Abstract
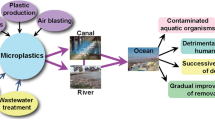
Microplastics (MPs) are unregulated and emerging contaminants, which are continuously released due to human activities in the environment through several pathways. The presence of MPs poses threats to the environment, organisms, and human health. The discharge of treated effluent from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) is a major source of MP input, especially in the form of microfibers, into the aquatic environment, whereas the application of sludge and compost is a crucial pathway transferring MPs to terrestrial environment. Meanwhile, MPs are produced from industrial processes and the use of plastic consumer goods and personal care products. MPs become more hazardous when they adsorb persistent organic pollutants and heavy metals or attach with pathogenic microorganisms from wastewater and sludge. However, there is little comprehensive information available about the collaborative role of wastewater and sludge in MP contamination. Studies about remediation strategies and their removal mechanisms of MPs in WWTPs are limited. Therefore, it is important to develop cost-effective detection methods of MPs for routine monitoring in wastewater and sludge samples and understanding of fate and inhibitory effects of MPs in wastewater and sludge treatment processes, before developing the mitigation measures of MP contamination. This chapter summarizes the sources and pathways of MPs, discusses the impacts of MPs on environment and human health, and reviews the current practices on detection, quantification, and qualification of MPs. In addition, this chapter provides insights into the source control of MPs through polices and education.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu A, Pedrotti ML (2019) Microplastics in the oceans: The solutions lie on land. Field Actions Sci Rep 19:62–67. Special Issue. http://journals.openedition.org/factsreports/5290. Accessed 17 July 2020
Almroth BMC, Åström L, Roslund S et al (2018) Quantifying shedding of synthetic fibers from textiles: A source of microplastics released into the environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(2):1191–1199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0528-7
Alvim CB, Mendoza-Roca JA, Bes-Piá A (2020) Wastewater treatment plant as microplastics release source – quantification and identification techniques. J Environ Manag 255:109739. https://doi.org/10.1016/2019.109739
Anderson JC, Park BJ, Palace VP (2016) Microplastics in aquatic environments: Implications for Canadian ecosystems. Environ Pollut 218:269–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/2016.06.074
Bandow N, Will V, Wachtendorf V et al (2017) Contaminant release from aged microplastic. Environ Chem 14(6):394–405. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN17064
Barnes DK, Galgani F, Thompson RC et al (2009) Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 364(1526):1985–1998. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0205
Boucher J, Friot D (2017) Primary microplastics in the oceans: a global evaluation of sources. IUCN, Gland. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.CH.2017.01.en
Brennecke D, Duarte B, Paiva F et al (2016) Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 178:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2015.12.003
Browne MA, Dissanayake A, Galloway TS et al (2008) Ingested microscopic plastic translocates to the circulatory system of the mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.). Environ Sci Technol 42(13):5026–5031. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800249a
Browne MA, Crump P, Niven SJ et al (2011) Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines worldwide: Sources and sinks. Environ Sci Technol 45(21):9175–9179. https://doi.org/10.1021/es201811s
Carr SA (2017) Sources and dispersive modes of micro-fibers in the environment. Integr Environ Assess Manag 13(3):466–469. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.1916
Carr SA, Liu J, Tesoro AG (2016) Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 91:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.01.002
Chang M (2015) Reducing microplastics from facial exfoliating cleansers in wastewater through treatment versus consumer product decisions. Mar Pollut Bull 101(1):330–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.10.074
Cho Y, Shim WJ, Jang M et al (2019) Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in market bivalves from South Korea. Environ Pollut 245:1107–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.091
Conley K, Clum A, Deepe J et al (2019) Wastewater treatment plants as a source of microplastics to an urban estuary: Removal efficiencies and loading per capita over one year. Water Res X 3(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wroa.2019.100030
Corradini F, Meza P, Eguiluz R et al (2019) Evidence of microplastic accumulation in agricultural soils from sewage sludge disposal. Sci Total Environ 671:411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.368
Dris R, Gasperi J, Rocher V et al (2015) Microplastic contamination in an urban area: A case study in Greater Paris. Environ Chem 12(5):592–599. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN14167
Dris R, Gasperi J, Rocher V et al (2018) Synthetic and non-synthetic anthropogenic fibers in a river under the impact of Paris Megacity: sampling methodological aspects and flux estimations. Sci Total Environ 618:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.009
Fred-Ahmadu OH, Bhagwat G, Oluyoye I et al (2020) Interaction of chemical contaminants with microplastics: principles and perspectives. Sci Total Environ 706:135978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135978
Gallo F, Fossi C, Weber R et al (2018) Marine litter plastics and microplastics and their toxic chemicals components: The need for urgent preventive measures. Environ Sci Eur 30:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-018-0139-z
Geyer R, Jambeck JR, Law KL (2017) Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci Adv 3(7):e1700782. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700782
Gies EA, LeNoble JL, Noël M et al (2018) Retention of microplastics in a major secondary wastewater treatment plant in Vancouver, Canada. Mar Pollut Bull 133:553–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.06.006
Gündoğdu S, Çevik C, Güzel E et al (2018) Microplastics in municipal wastewater treatment plants in Turkey: A comparison of the influent and secondary effluent concentrations. Environ Monit Assess 190:626–632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7010-y
Guzzetti E, Sureda A, Tejada S et al (2018) Microplastic in marine organism: Environmental and toxicological effects. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 64:164–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2018.10.009
Habib RZ, Thiemann T, Al Kendi R (2020) Microplastics and wastewater treatment plants – a review. J Water Resour Protect 12(1):1–35. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2020.121001
Hartley BL, Pahl S, Holland M et al (2018) Turning the tide on trash: empowering European educators and school students to tackle marine litter. Mar Policy 96:227–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2018.02.002
Hartline NL, Bruce NJ, Karba SN et al (2016) Microfiber masses recovered from conventional machine washing of new or aged garments. Environ Sci Technol 50(21):11532–11538. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b03045
He D, LuoY, Lu S et al (2018) Microplastics in soils: analytical methods, pollution characteristics and ecological risks. Trends Anal Chem 109:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.10.006
He P, Chen L, Shao L et al (2019) Municipal solid waste (MSW) landfill: a source of microplastics?-Evidence of microplastics in landfill leachate. Water Res 159:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.04.060
Hernandez E, Nowack B, Mitrano DM (2017) Polyester textiles as a source of microplastics from households: A mechanistic study to understand microfiber release during washing. Environ Sci Technol 51(12):7036–7046. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b01750
Hidalgo-Ruz V, Thiel M (2013) Distribution and abundance of small plastic debris on beaches in the SE Pacific (Chile): a study supported by a citizen science project. Mar Environ Res 87:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2013.02.015
Hidalgo-Ruz V, Gutow L, Thompson RC et al (2012) Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3060–3075. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2031505
Hurley RR, Lusher AL, Olsen M et al (2018) Validation of a method for extracting microplastics from complex, organic-rich, environmental matrices. Environ Sci Technol 52(13):7409–7417. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01517
Jambeck JR, Geyer R, Wilcox C et al (2015) Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 347(6223):768–771. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260352
Karkman A, Do TT, Walsh F et al (2018) Antibiotic-resistance genes in waste water. Trends Microbiol 26(3):220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2017.09.005
Koelmans AA, Besseling E, Foekema EM et al (2014) Leaching of plastic additives to marine organisms. Environ Pollut 187:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.12.013
Kwon JH, Chang S, Hong SH et al (2017) Microplastics as a vector of hydrophobic contaminants: importance of hydrophobic additives. Integr Environ Assess Manag 13:494–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.1906
Lares M, Ncibi MC, Sillanpaa M et al (2018) Occurrence, identification and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology. Water Res 133:236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.049
Lei L, Wu S, Lu S et al (2018) Microplastic particles cause intestinal damage and other adverse effects in zebrafish Danio rerio and nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci Total Environ 619:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.103
Leslie HA (2014) Review of microplastics in cosmetics. IVM Institute for Environmental Studies, Netherlands, no R14/29
Leslie HA, Brandsma SH, Velzen V et al (2017) Microplastics en route: field measurements in the Dutch river delta and Amsterdam canals, wastewater treatment plants, North Sea sediments and biota. Environ Int 101:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.01.018
Li J, Liu H, Chen P (2018) Microplastics in freshwater systems: a review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res 137:362–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.056
Liu X, Yuan W, Di M et al (2019) Transfer and fate of microplastics during the conventional activated sludge process in one wastewater treatment plant of China. Chem Eng J 362:176–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.033
Long Z, Pan Z, Wang W et al (2019) Microplastic abundance, characteristics, and removal in wastewater treatment plants in a coastal city of China. Water Res 155:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.02.028
Lwanga EH, Gertsen H, Gooren H et al (2017) Incorporation of microplastics from litter into burrows of Lumbricus terrestris. Environ Pollut 220:523–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.096
Ma Y, Huang A, Cao S et al (2016) Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on toxicity, bioaccumulation, and environmental fate of phenanthrene in fresh water. Environ Pollut 219:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.061
Maes T, Jessop R, Wellner N et al (2017) A rapid-screening approach to detect and quantify microplastics based on fluorescent tagging with Nile Red. Sci Rep 7:44501. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44501
Magni S, Binelli A, Pittura L et al (2019) The fate of microplastics in an Italian wastewater treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 652:602–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.269
Magnusson K, Norén F (2014) Screening of microplastic particles in and down-stream a wastewater treatment plant. Swedish Environmental Research Institute. Available at: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:773505/FULLTEXT01.pdf. (Accessed 25 June 2020)
Mahon AM, O’Connell B, Healy MG et al (2017) Microplastics in sewage sludge: Effects of treatment. Environ Sci Technol 51(2):810–818. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b04048
Massos A, Turner A (2017) Cadmium, lead and bromine in beached microplastics. Environ Pollut 227:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.034
McCormick A, Hoellein TJ, Mason SA et al (2014) Microplastic is an abundant and distinct microbial habitat in an urban river. Environ Sci Technol 48(20):11863–11871. https://doi.org/10.1021/es503610r
Mintenig SM, Int-Veen I, Löder MG et al (2017) Identification of microplastic in effluents of waste water treatment plants using focal plane array-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging. Water Res 108:365–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.11.015
Murphy F, Ewins C, Carbonnier F et al (2016) Wastewater treatment works (WwTW) as a source of microplastics in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol 50(11):5800–5808. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05416
Napper IE, Thompson RC (2016) Release of synthetic microplastic plastic fibres from domestic washing machines: Effects of fabric type and washing conditions. Mar Pollut Bull 112(1–2):39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.09.025
Napper IE, Bakir A, Rowland SJ et al (2015) Characterisation, quantity and sorptive properties of microplastics extracted from cosmetics. Mar Pollut Bull 99(1–2):178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.029
Nizzetto L, Futter M, Langaas S (2016) Are agricultural soils dumps for microplastics of urban origin? Environ Sci Technol 50:10777–10779. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b04140
Oberbeckmann S, Kreikemeyer B, Labrenz M (2018) Environmental factors support the formation of specific bacterial assemblages on microplastics. Front Microbiol 8:2709. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02709
Phuong NN, Poirier L, Pham QT et al (2018) Factors influencing the microplastic contamination of bivalves from the French Atlantic coast: location, season and/or mode of life? Mar Pollut Bull 129(2):664–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.10.054
Pico Y, Barceló D (2019) Analysis and prevention of microplastics pollution in water: Current perspectives and future directions. ACS Omega 4(4):6709–6719. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b00222
Plastics Europe (2019) Plastics – the facts. Plastic Europe. https://www.plasticseurope.org/application/files/9715/7129/9584/FINAL_web_version_Plastics_the_facts2019_14102019.pdf. Accessed 26 May 2020
Prata JC (2018) Microplastics in wastewater: state of the knowledge on sources, fate and solutions. Mar Pollut Bull 129(1):262–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.02.046
Prata JC, da Costa JP, Girão AV et al (2019) Identifying a quick and efficient method of removing organic matter without damaging microplastic samples. Sci Total Environ 686:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.456
Renner G, Schmidt TC, Schram J (2018) Analytical methodologies for monitoring micro (nano) plastics: which are fit for purpose? Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 1:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coesh.2017.11.001
Rios LM, Jones PR, Moore C et al (2010) Quantitation of persistent organic pollutants adsorbed on plastic debris from the Northern Pacific Gyre’s “eastern garbage patch”. Environ Monit Assess 12(12):2226–2236. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0em00239a
Rochman CM (2018) Microplastics research – from sink to source. Science 360(6384):28–29. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar7734
Rochman CM, Tahir A, Williams SL et al (2015) Anthropogenic debris in seafood: Plastic debris and fibers from textiles in fish and bivalves sold for human consumption. Sci Rep 5:14340. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14340
Rummel CD, Jahnke A, Gorokhova E et al (2017) Impacts of biofilm formation on the fate and potential effects of microplastic in the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol Lett 4(7):258–267. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.7b00164
Simon M, van Alst N, Vollertsen J (2018) Quantification of microplastic mass and removal rates at wastewater treatment plants applying Focal Plane Array (FPA)-based Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) imaging. Water Res 142:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.05.019
Smith M, Love DC, Rochman CM (2018) Microplastics in seafood and the implications for human health. Curr Environ Health Rep 5(3):375–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-018-0206-z
Sujathan S, Kniggendorf AK, Kumar A et al (2017) Heat and bleach: a cost-efficient method for extracting microplastics from return activated sludge. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 73(4):641–648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0415-8
Sun J, Dai X, Wang Q et al (2019) Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: detection, occurrence and removal. Water Res 152:21–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.050
Tagg AS, Sapp M, Harrison JP et al (2015) Identification and quantification of microplastics in wastewater using focal plane array-based reflectance micro-FT-IR imaging. Anal Chem 87(12):6032–6040. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00495
Talvitie J, Mikola A, Koistinen A et al (2017a) Solutions to microplastic pollution-removal of microplastics from wastewater effluent with advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res 123:401–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.005
Talvitie J, Mikola A, Setälä O et al (2017b) How well is microlitter purified from wastewater?-A detailed study on the stepwise removal of microlitter in a tertiary level wastewater treatment plant. Water Res 109:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.11.046
Tang G, Liu M, Zhou Q et al (2018) Microplastics and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Xiamen coastal areas: implications for anthropogenic impacts. Sci Total Environ 634:811–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.336
Teuten EL, Rowland SJ, Galloway TS et al (2007) Potential for plastics to transport hydrophobic contaminants. Environ Sci Technol 41(22):7759–7764. https://doi.org/10.1021/es071737s
Thompson RC (2015) Microplastics in the marine environment: sources, consequences and solutions. In: Bergmann M, Gutow L, Klages M (eds) Marine anthropogenic litter. Springer, Cham, pp 185–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16510-3_7
Thompson RC, Moore CJ, Vom Saal FS et al (2009) Plastics, the environment and human health: current consensus and future trends. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 364(1526):2153–2166. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0053
Van Cauwenberghe L, Janssen CR (2014) Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ Pollut 193:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.06.010
United States Environmental Protection Agency (US-EPA) (2010) Bisphenol a action plan (CASRN 80-05-7). Available at: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-09/documents/bpa_action_plan.pdf. (Accessed on 13 June 2020)
Wardrop P, Shimeta J, Nugegoda D et al (2016) Chemical pollutants sorbed to ingested microbeads from personal care products accumulate in fish. Environ Sci Technol 50(7):4037–4044. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b06280
Wei W, Huang QS, Sun J et al (2019) Polyvinyl chloride microplastics affect methane production from the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge through leaching toxic bisphenol-A. Environ Sci Technol 53(5):2509–2517. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b07069
Widmer WM, Reis RA (2010) An experimental evaluation of the effectiveness of beach ashtrays in preventing marine contamination. Braz Arch Biol Technol 53(5):1205–1216. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132010000500026
World Health Organization (WHO) (2019) Microplastics in drinking-water. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/326499/9789241516198-eng.pdf?ua=1. Accessed 13 Jun 2020
Wright SL, Kelly FJ (2017) Plastic and human health: A micro issue? Environ Sci Technol 51(12):6634–6647. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00423
Xanthos D, Walker TR (2017) International policies to reduce plastic marine pollution from single-use plastics (plastic bags and microbeads): a review. Mar Pollut Bull 118(1–2):17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.02.048
Xu X, Jian Y, Xue Y et al (2019) Microplastics in the wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs): occurrence and removal. Chemosphere 235:1089–1096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.197
Ye BS, Leung AOW, Wong MH (2017) The association of environmental toxicants and autism spectrum disorders in children. Environ Pollut 227:234–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.039
Yi M, Zhou S, Zhang L et al (2020) The effects of three different microplastics on enzyme activities and microbial communities in soil. Water Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1327
Yu F, Yang C, Zhu Z (2019) Adsorption behavior of organic pollutants and metals on micro/nanoplastics in the aquatic environment. Sci Total Environ 694(133643):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133643
Zettler ER, Mincer TJ, Amaral-Zettler LA (2013) Life in the “plastisphere”: Microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ Sci Technol 47(13):7137–7146. https://doi.org/10.1021/es401288x
Zhang F, Man YB, Mo WY et al (2019) Direct and indirect effects of microplastics on bivalves, with a focus on edible species: a mini-review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1700752
Ziajahromi S, Neale PA, Leusch FD (2016) Wastewater treatment plant effluent as a source of microplastics: review of the fate, chemical interactions and potential risks to aquatic organisms. Water Sci Technol 74(10):2253–2269. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.414
Ziajahromi S, Neale PA, Rintoul L et al (2017) Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics: development of a new approach to sample wastewater-based microplastics. Water Res 112:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.042
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong SAR, China (No. 18202116), the Departmental Collaborative Fund (No. 04488), Internal Research Grant (No. RG38/2019-2020R), and Dean’s Research Fund (Nos. IRS13/ROP10/RMP5) of The Education University of Hong Kong, and the State Key Laboratory of Marine Pollution (SKLMP) Seed Collaborative Research Fund (No. SCRF/0026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Section Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Khan, M.T., Cheng, Y.L., Hafeez, S., Tsang, Y.F., Yang, J., Nawab, A. (2022). Microplastics in Wastewater. In: Rocha-Santos, T., Costa, M.F., Mouneyrac, C. (eds) Handbook of Microplastics in the Environment. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39041-9_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-39041-9_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-39040-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-39041-9
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics