Abstract
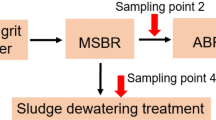
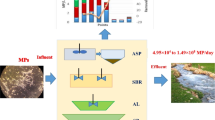
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are one of the significant pathways of microplastics (MPs) entering the environment. Thus, information regarding this issue is still requisite in Thailand. In this study, wastewater and sludge samples were collected from an activated sludge operation of an industrial WWTP in different seasons, that is, dry season and wet season. The MP particles were identified by size, shape, and polymer types under stereomicroscope and μFT-IR. From the wastewater, MPs were detected in the highest amounts after the aeration unit (134.35 ± 20.79 particles/L) during dry season and from influent (103.13 ± 59.48 particles/L) during wet season. In addition, sludge contained relatively low MP concentrations (2.27 ± 0.08 in the dry and 1.86 ± 0.28 particles/g dw. in the wet seasons). The size fraction in wastewater varied, but in sludge was > 300 μm commonly in both seasons. Fragments and pellets were identified as the most common shape of wastewater and sludge in both seasons. The treatment units and seasonal variation had a significant effect on MP abundance. The suspected particle was confirmed to be 71.13% plastic polymer, mainly polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE). The overall removal efficiency was 93.86%, indicating that there are many MPs still discharged to the river due to effluent MPs, which was approx. 1.8 × 108 particles per day. Consequently, this study suggests that, to define the effect of a season, prolonged monitoring is required. Moreover, the attention must be on WWTPs in Thailand, as they act as the greatest source of MP contamination in the environment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvim CB, Mendoza-Roca J, Bes-Piá A (2020) Wastewater treatment plant as microplastics release source–quantification and identification techniques. 255:109739
Andrady AL (2011) Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 62(8):1596–1605
Borges Ramirez MM, Dzul Caamal R, Rendon von Osten J (2019) Occurrence and seasonal distribution of microplastics and phthalates in sediments from the urban channel of the Ria and coast of Campeche, Mexico. Sci Total Environ 672:97–105
Brandsma S et al (2013) Microplastics in river suspended particulate matter and sewage treatment plants
Carr SA, Liu J, Tesoro AG (2016) Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 91:174–182
Cheung PK, Cheung LTO, Fok L (2016) Seasonal variation in the abundance of marine plastic debris in the estuary of a subtropical macro-scale drainage basin in South China. 562:658–665
Desforges JP, Galbraith M, Ross PS (2015) Ingestion of Microplastics by Zooplankton in the Northeast Pacific Ocean. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 69(3):320–330
Edo C et al (2020) Fate of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants and their environmental dispersion with effluent and sludge. 259:113837
Eriksen M, Mason S, Wilson S (2013) Mar Pollut Bull 77(null):177
Gao F et al (2019) Study on the capability and characteristics of heavy metals enriched on microplastics in marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 144:61–67
Gies EA et al (2018) Retention of microplastics in a major secondary wastewater treatment plant in Vancouver, Canada. Mar Pollut Bull 133:553–561
Hidalgo-Ruz V et al (2012) Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3060–3075
Hitchcock JN (2020) Storm events as key moments of microplastic contamination in aquatic ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 734
Hongprasith N et al (2020) IR microspectroscopic identification of microplastics in municipal wastewater treatment plants. 1–8
Jambeck JR et al (2015) Marine pollution. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 347(6223):768–71
Jiang J et al (2020) Investigation and fate of microplastics in wastewater and sludge filter cake from a wastewater treatment plant in China. Sci Total Environ 746:141378
Kole PJ et al (2017) Wear and Tear of Tyres: A Stealthy Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(10)
Lares M et al (2018) Occurrence, identification and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology. Water Res 133:236–246
Leslie HA et al (2017) Microplastics en route: field measurements in the Dutch river delta and Amsterdam canals, wastewater treatment plants, North Sea sediments and biota. Environ Int 101:133–142
Liu X et al (2019) Transfer and fate of microplastics during the conventional activated sludge process in one wastewater treatment plant of China. 362:176–182
Lusher A (2015) Microplastics in the Marine Environment: distribution, interactions and effects. pp 245–307
Lv X et al (2019) Microplastics in a municipal wastewater treatment plant: fate, dynamic distribution, removal efficiencies, and control strategies. J Clean Prod 225:579–586
Magni S et al (2019) The fate of microplastics in an Italian wastewater treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 652:602–610
Magnusson K, Norén F (2014) Screening of microplastic particles in and down-stream a wastewater treatment plant
Mason SA et al (2016) Microplastic Pollution Is Widely Detected in US Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent. 218:1045–1054
Masura J et al (2015) Laboratory methods for the analysis of microplastics in the marine environment: recommendations for quantifying synthetic particles in waters and sediments
Michielssen MR et al (2016) Fate of microplastics and other small anthropogenic litter (SAL) in wastewater treatment plants depends on unit processes employed. Environ Science-Water Res Technol 2(6):1064–1073
Mintenig SM et al (2017) Identification of microplastic in effluents of waste water treatment plants using focal plane array-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging. Water Res 108:365–372
Moore CJ et al (2002) A comparison of neustonic plastic and zooplankton abundance in southern California’s coastal waters. Mar Pollut Bull 44(10):1035–1038
Murphy F et al (2016) Wastewater treatment works (WwTW) as a source of microplastics in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol 50(11):5800–5808
Peters CA et al (2018) Pyr-GC/MS analysis of microplastics extracted from the stomach content of benthivore fish from the Texas Gulf Coast. Mar Pollut Bull 137:91–95
Rodrigues MO et al (2018) Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of a freshwater system (Antua River, Portugal). Sci Total Environ 633:1549–1559
Shruti VC et al (2019) Microplastics in freshwater sediments of Atoyac River basin, Puebla City, Mexico. Sci Total Environ 654:154–163
Sun J et al (2019) Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Detection, occurrence and removal. Water Res 152:21–37
Talvitie J et al (2015) Do wastewater treatment plants act as a potential point source of microplastics? Preliminary study in the coastal Gulf of Finland. Baltic Sea. Water Sci Technol 72(9):1495–1504
Talvitie J et al (2017) Solutions to microplastic pollution—removal of microplastics from wastewater effluent with advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res 123:401–407
Thompson RC, Swan SH, Moore CJ (2009) Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 364(null):1973
Ziajahromi S et al (2017) Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics: development of a new approach to sample wastewater-based microplastics. Water Res 112:93–99
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Microplastic and plastic waste cluster and Graduate School, Chulalongkorn University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Saiwaree, S., Kanokkantapong, V. (2021). Microplastics in Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plants: Dynamic Distribution, Seasonal Variation, and Removal Efficiencies. In: Jeon, HY. (eds) Sustainable Development of Water and Environment. ICSDWE 2021. Environmental Science and Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-75278-1_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-75278-1_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-75277-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-75278-1
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)