Abstract
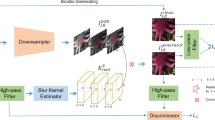
Recent research on single image super-resolution (SISR) has made some progress. However, most previous SISR methods simply assume that a low-resolution (LR) image is bicubicly downsampled from a high-resolution (HR) image. when the LR images don’t follow this assumption, these previous methods will generate poor HR images that still retain the blur and noise information. To solve this problem, we propose the super-resolution network for general static degradation model (SR-GSD). Specifically, we propose degradation factors proposal Network (DFPN) which can automatically identify blur kernel and noise level, and furthermore, we utilize predicted degradation factors and the LR images to reconstruct the HR images in a high-resolution reconstruction network (HRN). Moreover, to simplify the training process, we unify the two-stages steps into a neural network and jointly optimize it through a multi-task loss function. Extensive experiments show that our SR-GSD can achieve satisfactory results on the general static degradation model.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agustsson, E., Timofte, R.: Ntire 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: dataset and study, pp. 1122–1131, July 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2017.150
Bevilacqua, M., Roumy, A., Guillemot, C., Alberi-Morel, M.L.: Low-complexity single image super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbor embedding, September 2012. https://doi.org/10.5244/C.26.135
Chakrabarti, A.: A neural approach to blind motion deblurring. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9907, pp. 221–235. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46487-9_14
Chetouani, A., Beghdadi, A., Deriche, M.: A new reference-free image quality index for blur estimation in the frequency domain. In: 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), pp. 155–159. IEEE (2009)
Dai, T., Cai, J., Zhang, Y., Xia, S.T., Zhang, L.: Second-order attention network for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11065–11074 (2019)
Dong, C., Loy, C.C., He, K., Tang, X.: Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. CoRR abs/1501.00092 (2015)
Freeman, W.T., Pasztor, E.C., Carmichael, O.T.: Learning low-level vision. Int. J. Comput. Vision 40(1), 25–47 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026501619075
He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollár, P., Girshick, R.B.: Mask R-CNN. CoRR abs/1703.06870 (2017). http://arxiv.org/abs/1703.06870
Hu, X., Mu, H., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., Tan, T., Sun, J.: Meta-SR: a magnification-arbitrary network for super-resolution. CoRR abs/1903.00875 (2019). http://arxiv.org/abs/1903.00875
Huang, J.B., Singh, A., Ahuja, N.: Single image super-resolution from transformed self-exemplars (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299156
Kim, J., Lee, J.K., Lee, K.M.: Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. CoRR abs/1511.04587 (2015)
Kim, J., Lee, J.K., Lee, K.M.: Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution. CoRR abs/1511.04491 (2015)
Lim, B., Son, S., Kim, H., Nah, S., Mu Lee, K.: Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution, July 2017
Martin, D., Fowlkes, C., Tal, D., Malik, J.: A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. In: Proceedings Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2001, vol. 2, pp. 416–423, July 2001. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2001.937655
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R.B., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. CoRR abs/1506.01497 (2015)
Shi, W., et al.: Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network, June 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.207
Shi, W., et al.: Cardiac image super-resolution with global correspondence using multi-atlas PatchMatch. In: Mori, K., Sakuma, I., Sato, Y., Barillot, C., Navab, N. (eds.) MICCAI 2013. LNCS, vol. 8151, pp. 9–16. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40760-4_2
Sun, J., Cao, W., Xu, Z., Ponce, J.: Learning a convolutional neural network for non-uniform motion blur removal, March 2015
Tai, Y., Yang, J., Liu, X.: Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network, July 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.298
Tai, Y., Yang, J., Liu, X., Xu, C.: MemNet: a persistent memory network for image restoration. CoRR abs/1708.02209 (2017)
Yıldırım, D., Gungor, O.: A novel image fusion method using IKONOS satellite images. J. Geodesy Geoinform. 1, 27–34 (2012). https://doi.org/10.9733/jgg.170512.1
Zeyde, R., Elad, M., Protter, M.: On single image scale-up using sparse-representations. In: Boissonnat, J.-D., et al. (eds.) Curves and Surfaces 2010. LNCS, vol. 6920, pp. 711–730. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27413-8_47
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Zhang, L.: Learning a single convolutional super-resolution network for multiple degradations. CoRR abs/1712.06116 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Li, K., Li, K., Wang, L., Zhong, B., Fu, Y.: Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks, July 2018
Zhang, Y., Tian, Y., Kong, Y., Zhong, B., Fu, Y.: Residual dense network for image super-resolution. CoRR abs/1802.08797 (2018)
Zou, W.W.W., Yuen, P.C.: Very low resolution face recognition problem. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(1), 327–340 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2011.2162423
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61702044) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2019XD-A20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, Y., Zhou, W., Xing, Y. (2019). Super-Resolution Network for General Static Degradation Model. In: Gedeon, T., Wong, K., Lee, M. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11954. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36711-4_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36711-4_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36710-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36711-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)