Abstract
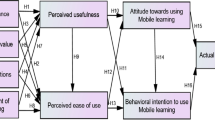
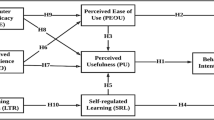
In recent years, more and more undergraduates begin to use app learning based on the TAM model. Among them, the emergence of MOOC is a good opportunity for educational reform. Because of the convenience, low cost, lifetime and pertinence, MOOC software played a great role in educational reform. This article reviews the related content of TAM model and learning efficiency, and builds MOOC learning behavior model of college students. Through the survey, a total of 255 valid questionnaires were collected. The relevant data were analyzed, and the model was hypothesized. Through the model conclusion, we find: The behavior of college students using MOOCs will be affected by behavioral intentions, and behavioral intentions will be affected by learning motivation, perceived usefulness, and attitudes. The attitude to use will be determined by college students’ perception of MOOC’s usefulness and perceived ease of use. Perceived ease of use is affected by cognitive load, and perceived usefulness is affected by learning effects and motivation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chee, K.N., Ibrahim, H.: Designing mobile learning communication aid as an android app. Adv. Sci. Lett. 22(12), 4023–4027 (2016)
Rose, S., Shah, B.J., Onken, J.: Bridging the G-APP: continuous professional development for gastroenterologists: replacing MOC with a model for lifelong learning and accountability. Gastroenterology 13(11), 1872–1892 (2015)
Yanik, E., Sezgin, T.M.: Active learning for sketch recognition. Comput. Graph. 52(C), 93–105 (2015)
Zhang, X., Chen, B., Liu, H.: Infinite max-margin factor analysis via data augmentation. Pattern Recogn. 52(C), 17–32 (2015)
Deshpande, S., Chahande, J., Rathi, A.: Mobile learning app: a novel method to teach clinical decision making in prosthodontics. Educ. Health 30(1), 31 (2017)
Paiz, F., Bonin, E.A., Cavazzola, L.T.: Surgical learning application (app) for smartphones and tablets: a potential tool for laparoscopic surgery teaching courses. Surg. Innovation 23(1), 106 (2015)
Khaddage, F., Müller, W., Flintoff, K.: Advancing mobile learning in formal and informal settings via mobile app technology: where to from here, and how? Educ. Technol. Soc. 19(3), 16–26 (2016)
Sharples, M., Aristeidou, M., Villasclaras-Fernández, E.: The sense-it app: a smartphone sensor toolkit for citizen inquiry learning. Int. J. Mob. Blended Learn. 9(2), 16–38 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, L. (2021). Influencing Factors of Undergraduates Using App Learning Based on TAM Model – Taking MOOC App as an Example. In: MacIntyre, J., Zhao, J., Ma, X. (eds) The 2020 International Conference on Machine Learning and Big Data Analytics for IoT Security and Privacy. SPIOT 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1282. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62743-0_73
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62743-0_73
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-62742-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-62743-0
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)