Abstract
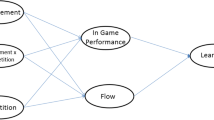
The goal of this paper is to study whether Game-Based Learning (GBL) can be used to improve academic performance and engagement. We present an experiment based on the design and deployment of a Monopoly-like board game, in the context of a primary school Geography curriculum, and look for improvements in students’ academic performance and will to learn, interest, and positive motivation. The paper examines if this game had a statistically significant influence on students’ performance, as well as how performance and interest are related and how performance differs between boys and girls. Results from the quantitative analysis of the data were positive to all the research queries: students’ performance improved substantially after the game, while, the strong correlation between the two variables that resulted made evident the relation between the students’ interest and performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schun, D.H.: Motivation—Education.com (2018). https://www.education.com/reference/article/motivation/. Accessed 16 May 2018
Ke, F., Abras, T.: Games for engaged learning of middle school children with special learning needs. Br. J. Edu. Technol. 44(2), 225–242 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2012.01326.x
Kerkhoven, A.H., Russo, P., Land-Zandstra, A.M., Saxena, A., Rodenburg, F.J.: Gender stereotypes in science education resources: a visual content analysis. PLoS One 11(11), 1–13 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0165037
Deater‐Deckard, K., Chang, M., Evans, M.E.: Engagement States and Learning from Educational Games. New Directions for Child and Adolescent Development, (139), 21–30 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/cad.20028
Pivec, M.: Affective and Emotional Aspects of Human-Computer Interaction: Game-Based and Innovative Learning Approaches Volume 1 Future of Learning. IOS Press, Amsterdam (2006)
Karpouzis, K., Yannakakis, G.N. (eds.): Emotion in Games. SC, vol. 4. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-41316-7
Yannakakis, G.N., Isbister, K., Paiva, A., Karpouzis, K.: Guest editorial: emotion in games. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 5(1), 1–2 (2014)
Plass, J.L., Homer, B.D., Kinzer, C.K.: Foundations of game-based learning. Educ. Psychol. 50(4), 258–283 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2015.1122533
Prensky, M.: Digital natives, digital immigrants. Horizon 9(5), 1–6 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1108/10748120110424816
Reinfried, S., Hertig, P.: Geographical Education: How Human- Environment-Society Processes Work, pp. 1–48 (2011)
Ryan, R.M., Deci, E.L.: Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. Am. Psychol. (2000). https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.55.1.68
Zernike, K.: Girls a Distant 2nd in Geography Gap Among U.S. Pupils (2000). https://www.nytimes.com. Accessed 29 June 2018
Yannakakis, G.N., et al.: Siren: towards adaptive serious games for teaching conflict resolution. In: 2010 European Conference on Game-based learning (ECGBL), pp. 412–418 (2010)
Karpouzis, K., Yannakakis, G.N., Shaker, N., Asteriadis, S.: The platformer experience dataset. In: 2015 International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII), China (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/acii.2015.7344647
Caridakis, G., Karpouzis, K., Wallace, M., Kessous, L., Amir, N.: Multimodal user’s affective state analysis in naturalistic interaction. J. Multimodal User Interfaces 3(1), 49–66 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work has been funded by the iRead project (https://iread-project.eu/) which has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation program under grant agreement No 731724.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vargianniti, I., Karpouzis, K. (2019). Effects of Game-Based Learning on Academic Performance and Student Interest. In: Liapis, A., Yannakakis, G., Gentile, M., Ninaus, M. (eds) Games and Learning Alliance. GALA 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11899. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34350-7_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-34350-7_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-34349-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-34350-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)