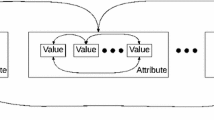
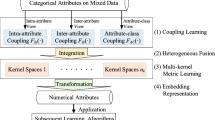
Abstract
Mixed-type data that contains both categorical and numerical features is prevalent in many real-world applications. Clustering mixed-type data is challenging, especially because of the complex relationship between categorical and numerical features. Unfortunately, widely adopted encoding methods and existing representation learning algorithms fail to capture these complex relationships. In this paper, we propose a new correlation-preserving embedding framework, COPE, to learn the representation of categorical features in mixed-type data while preserving the correlation between numerical and categorical features. Our extensive experiments with real-world datasets show that COPE generates high-quality representations and outperforms the state-of-the-art clustering algorithms by a wide margin.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andritsos, P., Tsaparas, P., Miller, R.J., Sevcik, K.C.: LIMBO: scalable clustering of categorical data. In: Bertino, E., et al. (eds.) EDBT 2004. LNCS, vol. 2992, pp. 123–146. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24741-8_9
Ankerst, M., Breunig, M.M., Kriegel, H.P., Sander, J.: Optics: ordering points to identify the clustering structure. ACM SIGMOD Rec. 28(2), 49–60 (1999)
Aytekin, C., Ni, X., Cricri, F., Aksu, E.: Clustering and unsupervised anomaly detection with l 2 normalized deep auto-encoder representations. In: 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2018)
Barbará, D., Li, Y., Couto, J.: Coolcat: an entropy-based algorithm for categorical clustering. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 582–589 (2002)
Behzadi, S., Ibrahim, M.A., Plant, C.: Parameter free mixed-type density-based clustering. In: Hartmann, S., Ma, H., Hameurlain, A., Pernul, G., Wagner, R.R. (eds.) DEXA 2018. LNCS, vol. 11030, pp. 19–34. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98812-2_2
Behzadi, S., Müller, N.S., Plant, C., Böhm, C.: Clustering of mixed-type data considering concept hierarchies. In: Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 555–573. Springer (2019)
Benesty, J., Chen, J., Huang, Y., Cohen, I.: Pearson correlation coefficient. In: Noise Reduction in Speech Processing. Springer Topics in Signal Processing, vol. 2, pp. 1–4. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00296-0_5
Bengio, Y., Courville, A., Vincent, P.: Representation learning: a review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(8), 1798–1828 (2013)
Böhm, C., Goebl, S., Oswald, A., Plant, C., Plavinski, M., Wackersreuther, B.: Integrative parameter-free clustering of data with mixed type attributes. In: Zaki, M.J., Yu, J.X., Ravindran, B., Pudi, V. (eds.) PAKDD 2010. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 6118, pp. 38–47. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-13657-3_7
Cao, F., et al.: An algorithm for clustering categorical data with set-valued features. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learning Syst. 29(10), 4593–4606 (2017)
Cherkassky, V., Ma, Y.: Practical selection of SVM parameters and noise estimation for SVM regression. Neural Netw. 17(1), 113–126 (2004)
Comaniciu, D., Meer, P.: Mean shift: a robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(5), 603–619 (2002)
Dua, D., Graff, C.: UCI machine learning repository (2017). http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml
Ester, M., Kriegel, H.P., Sander, J., Xu, X., et al.: A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. KDD 96, 226–231 (1996)
Fowlkes, E.B., Mallows, C.L.: A method for comparing two hierarchical clusterings. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 78(383), 553–569 (1983)
Guha, S., Rastogi, R., Shim, K.: Rock: a robust clustering algorithm for categorical attributes. Inf. Syst. 25(5), 345–366 (2000)
Hamka, F., Bouwman, H., De Reuver, M., Kroesen, M.: Mobile customer segmentation based on smartphone measurement. Telematics Inform. 31(2), 220–227 (2014)
Hartigan, J.A., Wong, M.A.: Algorithm as 136: a k-means clustering algorithm. J. Royal Stat. Soci. Series c (applied statistics) 28(1), 100–108 (1979)
Hershey, J.R., Olsen, P.A.: Approximating the kullback leibler divergence between Gaussian mixture models. In: 2007 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing-ICASSP’07, vol. 4, pp. IV-317. IEEE (2007)
Hornik, K.: Approximation capabilities of multilayer feedforward networks. Neural Netw. 4(2), 251–257 (1991)
Hosmer Jr., D.W., Lemeshow, S., Sturdivant, R.X.: Applied logistic regression, vol. 398. Wiley (2013)
Huang, Z.: Extensions to the k-means algorithm for clustering large data sets with categorical values. Data Min. Knowl. Disc. 2(3), 283–304 (1998)
Indyk, P., Motwani, R.: Approximate nearest neighbors: towards removing the curse of dimensionality. In: Proceedings of The Thirtieth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 604–613. ACM (1998)
Jian, S., Hu, L., Cao, L., Lu, K.: Metric-based auto-instructor for learning mixed data representation. In: Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2018)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Kohavi, R.: Scaling up the accuracy of Naive-bayes classifiers: a decision-tree hybrid. KDD 96, 202–207 (1996)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
van der Maaten, L., Hinton, G.: Visualizing data using t-sne. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9, 2579–2605 (2008)
Marchi, E., Vesperini, F., Eyben, F., Squartini, S., Schuller, B.: A novel approach for automatic acoustic novelty detection using a denoising autoencoder with bidirectional LSTM neural networks. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1996–2000. IEEE (2015)
Ni, X., Quadrianto, N., Wang, Y., Chen, C.: Composing tree graphical models with persistent homology features for clustering mixed-type data. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 2622–2631 (2017)
Salem, S.B., Naouali, S., Chtourou, Z.: A fast and effective partitional clustering algorithm for large categorical datasets using a k-means based approach. Comput. Electr. Eng. 68, 463–483 (2018)
Specht, D.F., et al.: A general regression neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 2(6), 568–576 (1991)
Tate, R.F.: Correlation between a discrete and a continuous variable. point-biserial correlation. Ann. Math. Stat. 25(3), 603–607 (1954)
Tavallaee, M., Bagheri, E., Lu, W., Ghorbani, A.A.: A detailed analysis of the KDD cup 99 data set. In: 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Security and Defense Applications, pp. 1–6. IEEE (2009)
Vincent, P., Larochelle, H., Bengio, Y., Manzagol, P.A.: Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1096–1103 (2008)
Vinh, N.X., Epps, J., Bailey, J.: Information theoretic measures for clusterings comparison: variants, properties, normalization and correction for chance. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11, 2837–2854 (2010)
Von Luxburg, U.: A tutorial on spectral clustering. Stat. Comput. 17(4), 395–416 (2007)
Wiwie, C., Baumbach, J., Röttger, R.: Comparing the performance of biomedical clustering methods. Nat. Methods 12(11), 1033 (2015)
Wold, S., Esbensen, K., Geladi, P.: Principal component analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2(1–3), 37–52 (1987)
Wu, Y., Duan, H., Du, S.: Multiple fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm in medical diagnosis. Technol. Health Care 23(s2), S519–S527 (2015)
Xie, J., Girshick, R., Farhadi, A.: Unsupervised deep embedding for clustering analysis. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 478–487 (2016)
Acknowledgement
This work has been supported in part by NSF CNS-1951430, the USC Integrated Media Systems Center, and unrestricted cash gifts from Microsoft and Google. The opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the sponsors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tran, L., Fan, L., Shahabi, C. (2021). Clustering Mixed-Type Data with Correlation-Preserving Embedding. In: Jensen, C.S., et al. Database Systems for Advanced Applications. DASFAA 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12682. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-73197-7_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-73197-7_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-73196-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-73197-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)