: A&A 528, A71 (2011)
Drago, A., Lavagno, A., Pagliara, G.: Phys. Rev. D 89, 043014 (2014)
Bombaci, I., Logoteta, D., Vidaña, I., Providencia, C.: Eur. Phys. J. A 52, 58 (2016)
Drago, A., Lavagno, A., Pagliara, G., Pigato, D.: Eur. Phys. J. A 52, 40 (2016)
Drago, A., Pagliara, G.: Eur. Phys. J. A 52, 41 (2016)
Drago, A., Lavagno, A., Metzger, B., Pagliara, G.: Phys. Rev. D 93, 103001 (2016)
Pili, A.G., Bucciantini, N., Drago, A., Pagliara, G., Del Zanna, L.: MNRAS 462, L26 (2016)
Bhattacharyya, S., Bombaci, I., Logoteta, D., Thampan, A.V.: Astrophys. J. 848, 65 (2017)
Drago, A., Pagliara, G.: Phys. Rev. D 102, 063003 (2020)
Hsu, S.D.H., Schwetz, M.: Phys. Lett. B 432, 203 (1998)
Fodor, Z., Katz, S.D.: JHEP 04, 050 (2004)
Bombaci, I., Datta, B.: Astrophys. J. 530, L69 (2000)
Olesen, M.L.: Madsen, J.: Phys. Rev. D 49, 2698 (1994)
Hulse, R.A., Taylor, J.H.: Astrophys J. 195, L51 (1975); Weisberg, J.M., Nice, D.J., Taylor, J. H.: Astrophys J. 722, 1030 (2010)
Patruno, A., Haskell, B., Andersson, N.: Astrophys. J. 850, 106 (2017)
Abbott, R., et al.: Astrophys. J. Lett. 896, L44 (2020)
Bombaci, I., Drago, A., Logoteta, D., Pagliara, G., Vidaña, I.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 162702 (2021)
Acknowledgements
I thank the editors of the present book, Sudip Bhattacharyya, Alessandro Papitto, and Dipankar Bhattacharya, for inviting me to write this chapter. I dedicate this work to my beloved son, Paride.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bombaci, I. (2022). The Equation of State of Neutron Star Matter. In: Bhattacharyya, S., Papitto, A., Bhattacharya, D. (eds) Millisecond Pulsars. Astrophysics and Space Science Library, vol 465. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85198-9_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85198-9_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-85197-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-85198-9
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)





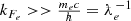 , thus for densities
, thus for densities 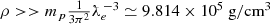 .
.