Abstract
This chapter describes the development and preclinical testing of hyperpolarized 13C-labeled probes and the required steps necessary for their translation to patient studies, with an emphasis on the preclinical platforms and techniques necessary to achieve this goal. The chapter starts with a description of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopic and biochemical techniques used for studying metabolism in human cells and tissues in order to identify pathways that could be probed using new hyperpolarized 13C-labeled probes, followed by a description of the in vitro and in vivo preclinical testing and optimization of new hyperpolarized probes along with a discussion of some of the biochemical questions that have been investigated using preclinical hyperpolarized 13C MRI. The role preclinical studies have played in the clinical translation of [1-13C]pyruvate and how they provided the motivation for several ongoing applications to pathologies in patients is also described. Finally, the role of preclinical studies for developing the best approaches for analyzing the dynamic hyperpolarized MR data and providing an understanding of the underlying biochemistry of the pathologies being studied is described. After reading this chapter and completing the associated problem set, the reader should have a basic knowledge of how hyperpolarized 13C MRI probes are developed, optimized, and used to investigate biomedical questions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triose phosphate
- DNP:
-
Dynamic nuclear polarization
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- FDG:
-
Fluoro deoxy glucose
- GMP:
-
Good manufacturing practice
- HP:
-
Hyperpolarization
- HR-MAS:
-
High resolution-magic angle spinning
- IND:
-
Investigational new drug
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- NCI:
-
National Cancer Institute
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- PDH:
-
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- RF:
-
Radio frequency
- SNR:
-
Signal to noise ratio
- TR:
-
Repetition time
- TRAMP:
-
Transgenic adenocarcinoma of the murine prostate
References
Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H., Fridlund, B., Gram, A., Hansson, G., Hansson, L., Lerche, M.H., Servin, R., Thaning, M., Golman, K.: Increase in signal-to-noise ratio of >10,000 times in liquid-state NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 10158–10163 (2003)
Golman, K.: Real-time metabolic imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103, 11270–11275 (2006)
Nelson, S.J., Kurhanewicz, J., Vigneron, D.B., Larson, P.E.Z., Harzstark, A.L., Ferrone, M., Van Criekinge, M., Chang, J.W., Bok, R., Park, I., Reed, G., Carvajal, L., Small, E.J., Munster, P., Weinberg, V.K., Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H., Chen, A.P., Hurd, R.E., Odegardstuen, L.-I., Robb, F.J., Tropp, J., Murray, J.A.: Metabolic imaging of patients with prostate cancer using hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate. Sci. Transl. Med. 5, 198ra108 (2013)
Wilson, D.M., Keshari, K.R., Larson, P.E.Z., Chen, A.P., Hu, S., Van Criekinge, M., Bok, R., Nelson, S.J., Macdonald, J.M., Vigneron, D.B., Kurhanewicz, J.: Multi-compound polarization by DNP allows simultaneous assessment of multiple enzymatic activities in vivo. J. Magn. Reson. 205, 141–147 (2010)
Kurhanewicz, J., Vigneron, D.B., Brindle, K., Chekmenev, E.Y., Comment, A., Cunningham, C.H., DeBerardinis, R.J., Green, G.G., Leach, M.O., Rajan, S.S., Rizi, R.R., Ross, B.D., Warren, W.S., Malloy, C.R.: Analysis of cancer metabolism by imaging hyperpolarized nuclei: prospects for translation to clinical research. Neoplasia. 13, 81–97 (2011)
McLean, M.A., Daniels, C.J., Grist, J., Schulte, R.F., Lanz, T., Chhabra, A., Earl, H.M., Basu, B., Wilkinson, I.B., Lomas, D.J., Caldas, C., Abraham, J.E., Graves, M., Gilbert, F., Brindle, K.M., Gallagher, F.A.: Feasibility of metabolic imaging of hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate in human breast cancer European Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine and Biology. Springer Nature, Cham (2018)
Miloushev, V.Z., Granlund, K.L., Boltyanskiy, R., Lyashchenko, S.K., DeAngelis, L.M., Mellinghoff, I.K., Brennan, C.W., Tabar, V., Yang, T.J., Holodny, A.I., Sosa, R.E., Guo, Y.W., Chen, A.P., Tropp, J., Robb, F., Keshari, K.R.: Metabolic imaging of the human brain with hyperpolarized 13C pyruvate demonstrates 13C lactate production in brain tumor patients. Cancer Res. 78(14), 3755–3760 (2018)
Park, I., Larson, P.E.Z., Gordon, J.W., Carvajal, L., Chen, H.-Y., Bok, R., Van Criekinge, M., Ferrone, M., Slater, J.B., Xu, D., Kurhanewicz, J., Vigneron, D.B., Chang, S., Nelson, S.J.: Development of methods and feasibility of using hyperpolarized carbon-13 imaging data for evaluating brain metabolism in patient studies. Magn. Reson. Med. 80, 864–873 (2018)
Cheng, L.L., Ma, M.J., Becerra, L., Ptak, T., Tracey, I., Lackner, A., González, R.G.: Quantitative neuropathology by high resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 94, 6408–6413 (1997)
Tessem, M.-B., Swanson, M.G., Keshari, K.R., Albers, M.J., Joun, D., Tabatabai, Z.L., Simko, J.P., Shinohara, K., Nelson, S.J., Vigneron, D.B., Gribbestad, I.S., Kurhanewicz, J.: Evaluation of lactate and alanine as metabolic biomarkers of prostate cancer using 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy of biopsy tissues. Magn. Reson. Med. 60, 510–516 (2008)
Keshari, K.R., Sriram, R., Van Criekinge, M., Wilson, D.M., Wang, Z.J., Vigneron, D.B., Peehl, D.M., Kurhanewicz, J.: Metabolic reprogramming and validation of hyperpolarized 13C lactate as a prostate cancer biomarker using a human prostate tissue slice culture bioreactor. Prostate. 73, 1171–1181 (2013)
Lumata, L., Jindal, A.K., Merritt, M.E., Malloy, C.R., Sherry, A.D., Kovacs, Z.: DNP by thermal mixing under optimized conditions yields >60,000-fold enhancement of 89Y NMR signal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 8673–8680 (2011)
Chiavazza, E., Kubala, E., Gringeri, C.V., Düwel, S., Durst, M., Schulte, R.F., Menzel, M.I.: Earth’s magnetic field enabled scalar coupling relaxation of 13C nuclei bound to fast-relaxing quadrupolar 14N in amide groups. J. Magn. Reson. 227, 35–38 (2013)
Lerche, M.H., Meier, S., Jensen, P.R., Baumann, H., Petersen, B.O., Karlsson, M., Duus, J.Ø., Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.: Study of molecular interactions with 13C DNP-NMR. J. Magn. Reson. 203, 52–56 (2010)
Jensen, P.R., Meier, S., Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H., Duus, J.Ø., Karlsson, M., Lerche, M.H.: Detection of low-populated reaction intermediates with hyperpolarized NMR. Chem. Commun. (Camb.). 2009, 5168–5170 (2009)
Zhang, G., Hilty, C.: Applications of dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization in chemistry and biochemistry. Magn. Reson. Chem. 56, 566–582 (2018)
de Araújo, M.E.G., Lamberti, G., Huber, L.A.: Homogenization of mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2015, 1009–1012 (2015)
Lumata, L., Yang, C., Ragavan, M., Carpenter, N., DeBerardinis, R.J., Merritt, M.E.: Hyperpolarized (13)C magnetic resonance and its use in metabolic assessment of cultured cells and perfused organs. Methods Enzymol. 561, 73–106 (2015)
Harrison, C., Yang, C., Jindal, A., DeBerardinis, R.J., Hooshyar, M.A., Merritt, M., Dean Sherry, A., Malloy, C.R.: Comparison of kinetic models for analysis of pyruvate-to-lactate exchange by hyperpolarized 13C NMR. NMR Biomed. 25, 1286–1294 (2012)
Hill, D.K., Orton, M.R., Mariotti, E., Boult, J.K.R., Panek, R., Jafar, M., Parkes, H.G., Jamin, Y., Miniotis, M.F., Al-Saffar, N.M.S., Beloueche-Babari, M., Robinson, S.P., Leach, M.O., Chung, Y.-L., Eykyn, T.R.: Model free approach to kinetic analysis of real-time hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy data. PLoS One. 8, e71996 (2013)
Reineri, F., Daniele, V., Cavallari, E., Aime, S.: Assessing the transport rate of hyperpolarized pyruvate and lactate from the intra- to the extracellular space. NMR Biomed. 29, 1022–1027 (2016)
Yang, C., Harrison, C., Jin, E.S., Chuang, D.T., Sherry, A.D., Malloy, C.R., Merritt, M.E., Deberardinis, R.J.: Simultaneous steady-state and dynamic 13C NMR can differentiate alternative routes of pyruvate metabolism in living cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 6212–6224 (2014)
Szwergold, B.S.: NMR spectroscopy of cells. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 54, 775–798 (1992)
Sriram, R., Nguyen, J., Santos, J.D., Nguyen, L., Sun, J., Vigneron, S., Van Criekinge, M., Kurhanewicz, J., MacKenzie, J.D.: Molecular detection of inflammation in cell models using hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate. Theranostics. 8, 3400–3407 (2018)
Chaumeil, M.M., Radoul, M., Najac, C., Eriksson, P., Viswanath, P., Blough, M.D., Chesnelong, C., Luchman, H.A., Cairncross, J.G., Ronen, S.M.: Hyperpolarized 13C MR imaging detects no lactate production in mutant IDH1 gliomas: implications for diagnosis and response monitoring. NeuroImage Clin. 12, 180–189 (2016)
Keshari, K.R., Wilson, D.M., Van Criekinge, M., Sriram, R., Koelsch, B.L., Wang, Z.J., VanBrocklin, H.F., Peehl, D.M., O’Brien, T., Sampath, D., Carano, R.A.D., Kurhanewicz, J.: Metabolic response of prostate cancer to nicotinamide phophoribosyltransferase inhibition in a hyperpolarized MR/PET compatible bioreactor. Prostate. 75, 1601–1609 (2015)
Sriram, R., Van Criekinge, M., DeLos, S.J., Keshari, K.R., Peehl, D.M., Wang, Z.J.: Non-invasive differentiation of benign renal tumors from clear cell renal cell carcinomas using clinically translatable hyperpolarized 13C pyruvate magnetic resonance. Tomography. 2, 35–42 (2016)
Sriram, R., Gordon, J., Baligand, C., Ahamed, F., DeLos, S.J., Qin, H., Bok, R.A., Vigneron, D.B., Kurhanewicz, J., Larson, P.E.Z., Wang, Z.J.: Non-invasive assessment of lactate production and compartmentalization in renal cell carcinomas using hyperpolarized 13C pyruvate MRI. Cancer. 10, 313 (2018)
Merritt, M.E., Harrison, C., Storey, C., Jeffrey, F.M., Sherry, A.D., Malloy, C.R.: Hyperpolarized 13C allows a direct measure of flux through a single enzyme-catalyzed step by NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104, 19773–19777 (2007)
Josan, S., Hurd, R., Billingsley, K., Senadheera, L., Park, J.M., Yen, Y.-F., Pfefferbaum, A., Spielman, D., Mayer, D.: Effects of isoflurane anesthesia on hyperpolarized 13C metabolic measurements in rat brain. Magn. Reson. Med. 70(4), 1117–1124 (2012)
Marjańska, M., Shestov, A.A., Deelchand, D.K., Kittelson, E., Henry, P.-G.: Brain metabolism under different anesthetic conditions using hyperpolarized [1- 13C]pyruvate and [2-13C]pyruvate. NMR Biomed. 31, e4012 (2018)
Hu, S., Chen, A.P., Zierhut, M.L., Bok, R., Yen, Y.F., Schroeder, M.A., Hurd, R.E., Nelson, S.J., Kurhanewicz, J., Vigneron, D.B.: In vivo carbon-13 dynamic MRS and MRSI of normal and fasted rat liver with hyperpolarized 13C-pyruvate. Mol. Imaging Biol. 11, 399–407 (2009)
Bastiaansen, J.A.M., Merritt, M.E., Comment, A.: Measuring changes in substrate utilization in the myocardium in response to fasting using hyperpolarized [1-(13)C]butyrate and [1-(13)C]pyruvate. Sci. Rep. 6, 25573 (2016)
Schroeder, M.A., Atherton, H.J., Cochlin, L.E., Clarke, K., Radda, G.K., Tyler, D.J.: The effect of hyperpolarized tracer concentration on myocardial uptake and metabolism. Magn. Reson. Med. 61, 1007–1014 (2009)
Gómez Damián, P.A., Sperl, J.I., Janich, M.A., Khegai, O., Wiesinger, F., Glaser, S.J., Haase, A., Schwaiger, M., Schulte, R.F., Menzel, M.I.: Multisite kinetic modeling of (13)C metabolic MR using [1-(13)C]pyruvate. Radiol Res Pract. 2014, 871619 (2014)
Janich, M.A., Menzel, M.I., Wiesinger, F., Weidl, E., Khegai, O., Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H., Glaser, S.J., Haase, A., Schulte, R.F., Schwaiger, M.: Effects of pyruvate dose on in vivo metabolism and quantification of hyperpolarized 13C spectra. NMR Biomed. 25, 142–151 (2012)
Killion, J.J., Radinsky, R., Fidler, I.J.: Orthotopic models are necessary to predict therapy of transplantable tumors in mice | SpringerLink. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 17, 279–284 (1998)
Rodrigues, T.B., Serrao, E.M., Kennedy, B.W.C., Hu, D.-E., Kettunen, M.I., Brindle, K.M.: Magnetic resonance imaging of tumor glycolysis using hyperpolarized 13C-labeled glucose. Nat. Med. 20, 93–97 (2013)
Albers, M.J., Bok, R., Chen, A.P., Cunningham, C.H., Zierhut, M.L., Zhang, V.Y., Kohler, S.J., Tropp, J., Hurd, R.E., Yen, Y.-F., Nelson, S.J., Vigneron, D.B., Kurhanewicz, J.: Hyperpolarized 13C lactate, pyruvate, and alanine: noninvasive biomarkers for prostate cancer detection and grading. Cancer Res. 68, 8607–8615 (2008)
Seth, P., Grant, A., Tang, J., Vinogradov, E., Wang, X., Lenkinski, R., Sukhatme, V.P.: On-target inhibition of tumor fermentative glycolysis as visualized by hyperpolarized pyruvate. Neoplasia. 13, 60–71 (2011)
Thind, K., Chen, A., Friesen-Waldner, L., Ouriadov, A., Scholl, T.J., Fox, M., Wong, E., Vandyk, J., Hope, A., Santyr, G.: Detection of radiation-induced lung injury using hyperpolarized (13) C magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 70, 601–609 (2012)
Thind, K., Jensen, M.D., Hegarty, E., Chen, A.P., Lim, H., Martinez-Santiesteban, F., Van Dyk, J., Wong, E., Scholl, T.J., Santyr, G.E.: Mapping metabolic changes associated with early radiation induced lung injury post conformal radiotherapy using hyperpolarized (13)C-pyruvate magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Radiother. Oncol. 110, 317–322 (2014)
Chen, A.P., Chu, W., Gu, Y.-P., Cunnhingham, C.H.: Probing early tumor response to radiation therapy using hyperpolarized [1-(13)C]pyruvate in MDA-MB-231 Xenografts. PLoS One. 8, e56551 (2013)
Brindle, K.: New approaches for imaging tumour responses to treatment. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 8, 1–14 (2008)
von Morze, C., Larson, P., Hu, S., Yoshihara, H.: Investigating tumor perfusion and metabolism using multiple hyperpolarized 13 C compounds: HP001, pyruvate and urea. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 30(3), 305–311 (2012)
Rider, O.J., Tyler, D.J.: Clinical implications of cardiac hyperpolarized magnetic resonance imaging. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 15, 93 (2013)
Park, J.M., Josan, S., Mayer, D., Hurd, R.E., Chung, Y., Bendahan, D., Spielman, D.M., Jue, T.: Hyperpolarized 13C NMR observation of lactate kinetics in skeletal muscle. J. Exp. Biol. 218, 3308–3318 (2015)
Bastiaansen, J.A., Yoshihara, H.A., Takado, Y., Gruetter, R., Comment, A.: Hyperpolarized 13C lactate as a substrate for in vivo metabolic studies in skeletal muscle. Metabolomics. 10, 986–994 (2014)
Bastiaansen, J.A.M., Cheng, T., Mishkovsky, M., Duarte, J.M.N., Comment, A., Gruetter, R.: In vivo enzymatic activity of acetylCoA synthetase in skeletal muscle revealed by (13)C turnover from hyperpolarized [1-(13)C]acetate to [1-(13)C]acetylcarnitine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1830, 4171–4178 (2013)
Chen, A.P., Albers, M.J., Cunningham, C.H., Kohler, S.J., Yen, Y.-F., Hurd, R.E., Tropp, J., Bok, R., Pauly, J.M., Nelson, S.J., Kurhanewicz, J., Vigneron, D.B.: Hyperpolarized C-13 spectroscopic imaging of the TRAMP mouse at 3T-initial experience. Magn. Reson. Med. 58, 1099–1106 (2007)
Sriram, R., Van Criekinge, M., Santos, J.D., Vigneron, D.B., Bok, R.A., Peehl, D.M., Keshari, K.R., Kurhanewicz, J.: Hyperpolarized lactate production correlates with gleason grade in patient-derived tissues of prostate cancer. ISMRM, Toronto (2015)
Granlund, K.L., Vargas, H.A., Lyashchenko, S.K., DeNoble, P.J., Laudone, V.A., Eastham, J., Sosa, R.A., Kennedy, M.A., Nicholson, D., Guo, Y.W., Chen, A.P., Tropp, J., Hricak, H., Keshari, K.R.: Metabolic dynamics of hyperpolarized [1-13C] pyruvate in human prostate cancer. Proceedings of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Singapore (2016)
Aggarwal, R., Vigneron, D.B., Kurhanewicz, J.: Hyperpolarized 1-[13C]-pyruvate magnetic resonance imaging detects an early metabolic response to androgen ablation therapy in prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 72, 1028–1029 (2017)
Zhu, Z., Gordon, J.W., Chen, H.-Y., Milshteyn, E., Mammoli, D., Carvajal, L., Shin, P.J., Aggarwal, R., Bok, R., Kurhanewicz, J., Munster, P., Vigneron, D.B.: Human hyperpolarized 13C MR of liver and bone metastases using both EPSI and EPI acquisitions. Proceedings of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Paris (2018)
von Morze, C., Tropp, J., Chen, A.P., Marco-Rius, I., Van Criekinge, M., Skloss, T.W., Mammoli, D., Kurhanewicz, J., Vigneron, D.B., Ohliger, M.A., Merritt, M.E.: Sensitivity enhancement for detection of hyperpolarized 13 C MRI probes with 1 H spin coupling introduced by enzymatic transformation in vivo. Magn. Reson. Med. 80, 36–41 (2017)
Salamanca-Cardona, L., Keshari, K.R.: 13C-labeled biochemical probes for the study of cancer metabolism with dynamic nuclear polarization-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer Metab. 3, 9 (2015)
Hurd, R.E., Spielman, D., Josan, S., Yen, Y.-F., Pfefferbaum, A., Mayer, D.: Exchange-linked dissolution agents in dissolution-DNP (13) C metabolic imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 70, 936–942 (2012)
Kettunen, M.I., Hu, D.-E., Witney, T.H., Mclaughlin, R., Gallagher, F.A., Bohndiek, S.E., Day, S.E., Brindle, K.M.: Magnetization transfer measurements of exchange between hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate and [1-13C]lactate in a murine lymphoma. Magn. Reson. Med. 63, 872–880 (2010)
Kettunen, M.I., Kennedy, B.W.C., Hu, D.-E., Brindle, K.M.: Spin echo measurements of the extravasation and tumor cell uptake of hyperpolarized [1-(13) C]lactate and [1-(13) C]pyruvate. Magn. Reson. Med. 70(5), 1200–1209 (2013)
Serrao, E.M., Kettunen, M.I., Rodrigues, T.B., Lewis, D.Y., Gallagher, F.A., Hu, D.E., Brindle, K.M.: Analysis of 13C and 14C labeling in pyruvate and lactate in tumor and blood of lymphoma-bearing mice injected with 13C- and 14C-labeled pyruvate. NMR Biomed. 50, e3901 (2018)
Hill, D.K., Jamin, Y., Orton, M.R., Tardif, N., Parkes, H.G., Robinson, S.P., Leach, M.O., Chung, Y.-L., Eykyn, T.R.: 1H NMR and hyperpolarized 13C NMR assays of pyruvate-lactate: a comparative study. NMR Biomed. 26, 1321–1325 (2013)
Qin, H., Carroll, V.N., Sriram, R., Villanueva-Meyer, J.E., von Morze, C., Wang, Z.J., Mutch, C.A., Keshari, K.R., Flavell, R.R., Kurhanewicz, J., Wilson, D.M.: Imaging glutathione depletion in the rat brain using ascorbate-derived hyperpolarized MR and PET probes. Sci. Rep. 8, 7928 (2018)
Costello, L.C., Franklin, R.B.: The clinical relevance of the metabolism of prostate cancer; zinc and tumor suppression: connecting the dots. Mol. Cancer. 5, 17 (2006)
Bohndiek, S.E., Kettunen, M.I., Hu, D.-E., Kennedy, B.W.C., Boren, J., Gallagher, F.A., Brindle, K.M.: Hyperpolarized [1-13C]-ascorbic and dehydroascorbic acid: vitamin C as a probe for imaging redox status in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 11795–11801 (2011)
Sriram, R., Van Criekinge, M., Hansen, A., Wang, Z.J., Vigneron, D.B., Wilson, D.M., Keshari, K.R., Kurhanewicz, J.: Real-time measurement of hyperpolarized lactate production and efflux as a biomarker of tumor aggressiveness in an MR compatible 3D cell culture bioreactor. NMR Biomed. 28, 1141–1149 (2015)
Breukels, V., Jansen, K.C.F.J., van Heijster, F.H.A., Capozzi, A., van Bentum, P.J.M., Schalken, J.A., Comment, A., Scheenen, T.W.J.: Direct dynamic measurement of intracellular and extracellular lactate in small-volume cell suspensions with 13C hyperpolarised NMR. NMR Biomed. 28, 1040–1048 (2015)
Sriram, R., Sun, J., Villanueva-Meyer, J., Mutch, C., De Los, S.J., Peters, J., Korenchan, D.E., Neumann, K., Van Criekinge, M., Kurhanewicz, J., Rosenberg, O., Wilson, D., Ohliger, M.A.: Detection of bacteria-specific metabolism using hyperpolarized [2-13C]pyruvate. ACS Infect Dis. 4(5), 797–805 (2018)
Further Reading
Bottomley, P.A., Griffiths, J.R.: Handbook of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo: MRS theory, practice and applications. Wiley, Chichester (2016)
Acknowledgements
Grants/People: We would like to acknowledge the funding sources P41 EB013598 (NIH) and PC160630 (DoD) and the members of the Hyperpolarized MRI Technology Resource Center and the Pre-Clinical MR Imaging and Spectroscopy Core.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Problems
Problems
-
1.
Hyperpolarized [1-13C] dehydroascorbate (DHA) is a probe used to interrogate the redox status of the cell. In in vivo systems, the cyclic regeneration of the reactive oxygen species and its reductants serve to continuously reduce and oxidize ascorbic acid as shown below.
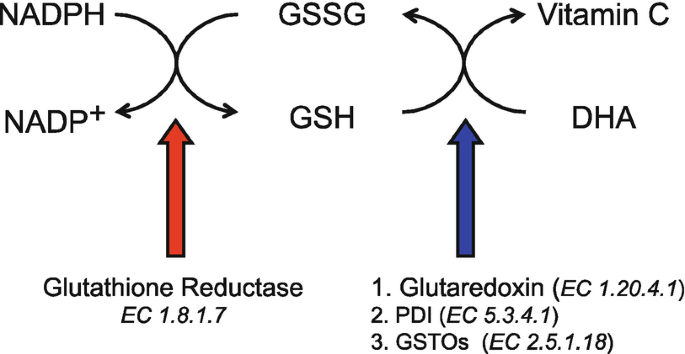
What are all the components that will be required to estimate the apparent zero-order reaction rate of hyperpolarized DHA in a simple enzyme solution?
-
2.
In order to test the hypothesis that increased cellular production of lactate and its efflux occur in renal cell cancers is associated with cancer aggressiveness, we designed a cell culture bioreactor study using UOK262 cells, which were established from a highly aggressive metastatic RCC. The figure below shows the bioreactor set-up containing UOK262 cells encapsulated in alginate beads with continuous flow of media and continuous infusion of hyperpolarized agent over a 90 s time period.
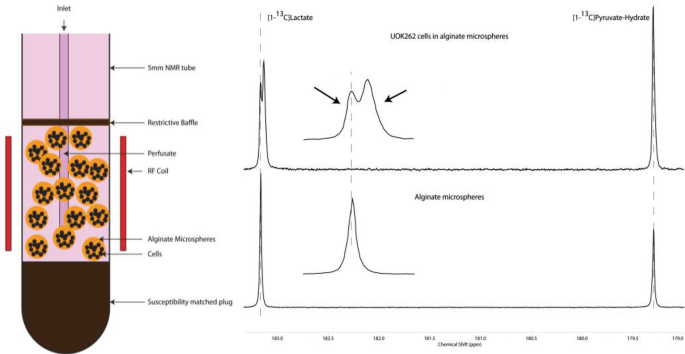
The figure on the left is a schematic of the cells encapsulated in alginate microspheres being perfused in a bioreactor. The figure to the right represents hyperpolarized 13C spectra under two different conditions from the bioreactor. The bottom 13C spectra in the figure (below) is of alginate microspheres devoid of cells, infused with co-hyperpolarized [1-13C]lactate and [1-13C]pyruvate. Only one peak was observed for the [1-13C]lactate signal (bottom spectra). While two peaks were observed in the alginate microspheres with UOK262 cells when infused with HP [1-13C]pyruvate only (top spectra). The top inset (2.5× magnification, with black arrows) clearly shows that there are two distinct peaks for lactate (although the chemical shift difference is very small—0.031 ± 0.0005 ppm), where the chemical shift of the downfield peak coincides with that of the signal of lactate in empty alginate microspheres. A series of studies were performed to try to identify the origin of these two lactate resonances.
-
(a)
Increasing the cell density in the bioreactor resulted in an increase in the upfield lactate peak.
-
(b)
Stopping the flow of media in the bioreactor resulted in an increase in the downfield resonance.
-
(c)
The downfield lactate resonance decreased when the cells were pretreated with DIDS, a small molecule blocker of MCT4 transporter.
Based on the above hyperpolarized 13C studies, what could be the explanation for the two lactate peaks observed when hyperpolarized [1-13C]lactate is metabolically produced by UOK262 cells after injection of hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate? Please make sure you explain all of the experimental findings.
-
(a)
-
3.
What are some biological challenges with live animal imaging studies involving hyperpolarized MRI and interpreting the subsequent metabolites?
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sriram, R., Baligand, C., Kurhanewicz, J. (2021). Using Hyperpolarized NMR to Understand Biochemistry from Cells to Humans. In: Jue, T., Mayer, D. (eds) Dynamic Hyperpolarized Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Handbook of Modern Biophysics. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-55043-1_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-55043-1_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-55041-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-55043-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)



