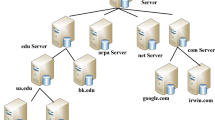
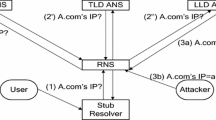
Abstract
Domain Name System (DNS) has become a target of the Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. When a DNS is under a DDoS flood attack, all the domain information under that DNS becomes unreachable, eventually causing unavailability of those particular domain names. In this paper, we propose a method which includes periodic stale content update and maintains a list of most frequently queried domain names of different DNS servers. Our simulation results show that the our method can serve more than \(70\%\) of the total cache responses during a massive DNS Flood attack.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mahjabin, T., Xiao, Y., Sun, G., Jiang, W.: A survey of distributed denial-of-service attack, prevention, andmitigation techniques. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 13(12), 1–33 (2017)
Zeifman, I., Margolius, D.: The long and short of TTL – understanding DNS redundancy and the Dyn DDoS attack. https://www.incapsula.com/blog/the-long-and-short-of-ttl-the-ddos-perspective.html. Accessed 18 June 2018
Vlajic, N., Andrade, M., Nguyen, U.T.: The role of DNS TTL values in potential DDoS attacks: what do the major banks know about it? Procedia Comput. Sci. 10, 466–473 (2012)
Mahjabin, T., Xiao, Y.: Mitigation process for DNS flood attacks. In: Proceeding of 2019 16th IEEE Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas (Short Paper), 11–14 January 2019
Shang, H., Wills, C.E.: Piggybacking related domain names to improve DNS performance. Comput. Netw. 50(11), 1733–1748 (2006)
Chen, H., Xiao, Y.: Cache access and replacement for future wireless internet. IEEE Commun. Mag. 44, 113–123 (2006)
Xiao, Y., Chen, H.: Optimal callback with two-level adaptation for wireless data access. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 5(8), 1087–1102 (2006)
Wei-min, L., Lu-ying, C., Zhen-ming, L.: Alleviating the impact of DNS DDoS attacks. In: Second International Conference on Networks Security, Wireless Communications and Trusted Computing, vol. 1, pp. 240–243. IEEE, April 2010
Ballani, H., Francis, P.: Mitigating DNS DoS attacks. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, pp. 189–198. ACM, October 2008
Jung, J., Sit, E., Balakrishnan, H., Morris, R.: DNS performance and the effectiveness of caching. IEEE/ACM Trans. Networking 10(5), 589–603 (2002)
Cohen, E., Kaplan, H.: Proactive caching of DNS records: addressing a performance bottleneck. Comput. Netw. 41(6), 707–726 (2003)
Cao, P., Irani, S.: Cost-aware WWW proxy caching algorithms. In: USENIX Symposium on Internet Technologies and Systems, vol. 12, no. 97, pp. 193–206 (1997)
Jang, B., Lee, D., Chon, K., Kim, H.: DNS resolution with renewal using piggyback. J. Commun. Netw. 11(4), 416–427 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mahjabin, T., Xiao, Y. (2019). DNS Flood Attack Mitigation Utilizing Hot-Lists and Stale Content Updates. In: Wang, G., Feng, J., Bhuiyan, M., Lu, R. (eds) Security, Privacy, and Anonymity in Computation, Communication, and Storage. SpaCCS 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11611. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24907-6_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24907-6_22
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-24906-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-24907-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)