Abstract
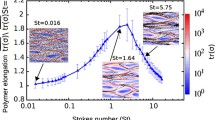
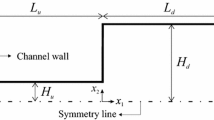
The simplest numerical framework to study turbulent particle dispersion assumes that particles can be modeled as point-like spheres brought about by the flow. In spite of its simplicity, this framework has led to significant advancements in the study of particle-turbulence interactions. In this paper we examine how particle dispersion in dilute turbulent suspensions changes when particles are non-spherical (elongated) and may actively move within the fluid (motile). In particular, we show how elongation and motility add to particle inertia to modulate preferential concentration. Results for particles suspended in wall-bounded turbulence are presented to highlight effects on wall accumulation and segregation, which represent the macroscopic manifestation of preferential concentration.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balachandar, S., Eaton, J.K.: Turbulent dispersed multiphase flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 42, 111–133 (2010)
Brenner, H.: The Stokes resistance of an arbitrary particle. Chem. Eng. Sci. 18, 1–25 (1963)
Cressman, J.R., Davoudi, J., Goldburg, W.I., Schumacher, J.: Eulerian and Lagrangian studies in surface flow turbulence. New J. Phys. 6, 53 (2004)
Durham, W.M., Climent, E., Barry, W.M., De Lillo, F., Boffetta, G., Cencini, M., Stocker, R.: Turbulence drives microscale patches of motile phytoplankton. Nat. Commun. 4, 2148 (2013)
Fessler, J.R., Kulick, J.D., Eaton, J.K.: Preferential concentration of heavy particles in a turbulent channel flow. Phys. Fluids 6, 3742–3749 (1994)
Jeffery, G.B.: The motion of ellipsoidal particles immersed in a viscous fluid. Proc. Roy. Soc. 102, 161–179 (1922)
Kermani, A., Khakpour, H.R., Shen, L., Igusa, T.: Statistics of surface-renewal of passive scalars in free-surface turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 678, 379 (2011)
Larkin, J., Bandi, M.M., Pumir, A., Goldburg, W.I.: Power-law distributions of particle concentration in free-surface flows. Phys. Rev. E 80, 066301 (2009)
Lovecchio, S., Zonta, F., Soldati, A.: Upscale energy transfer and flow topology in free surface turbulence. Phys. Rev. E 91, 033010 (2015)
Lovecchio, S., Zonta, F., Soldati, A.: Influence of thermal stratification on the surfacing and clustering of floaters in free surface turbulence. Adv. Water Res. 72, 22–31 (2014)
Lovecchio, S., Marchioli, C., Soldati, A.: Time persistence of floating particle clusters in free-surface turbulence. Phys. Rev. E 88, 033003 (2013)
Marchioli, C.: Large-eddy simulation of turbulent dispersed flows: a review of modelling approaches. Acta Mech. 228, 738–768 (2017)
Marchioli, C., Zhao, L., Andersson, H.I.: On the relative rotational motion between rigid fibers and fluid in turbulent channel flow. Phys. Fluids 28, 013301 (2016)
Marchioli, C., Fantoni, M., Soldati, A.: Orientation, distribution and deposition of elongated, inertial fibers in turbulent channel flow. Phys. Fluids 22, 033301 (2010)
Marchioli, C., et al.: Statistics of particle dispersion in direct numerical simulations of wall-bounded turbulence: results of an international collaborative benchmark test. Int. J. Multiphase Flow 34, 879–893 (2008)
Mashayekhpour, M., Marchioli, C., Lovecchio, S., Nemati Lay, E., Soldati, A.: Wind effect on gyrotactic micro-organism surfacing in free-surface turbulence. Adv. Water Resour. 129, 328–337 (2019)
Maxey, M., Riley, J.: Equation of motion for a small rigid sphere in a nonuniform flow. Phys. Fluids 26, 883–889 (1983)
Nagaosa, R., Handler, R.A.: Statistical analysis of coherent vortices near a free surface in a fully developed turbulence. Phys. Fluids 15, 375–394 (2003)
Pedley, T.J., Kessler, J.O.: Hydrodynamic phenomena in suspensions of swimming microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 24, 313–358 (1992)
Picciotto, M., Marchioli, C., Soldati, A.: Characterization of near-wall accumulation regions for particles in turbulent boundary layers. Phys. Fluids 17, 098101 (2005)
Reeks, M.W.: The transport of discrete particles in inhomogeneous turbulence. J. Aerosol Sci. 310, 729–739 (1983)
Soldati, A., Marchioli, C.: Physics and modelling of turbulent particle deposition and entrainment. Int. J. Multiphase Flow 35, 827 (2009)
Zhao, L., Marchioli, C., Andersson, H.I.: Slip velocity of rigid fibers in turbulent channel flow. Phys. Fluids 26, 063302 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Marchioli, C., Bhatia, H., Dotto, D. (2021). Influence of Particle Anisotropy and Motility on Preferential Concentration in Turbulence. In: Deville, M., et al. Turbulence and Interactions. TI 2018 2018. Notes on Numerical Fluid Mechanics and Multidisciplinary Design, vol 149. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65820-5_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65820-5_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-65819-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-65820-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)