Abstract
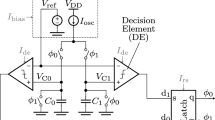
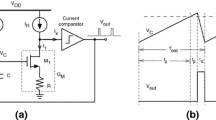
This chapter presents a family of current-mode relaxation oscillators that can be designed either as a compensated digital clock source, or as an oscillator-based sensor whose frequency reports the temperature or supply voltage. One compensated timer implementation in 0.18 \(\upmu \)m CMOS achieves a figure of merit of 120 pW/kHz, making it one of the most efficient relaxation oscillators reported to date. The oscillator design is then extended to produce a \(V_{DD}\)-controlled oscillator and a temperature-controlled oscillator. Finally, we introduce a low-power hybrid oscillator sensor, which encodes measurements of both the supply voltage and temperature into the durations of its two alternating digital clock phases. The underlying dual-phase current-mode relaxation oscillator and the resulting sensor circuits are easy to implement, are area- and energy-efficient, and offer straightforward power and speed tradeoffs for a wide range of applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferro, E., Brea, V.M., López, P., Cabello, D.: Micro-energy harvesting system including a pmu and a solar cell on the same substrate with cold startup from 2.38 nw and input power range up to 10 \(\upmu \)W using continuous MPPT. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 34(6), 5105–5116 (2018)
Sadagopan, K.R., Kang, J., Ramadass, Y., Natarajan, A.: A cm-scale 2.4-GHz wireless energy harvester with nanowatt boost converter and antenna-rectifier resonance for WiFi powering of sensor nodes. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 53(12), 3396–3406 (2018)
Jia, Y., et al.: Wireless opto-electro neural interface for experiments with small freely behaving animals. J. Neural Eng. 154, 046032 (2018)
Anand, T., Makinwa, K.A., Hanumolu, P.K.: A VCO based highly digital temperature sensor with 0.034 \(^\circ \)/mV supply sensitivity. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 51(11), 2651–2663 (2016)
Mordakhay, A., Shor, J.: Miniaturized, 0.01 mm\(^2\), resistor-based thermal sensor with an energy consumption of 0.9 nJ and a conversion time of 80 \(\upmu \)s for processor applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 53(10), 2958–2969 (2018)
Dai, S., Rosenstein, J.K.: A 14.4 nW 122 kHz dual-phase current-mode relaxation oscillator for near-zero-power sensors. In: IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC) (2015)
Dai, S., Tulloss, C.R., Lian, X., Hu, K., Reda, S., Rosenstein, J.K.: Temperature and supply voltage monitoring with current-mode relaxation oscillators. In: IFIP/IEEE International Conference on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI-SoC) (2020)
Jiang, H., Wang, P.H.P., Mercier, P.P., Hall, D.A.: A 0.4-V 0.93-nW/kHz relaxation oscillator exploiting comparator temperature-dependent delay to achieve 94-ppm/\(^\circ \)C stability. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 53(10), 3004–3011 (2018)
Banba, H., et al.: A CMOS bandgap reference circuit with sub-1-V operation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 34(5), 670–674 (1999)
Chen, S.W., Chang, M.H., Hsieh, W.C. Hwang, W.: Fully on-chip temperature, process, and voltage sensors. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) (2010)
Kobayashi, A., Hayashi, K., Arata, S., Murakami, S., Xu, G., Niitsu, K.: A 65-nm CMOS 1.4-nW self-controlled dual-oscillator-based supply voltage monitor for biofuel-cell-combined biosensing systems. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 1–5 (2019)
Vezyrtzis, C., et al.: Droop mitigation using critical-path sensors and an on-chip distributed power supply estimation engine in the z14\(^{TM}\) enterprise processor. In: IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) (2018)
Hsu, C.-H., Huang, S.-Y., Kwai, D.-M., Chou, Y.-F.: Worst-case IR-drop monitoring with 1 GHz sampling rate. In: International Symposium on VLSI Design, Automation, and Test, VLSI-DAT, pp. 1–4 (2013)
Makinwa, K.A.A.: Smart Temperature Sensor Survey. https://ei.ewi.tudelft.nl/docs/TSensor_survey.xls
Pan, S., Luo, Y., Shalmany, S.H., Makinwa, K.A.: A resistor-based temperature sensor with a 0.13 pJ \(\cdot \) K\(^2\) resolution FoM. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 53(1), 164–173 (2018)
Park, H., Kim, J.: A 0.8-V resistor-based temperature sensor in 65-nm CMOS with supply sensitivity of 0.28 \(^\circ \)C/V. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 53(3), 906–912 (2018)
Choi, W., et al.: A compact resistor-based CMOS temperature sensor with an inaccuracy of 0.12\(^{\circ }\)C (3\(\sigma \)) and a resolution FoM of 0.43 pJ \(\cdot \) K\(^2\) in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 53, 3356 (2018)
Sonmez, U., Sebastiano, F., Makinwa, K.A.: Compact thermal-diffusivity-based temperature sensors in 40 nm CMOS for SoC thermal monitoring. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 52(3), 834–843 (2017)
Yang, K., et al.: A 0.6 nJ \(-\)0.22/+0.19 \(^\circ \)C inaccuracy temperature sensor using exponential subthreshold oscillation dependence. In: IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), pp. 160–161 (2017)
Wang, X., Wang, P.H.P., Cao, Y., Mercier, P.P.: A 0.6 V 75 nW all-CMOS temperature sensor with 1.67 m\(^\circ \)/mV supply sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regular Papers (TCASi) 64(9), 2274–2283 (2017)
Someya, Teruki, Mahfuzul Islam, A.K.M., Sakurai, T., Takamiya, M.: An 11-nW CMOS temperature-to-digital converter utilizing sub-threshold current at sub-thermal drain voltage. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 54(3), 613–622 (2019)
Wang, B., Law, M.K., Tsui, C.Y., Bermak, A.: A 10.6 pJ\(\cdot \)K\(^2\) resolution FoM temperature sensor using a stable multi vibrator. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs (TCASII) 65(7), 869–873 (2018)
Said, M., Chetoui, S., Belouchrani, A., Reda, S.: Understanding the sources of power consumption in mobile SoCs. In: IEEE Ninth International Green and Sustainable Computing Conference (IGSC) (2018)
Piguet, C.: Logic synthesis of race-free asynchronous CMOS circuits. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 26(3), 371–380 (1991)
Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by grant FA8650-18-2-7851 from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). C. R. Tulloss is also grateful for support from the Jayakumar Undergraduate Summer Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dai, S., Tulloss, C.R., Lian, X., Hu, K., Reda, S., Rosenstein, J.K. (2021). Low Power Current-Mode Relaxation Oscillators for Temperature and Supply Voltage Monitoring. In: Calimera, A., Gaillardon, PE., Korgaonkar, K., Kvatinsky, S., Reis, R. (eds) VLSI-SoC: Design Trends. VLSI-SoC 2020. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 621. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81641-4_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81641-4_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-81640-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-81641-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)