Abstract
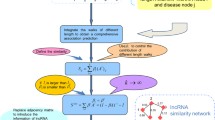
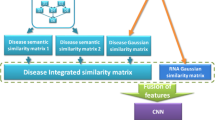
Accumulated evidence indicates that lncRNAs are critical for many biological processes, especially diseases. Therefore, identifying potential lncRNA-disease associations is significant for disease prevention, diagnosis, treatment and understanding of cell life activities at the molecular level. Although novel technologies have generated considerable associations for various lncRNAs and diseases, it has inevitable drawbacks such as high cost, time consumption, and error rate. For this reason, integrating various biological databases to predict the potential association of lncRNA and disease is of great attraction. In this paper, we proposed the model called ECLDA to predict lncRNA-disease associations by combining CNN and highspeed ELM. Firstly, the feature vectors are constructed by integrating lncRNA functional similarity, disease semantic similarity and Gaussian interaction profile kernel similarity. Secondly, CNN is carried out to mine local and higher-level abstract features of the vectors. Finally, high speed ELM is used to identify the novel lncRNA disease associations. The ECLDA computational model achieved AUCs of 0.9014 in 5-fold cross validation. The results showed that ECLDA is expected to be a practical tool for biomedical research in the future.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Djebali, S., et al.: Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 489(7414), 101 (2012)
Bertone, P., et al.: Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Science 306(5705), 2242–2246 (2004)
ENCODE Project Consortium: Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature 447(7146), 799 (2007)
Schmitt, A.M., Chang, H.Y.: Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell 29(4), 452–463 (2016)
Alvarez-Dominguez, J.R., Lodish, H.F.: Emerging mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function during normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Blood 130(18), 1965–1975 (2017)
Johnson, R.: Long non-coding RNAs in Huntington’s disease neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 46(2), 245–254 (2012)
Hrdlickova, B., de Almeida, R.C., Borek, Z., Withoff, S.: Genetic variation in the non-coding genome: Involvement of micro-RNAs and long non-coding RNAs in disease. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 1842(10), 1910–1922 (2014)
Qiu, M.-T., Hu, J.-W., Yin, R., Xu, L.: Long noncoding RNA: an emerging paradigm of cancer research. Tumor Biol. 34(2), 613–620 (2013)
Zhu, L., You, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S., Wang, B.: t-LSE: a novel robust geometric approach for modeling protein-protein interaction networks. PLoS ONE 8(4), e58368 (2013)
Zhu, L., You, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S.: Identifying spurious interactions in the protein-protein interaction networks using local similarity preserving embedding. In: Basu, M., Pan, Y., Wang, J. (eds.) ISBRA 2014. LNCS, vol. 8492, pp. 138–148. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-08171-7_13
Zhu, L., You, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S.: Increasing the reliability of protein–protein interaction networks via non-convex semantic embedding. Neurocomputing 121, 99–107 (2013)
Zhu, L., Deng, S.-P., You, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S.: Identifying spurious interactions in the protein-protein interaction networks using local similarity preserving embedding. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. (TCBB) 14(2), 345–352 (2017)
You, Z.-H., Zhou, M., Luo, X., Li, S.: Highly efficient framework for predicting interactions between proteins. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(3), 731–743 (2017)
You, Z.-H., Yu, J.-Z., Zhu, L., Li, S., Wen, Z.-K.: A MapReduce based parallel SVM for large-scale predicting protein-protein interactions. Neurocomputing 145, 37–43 (2014)
You, Z.-H., Ming, Z., Huang, H., Peng, X.: A novel method to predict protein-protein interactions based on the information of protein sequence. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering (ICCSCE), pp. 210–215. IEEE (2012)
You, Z.-H., Li, S., Gao, X., Luo, X., Ji, Z.: Large-scale protein-protein interactions detection by integrating big biosensing data with computational model. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014 (2014)
You, Z.-H., Li, L., Ji, Z., Li, M., Guo, S.: Prediction of protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequences using extreme learning machine combined with auto covariance descriptor. In: 2013 IEEE Workshop on Memetic Computing (MC), pp. 80–85. IEEE (2013)
You, Z.-H., et al.: Detecting protein-protein interactions with a novel matrix-based protein sequence representation and support vector machines. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 1 (2015)
You, Z.-H., Lei, Y.-K., Zhu, L., Xia, J., Wang, B.: Prediction of protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequences with ensemble extreme learning machines and principal component analysis. BMC Bioinform. 14(Suppl 8), S10 (2013)
You, Z.-H., Lei, Y.-K., Gui, J., Huang, D.-S., Zhou, X.: Using manifold embedding for assessing and predicting protein interactions from high-throughput experimental data. Bioinformatics 26(21), 2744–2751 (2010)
You, Z.-H., Huang, W., Zhang, S., Huang, Y.-A., Yu, C.-Q., Li, L.-P.: An efficient ensemble learning approach for predicting protein-protein interactions by integrating protein primary sequence and evolutionary information. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 16(3), 809–817 (2018)
You, Z.-H., Chan, K.C., Hu, P.: Predicting protein-protein interactions from primary protein sequences using a novel multi-scale local feature representation scheme and the random forest. PLoS ONE 10(5), e0125811 (2015)
You, Z.H., Zhu, L., Zheng, C.H., Yu, H.J., Deng, S.P., Ji, Z.: Prediction of protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequences using a novel multi-scale continuous and discontinuous feature set. BMC Bioinform. 15(S15), S9 (2014)
Wong, L., You, Z.-H., Ming, Z., Li, J., Chen, X., Huang, Y.-A.: Detection of interactions between proteins through rotation forest and local phase quantization descriptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17(1), 21 (2015)
Wen, Y.-T., Lei, H.-J., You, Z.-H., Lei, B.-Y., Chen, X., Li, L.-P.: Prediction of protein-protein interactions by label propagation with protein evolutionary and chemical information derived from heterogeneous network. J. Theor. Biol. 430, 9–20 (2017)
Wang, Y.-B., You, Z.-H., Li, L.-P., Huang, Y.-A., Yi, H.-C.: Detection of interactions between proteins by using legendre moments descriptor to extract discriminatory information embedded in pssm. Molecules 22(8), 1366 (2017)
Wang, Y.-B., You, Z.-H., Li, L.-P., Huang, D.-S., Zhou, F.-F., Yang, S.: Improving prediction of self-interacting proteins using stacked sparse auto-encoder with PSSM profiles. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 14(8), 983–991 (2018)
Wang, Y.B., et al.: Predicting protein-protein interactions from protein sequences by a stacked sparse autoencoder deep neural network. Mol. BioSyst. 13(7), 1336–1344 (2017)
Wang, Y., et al.: Predicting protein interactions using a deep learning method-stacked sparse autoencoder combined with a probabilistic classification vector machine. Complexity 2018 (2018)
Wang, L., et al.: Advancing the prediction accuracy of protein-protein interactions by utilizing evolutionary information from position-specific scoring matrix and ensemble classifier. J. Theor. Biol. 418, 105–110 (2017)
Li, Z.-W., You, Z.-H., Chen, X., Gui, J., Nie, R.: Highly accurate prediction of protein-protein interactions via incorporating evolutionary information and physicochemical characteristics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17(9), 1396 (2016)
Li, Z.W., et al.: Accurate prediction of protein-protein interactions by integrating potential evolutionary information embedded in PSSM profile and discriminative vector machine classifier. Oncotarget 8(14), 23638 (2017)
Lei, Y.-K., You, Z.-H., Ji, Z., Zhu, L., Huang, D.-S.: Assessing and predicting protein interactions by combining manifold embedding with multiple information integration. BMC Bioinform. 13(Suppl 7), S3 (2012)
Lei, Y.-K., You, Z.-H., Dong, T., Jiang, Y.-X., Yang, J.-A.: Increasing reliability of protein interactome by fast manifold embedding. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 34(4), 372–379 (2013)
Huang, Y.-A., et al.: Construction of reliable protein–protein interaction networks using weighted sparse representation based classifier with pseudo substitution matrix representation features. Neurocomputing 218, 131–138 (2016)
Huang, Y.-A., You, Z.-H., Chen, X., Yan, G.-Y.: Improved protein-protein interactions prediction via weighted sparse representation model combining continuous wavelet descriptor and PseAA composition. BMC Syst. Biol. 10(4), 120 (2016)
Huang, Q., You, Z., Zhang, X., Zhou, Y.: Prediction of protein-protein interactions with clustered amino acids and weighted sparse representation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16(5), 10855–10869 (2015)
Chen, Z.-H., You, Z.-H., Li, L.-P., Wang, Y.-B., Li, X.: RP-FIRF: prediction of self-interacting proteins using random projection classifier combining with finite impulse response filter. In: Huang, D.-S., Jo, K.-H., Zhang, X.-L. (eds.) ICIC 2018. LNCS, vol. 10955, pp. 232–240. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95933-7_29
An, J.Y., Meng, F.R., You, Z.H., Chen, X., Yan, G.Y., Hu, J.P.: Improving protein–protein interactions prediction accuracy using protein evolutionary information and relevance vector machine model. Protein Sci. 25(10), 1825–1833 (2016)
You, Z.-H., et al.: PRMDA: personalized recommendation-based MiRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 8(49), 85568 (2017)
Wang, L., et al.: MTRDA: using logistic model tree to predict miRNA-disease associations by fusing multi-source information of sequences and similarities. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15(3), e1006865 (2019)
Huang, Y.-A., You, Z.-H., Chen, X., Huang, Z.-A., Zhang, S., Yan, G.-Y.: Prediction of microbe–disease association from the integration of neighbor and graph with collaborative recommendation model. J. Transl. Med. 15(1), 209 (2017)
Chen, X., Zhang, D.-H., You, Z.-H.: A heterogeneous label propagation approach to explore the potential associations between miRNA and disease. J. Transl. Med. 16(1), 348 (2018)
Chen, X., Xie, D., Zhao, Q., You, Z.-H.: MicroRNAs and complex diseases: from experimental results to computational models. Briefings Bioinform. 20(2), 515–539 (2017)
Chen, X., Wang, C.-C., Yin, J., You, Z.-H.: Novel human miRNA-disease association inference based on random forest. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 13, 568–579 (2018)
Chen, X., Huang, Y.-A., Wang, X.-S., You, Z.-H., Chan, K.C.: FMLNCSIM: fuzzy measure-based lncRNA functional similarity calculation model. Oncotarget 7(29), 45948 (2016)
Chen, X., You, Z.H., Yan, G.Y., Gong, D.W.: IRWRLDA: improved random walk with restart for lncRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 7(36), 57919–57931 (2016)
Huang, Y., Chen, X., You, Z., Huang, D., Chan, K.: ILNCSIM: improved lncRNA functional similarity calculation model. Oncotarget 7(18), 25902 (2016)
Zhan, Z.-H., You, Z.-H., Zhou, Y., Li, L.-P., Li, Z.-W.: Efficient framework for predicting ncRNA-protein interactions based on sequence information by deep learning. In: Huang, D.-S., Jo, K.-H., Zhang, X.-L. (eds.) ICIC 2018. LNCS, vol. 10955, pp. 337–344. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-95933-7_41
Yi, H.-C., You, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S., Li, X., Jiang, T.-H., Li, L.-P.: A deep learning framework for robust and accurate prediction of ncRNA-protein interactions using evolutionary information. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 11, 337–344 (2018)
Chan, K.C., You, Z.-H.: Large-scale prediction of drug-target interactions from deep representations. In: 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1236–1243. IEEE (2016)
Chen, X., et al.: NRDTD: a database for clinically or experimentally supported non-coding RNAs and drug targets associations. Database 2017 (2017)
Huang, Y.-A., You, Z.-H., Chen, X.: A systematic prediction of drug-target interactions using molecular fingerprints and protein sequences. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 19(5), 468–478 (2018)
Li, Z., et al.: In silico prediction of drug-target interaction networks based on drug chemical structure and protein sequences. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 11174 (2017)
Meng, F.-R., You, Z.-H., Chen, X., Zhou, Y., An, J.-Y.: Prediction of drug–target interaction networks from the integration of protein sequences and drug chemical structures. Molecules 22(7), 1119 (2017)
Sun, X., Bao, J., You, Z., Chen, X., Cui, J.: Modeling of signaling crosstalk-mediated drug resistance and its implications on drug combination. Oncotarget 7(39), 63995 (2016)
Wang, L., et al.: Computational methods for the prediction of drug-target interactions from drug fingerprints and protein sequences by stacked auto-encoder deep neural network. In: Cai, Z., Daescu, O., Li, M. (eds.) ISBRA 2017. LNCS, vol. 10330, pp. 46–58. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59575-7_5
Wang, L., et al.: A computational-based method for predicting drug–target interactions by using stacked autoencoder deep neural network. J. Comput. Biol. 25(3), 361–373 (2018)
Wang, L., You, Z.-H., Chen, X., Yan, X., Liu, G., Zhang, W.: Rfdt: a rotation forest-based predictor for predicting drug-target interactions using drug structure and protein sequence information. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 19(5), 445–454 (2018)
Chen, G., et al.: LncRNADisease: a database for long-non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(D1), D983–D986 (2012)
Wang, D., Wang, J., Lu, M., Song, F., Cui, Q.: Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on microRNA-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 26(13), 1644–1650 (2010)
Chen, X., Yan, C.C., Luo, C., Ji, W., Zhang, Y., Dai, Q.: Constructing lncRNA functional similarity network based on lncRNA-disease associations and disease semantic similarity. Sci. Rep. 5, 11338 (2015)
Huang, G.-B., Zhu, Q.-Y., Siew, C.-K.: Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70(1–3), 489–501 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Guo, ZH., You, ZH., Li, LP., Wang, YB., Chen, ZH. (2019). Combining High Speed ELM with a CNN Feature Encoding to Predict LncRNA-Disease Associations. In: Huang, DS., Jo, KH., Huang, ZK. (eds) Intelligent Computing Theories and Application. ICIC 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11644. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26969-2_39
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26969-2_39
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-26968-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-26969-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)