Abstract
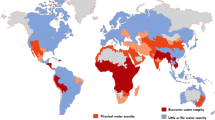
Oman is a country under severe water stress. Currently Oman produces around 1 Mm3/day of desalinated seawater for urban purposes to expand supply. This policy was partially imposed by the irregularity of rain and the concentration of the population on the coastal areas. Most of the conventional water resources are in the form of groundwater and are used in the agricultural sector. Abstractions from wells are subject to licenses. But licenses so far do not carry any limits. The result is a race for water with overabstractions in the coastal areas causing seawater intrusion and damage to the aquifers. The government is planning to introduce progressively water quotas to farmers and monitoring through smart meters and online system. Large volumes of tertiary treated wastewater are produced daily and are only partially reused for landscaping. There is a mismatch between the willingness of farmers to pay for treated wastewater and the price set by the public authority leading to a limited demand. The actual context of free and unlimited access to groundwater does not encourage to shift the demand toward high-quality treated wastewater. Plans are being considered for recharging some of the aquifers with the treated wastewater. Irrigation efficiency improvements have been observed mainly for vegetable producers where the adoption of irrigation technology resulted in higher revenues and lower labor costs. Urban water prices are at 1/3 of their costs discouraging water saving and adoption of water saving/recycling devices at homes or industries. Urban water security is being addressed by aquifer storage and recovery techniques using excess winter desalinated water.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Barwani, H. H., & Purnama, A. (2011). A computational model study of brine discharges from seawater desalination plants at Barka. In R. Y. Ning (Ed.), Expanding issues in desalination. Rijeka: InTech Open Access Publisher.
Al-Maktoumi, A., El-Rawy, M., & Zekri, S. (2016). Management options for a multipurpose coastal aquifer in Oman. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(14). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2661-x.
Baerenklau, K., Schwabe, K., & Dinar, A. (2014). Allocation-based water pricing promotes conservation while keeping user costs low. ARE Update, 17(6), 1–4. University of California. Giannini Foundation of Agricultural Economics.
Bashitialshaaer, R. (2016, January/February). Desalination report for Omani public Authority for Electricity and Water (PAEW), six weeks in Oman. International Desalination Association IDA-NEWSLETTER, 25(1), 7–8.
Bleninger, T., & Jirka, G. H. (2010). Final report on environmental planning, prediction and Management of Brine Discharges from desalination plants, Middle East desalination research center Muscat, Sultanate of Oman, MEDRC series of R&D reports, MEDRC project: 07-AS-003.
El-Rawy, M., Al-Maktoumi, A., Zekri, S., & Al-Abri, R. (2018). Hydrological and economical feasibility of mitigating a stressed coastal aquifer using managed aquifer recharge: A case study of Jamma aquifer, Oman. J Arid Land (2019), 11(1), 148–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-019-0093-7.
FAO. (2008). Policy options and alternatives for the cultivation of fodder crops in Al-Batinah Region Sultanate of Oman. Final Report. 180 pages.
FAO. (2016). www.faostat.fao.org.
FAO-MAF. (2016). Sustainable agriculture and rural development strategy towards 2040. 133 pages.
Haya. (2018). Haya water treated effluent utilization strategy. Oman Water & Wastewater Conference, 30th April–2 May 2018. OmanExpo, Muscat, Sultanate of Oman.
International Water Summit. (2018). Energy efficient desalination, meeting the GCC’s water needs in an environmentally sustainable way. Available online: https://www.internationalwatersummit.com/_media/Energy-Efficient-Desalination-2018.pdf
IRENA, International Renewable Energy Agency. (2014). Sultanate of Oman a renewables readiness assessment. Available online: https://www.paew.gov.om/PublicationsDoc/RE-Renwable-Radiness-Assessment
IRENA, International Renewable Energy Agency. (2015). Renewable energy in the water, energy and food Nexus. Available online: http://www.irena.org/documentdownloads/publications/irena_water energy_food_nexus_2015.pdf
Joseph, Sokina. (2017). The Sultanate of Oman’s agricultural and domestic sector: Using water footprint and virtual water tools to quantify and assess impacts of water use. MSc Thesis, Imperial College London, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Centre for Environment Policy.
Kotagama, H., Zekri, S., Al Harthi, R., & Boughanmi, H. (2016). Demand function estimate for residential water in Oman. International Journal of WaterResources Development. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2016.1238342.
Lattemann, S., & Hoepner, T. (2008). Impact of desalination plants on marine coastal water quality. In Barth, Abuzinada, Krupp, & Böer (Eds.), Marine pollution in the gulf environment. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
MAF. (2004). Ministry of agriculture and fisheries, annual book of agriculture statistics.
MAF. (2012). Ministry of Agriculture and fisheries (MAF). Sultanate of Oman, International Center for Biosaline Agriculture (ICBA) Dubai, UAE, “Oman salinity strategy: Assessment of Salinity Problem”.
MAF. (2013). Ministry of Agriculture and fisheries. Agricultural Census.
MRMWR, Ministry of Regional Municipalities and Water Resources, Water Resources in Oman (2008). Available online: http://www.omanws.org.om/images/publications/5465_Water_Atlas_E.pdf
MRMWR. (2013). Ministry of Regional Municipalities and Water Resources. Sultanate of Oman. http://www.mrmwr.gov.om
MRMEWR. (2005). Ministerial decision no: 159/2005 promulgating the bylaws to discharge liquid waste in the maarine environment (p. 10).
NCSI. (2017). National Center for statistics and information. Statistical year book, issue 45, August 2017.
OPWP. (2016). Oman Power and Water Procurement Company, annual report. Available online: http://www.omanpwp.com/PDF/AnnualReport2016.pdf
OPWP, OPWP’s 7-Year Statement. (2016–2022). Available online: http://www.omanpwp.com/PDF/7YS% 202016-2022%20Final%20.pdf
PAEW. (2016). Public Authority for Electricity and Water. Annual report. Available online: https://www.paew.gov.om/getattachment/1340e690-b826-4510-a83d-ed9b55b69a6c/
Purnama, A. (2011). Analytical model for brine discharges from a sea outfall with multiport diffusers, proc. International conference on environmental systems engineering and technology, Paris, France, August 24–26, 2011 (World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, Volume 80, August 2011, pp 57–61).
Purnama, A., Al-Barwani, H. H., Bleninger, T., & Doneker, R. L. (2011). CORMIX simulations of brine discharges from Barka plants, Oman. Desalination and Water Treatment, 32(1–3), 329–338. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2011.2718.
Wichelns, D. (2014). Do estimates of water productivity enhance understanding of farm-level water management? Water, 2014(6), 778–795. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6040778.
Zekri, S. (2008). Using economic incentives and regulations to reduce seawater intrusion in the Batinah coastal area of Oman. Agricultural Water Management, 95(3), 243–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2007.10.006.
Zekri, S. (2009). Controlling groundwater abstraction online. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(11), 3581–3588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.06.019.
Zekri, S., & Al-Marshudi, A. S. (2008). A millenarian water rights system and water markets in Oman. Water International, 33(3), 350–360. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060802256120.
Zekri, S., Kotagama, H., & Boughanmi, H. (2006). Temporary water markets in Oman. Agricultural and Marine Sciences, 11(SI), 77–84.
Zekri, S., Fouzai, A., Naifer, A., & Helmi, T. (2012). Damage cost in dry Aflaj in the Sultanate of Oman. Agricultural and Marine Sciences, 17, 9–19.
Zekri, S., Al Harthi, S., Kotagama, H., & Bose, S. (2016). An estimate of the willingness to pay for treated wastewater for irrigation in Oman. Journal of Agricultural and Marine Sciences, 21(1), 57–63. https://doi.org/10.24200/jams.vol21iss0pp57-64.
Zekri, S., Madani, K., Bazargan-Lari, M., Kotagama, H., & Kalbus, E. (2017, February). Feasibility of adopting smart water meters in aquifer management: An integrated hydro-economic analysis. Agricultural Water Management, 181, 85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.11.022
Zekri, S., Triki, C., Al-Maktoumi, A., Bazargan-Lari, M. (2019). Optimal storage and recovery of surplus desalinated water. 8th ICWRAE International Conference on Water Resources and Arid Environments. 22–24 January 2019. King Saud University. Riyadh. Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zekri, S. (2020). Oman Water Policy. In: Zekri, S. (eds) Water Policies in MENA Countries. Global Issues in Water Policy, vol 23. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29274-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29274-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-29273-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-29274-4
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)