Abstract
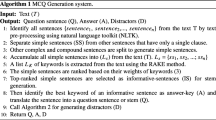
In this paper, we propose three novel algorithms to help educators generate questions to evaluate learners’ comprehension of the learning material. First, we propose the Automatic Question Generator algorithm that automatically generates multiple-choice, true-or-false, and fill-in-the-blank questions from any arbitrary text. Second, we propose the Automatic Distractors Generator algorithm that automatically generates multiple wrong but relevant answers for the multiple-choice questions. Third, we propose the Automatic Answers Generator algorithm that automatically generates multiple synonyms to the correct answer of the fill-in-the-blank questions to be accepted as correct answers. The algorithms have been used on finance and business learning material as case studies for evaluation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal , M., Mannem, P.: Automatic gap-fill question generation from text books. In: Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications, pp. 56–64. Association for Computational Linguistics (2011)
Baroni, M., Bernardini, S., Ferraresi, A., Zanchetta, E.: The wacky wide web: a collection of very large linguistically processed web-crawled corpora. Lang. Resour. Eval. 43, 209–226 (2009)
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805 (2018)
Gardner, M., Grus, J., Neumann, M., Tafjord, O., Dasigi, P., Liu, N., Peters, M., Schmitz, M., Zettlemoyer, L.: AllenNLP: a deep semantic natural language processing platform. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1803.07640 (2018)
Heilman, M.: Automatic Factual Question Generation from Text. Ph.D. thesis, Carnegie Mellon University (2011)
IBM: Natural language understanding: IBM cloud (2020)
Kretch, A.: Question generation: Using nlp to solve “inverse” task (2018)
Manning, C.D., Surdeanu, M., Bauer, J., Finkel, J.R., Bethard, S., McClosky, D.: The stanford CoreNLP natural language processing toolkit. In: Proceedings of 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, pp. 55–60 (2014)
Miller, G.A.: WordNet: a lexical database for English. Commun. ACM 38(11), 39–41 (1995)
Intel AI Developer Program: Using natural language processing for smart question generation (2018)
Ross, S.A., Westerfield, R.W., Jordan, B.D., Roberts, G., Pandes, J.A., Holloway, T.: Fundamentals Of Corporate Finance (10th edition). McGraw-Hill Irwin, Toronto (2019)
Sanh, V., Debut, L., Chaumond, J., Wolf, T.: DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.01108 (2019)
Smith, S., Avinesh, P.V.S., Kilgarriff, A.: Corpus-driven item generation, Gap-fill tests for language learners (2010)
Wolf, T.: Lysandre debut, victor sanh, julien chaumond, clement delangue, anthony moi, pierric cistac, tim rault, r’emi louf, morgan funtowicz, and jamie brew. 2019. Huggingface’s transformers: State-of-the-art natural language processing. ArXiv, abs (1910)
Angela Workman-Stark: Creating the Inclusive Workplace. Athabasca University (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
De La Cruz, R.R., Khalil, A., Khalifa, S. (2021). Automatic Multiple-Choice and Fill-in-the-Blank Question Generation from Arbitrary Text. In: Arai, K. (eds) Advances in Information and Communication. FICC 2021. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1364. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-73103-8_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-73103-8_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-73102-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-73103-8
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)