Abstract
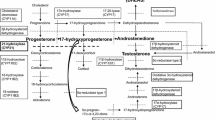
Nonclassical congenital adrenal hyperplasia (NCAH) is a relatively common autosomal recessive disorder that arises from mutations in the genes encoding 21-hydroxylase (CYP21A2), 11-β-hydroxylase (CYP11B1), or 3-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3βHSD2). Genetically confirmed nonclassical forms of 11-β-hydroxylase or 3-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiencies are extremely rare; the vast majority of subjects diagnosed with NCAH have mutations in both alleles of CYP21A2 that result in an overall 30–50% reduction in the activity of 21-hydroxylase enzyme. We will here review current challenges in the diagnosis of nonclassical 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21-OHd), including the reasons that justify screening for this disorder, the clinical situations in which such screening is required, recent advances in the methods used in different settings, and the consequences that might arise from a diagnosis of 21-OHd NCAH.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmina E, Dewailly D, Escobar-Morreale HF, Kelestimur F, Moran C, Oberfield S, et al. Non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency revisited: an update with a special focus on adolescent and adult women. Hum Reprod Update. 2017;3:580–99. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmx014.
Merke DP, Auchus RJ. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1248–61. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1909786.
Haider S, Islam B, D’Atri V, Sgobba M, Poojari C, Sun L, et al. Structure-phenotype correlations of human CYP21A2 mutations in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:2605–10. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1221133110.
Escobar-Morreale HF, Sanchon R, San Millan JL. A prospective study of the prevalence of nonclassical congenital adrenal hyperplasia among women presenting with hyperandrogenic symptoms and signs. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:527–33. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2007-2053.
Moran C, Azziz R, Weintrob N, Witchel SF, Rohmer V, Dewailly D, et al. Reproductive outcome of women with 21-hydroxylase-deficient nonclassic adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:3451–6. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2006-0062.
Wilson JMG, Jungner G. Principles and practice of screening for disease. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1968.
Speiser PW, Arlt W, Auchus RJ, Baskin LS, Conway GS, Merke DP, et al. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103:4043–88. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2018-01865.
Nandagopal R, Sinaii N, Avila NA, Van Ryzin C, Chen W, Finkielstain GP, et al. Phenotypic profiling of parents with cryptic nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia: findings in 145 unrelated families. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011;164:977–84. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-11-0019.
Falhammar H, Torpy DJ. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency presenting as adrenal incidentaloma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocr Pract. 2016;22:736–52. https://doi.org/10.4158/EP151085.
Taylor AE, Keevil B, Huhtaniemi IT. Mass spectrometry and immunoassay: how to measure steroid hormones today and tomorrow. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015;173:D1–12. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-15-0338.
Azziz R, Dewailly D, Owerbach D. Nonclassic adrenal hyperplasia: current concepts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994;78:810–5. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.78.4.8157702.
Ueland G, Methlie P, Øksnes M, Thordarson H, Sagen J, Kellmann R, et al. The short cosyntropin test revisited: new normal reference range using LC-MS/MS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103:1696–703. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2017-02602.
Baumgartner-Parzer S, Witsch-Baumgartner M. Hoeppner W. EMQN best practice guidelines for molecular genetic testing and reporting of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Europ. J Hum Genet. 2020;28:1341–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-0653-5.
Tonetto-Fernandes V, Lemos-Marini SH, Kuperman H, Ribeiro-Neto LM, Verreschi IT, Kater CE. Serum 21-deoxycortisol, 17-hydroxyprogesterone, and 11-deoxycortisol in classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia: clinical and hormonal correlations and identification of patients with 11beta-hydroxylase deficiency among a large group with alleged 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:2179–84. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2005-1890.
Turcu AF, Rege J, Chomic R, Liu J, Nishimoto HK, Else T, et al. Profiles of 21-carbon steroids in 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:2283–90. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-1023.
Fiet J, Le Bouc Y, Guechot J, Helin N, Maubert MA, Farabos D, et al. A liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectometry profile of 16 serum steroids, including 21-deoxycortisol and 21-deoxycorticosterone, for management of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Endocr Soc. 2017;1:186–201. https://doi.org/10.1210/js.2016-1048.
Travers S, Martinerie L, Bouvattier C, Boileau P, Lombès M, Pussard E. Multiplexed steroid profiling of gluco- and mineralocorticoids pathways using a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;165:202–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.06.005.
Turcu AF, El-Maouche D, Zhao L, Nanba AT, Gaynor A, Veeraraghavan P, et al. Androgen excess and diagnostic steroid biomarkers for nonclassic 21-hydroxylase deficiency without cosyntropin stimulation. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020;183:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-20-0129.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Instituto de Salud Carlos III (Plan Estatal de I+D+I 2013-2016), grants PI1400649, PI15/01686, PIE16/00050, and PI1801122, and cofinanced by the European Development Regional Fund “A way to achieve Europe” (EDRF). CIBERDEM and IRYCIS are also initiatives of the Instituto de Salud Carlos III.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Escobar-Morreale, H.F., Luque-Ramírez, M. (2021). Diagnostic Challenges in Nonclassical Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. In: Ertorer, M.E. (eds) Fertility and Reproductive Outcomes in Different Forms of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-82591-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-82591-1_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-82590-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-82591-1
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)