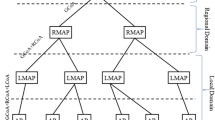
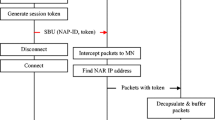
Abstract
Today, the Internet usage has increased due to its efficiency and performance. IPv4 and IPv6 are the most common protocols used for providing Internet communication among the mobile users. There is a big consideration regarding the mobile users’ need to access the Internet by different versions of the protocol in MANET. So far, no authors have proposed to design an architecture for intermobility and intertransaction for the transition communication in MANET. For that, 64MANET architecture is proposed to allow the mobile node to roam from one version to another version of the network along with the features of addressing mobility and transition mechanisms of MANET nodes. The performance of 64MANET is evaluated by different performance evaluation metrics. The results show that 64MANET is suitable for intermobility and interoperability between IPv4 mobile node and IPv6 mobile node in MANET communication.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IPv4:
-
Internet Protocol version 4
- IPv6:
-
Internet Protocol version 6
- IETF:
-
Internet Engineering Task Force
- BGP:
-
Border Gateway Protocol
- ISP:
-
Internet Service Provider
- NTT:
-
Nippon Telegraph and Telephone
- ERNET:
-
Education and Research Network
- AOL:
-
America Online
- AT&T:
-
American Telephone and Telegraph Company
- MCI:
-
Microwave Communication Commission
- VSNL:
-
Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited
- DSTM:
-
Dual Stack Transition Mechanism
- DSMIPv6:
-
Dual Stack MIPv6
- NAT-PT:
-
Network Address Translation-Protocol Translator
- NAPT-PT:
-
Network Address Port Translation-PT
- SIIT:
-
Stateless IP/ICMP Translation Algorithm
- BIS:
-
Bump in the Stack
- BDMS:
-
Bi-directional Mapping System
- TRT:
-
Transport Relay Translator
- SOCKS:
-
Socket Secure
- BIA:
-
Bump-In the-API
- MIP-ALG:
-
Mobile Internet Protocol-Application Level Gateway
- PET:
-
Prefixing Encapsulation and Translation
- DNS:
-
Domain Name System
- NAT:
-
Network Address Translation
- MAP-T:
-
Mapping of Address and Port using Translation
- SIIT-DC:
-
Stateless IP/ICMP Translation for IPv6 Internet Data Center Environments
- V4GT:
-
IPv4-Enabled Gateway Translator
- V6GT:
-
IPv6-Enabled Gateway Translator
- NS:
-
Network Simulator
- TCL:
-
Tool Command Language
- ByER:
-
Byte-Per-Rate
- MTU:
-
Maximum Transmission Unit
- PDR:
-
Packet Delivery Ratio
- MN:
-
Mobile Node
- HN:
-
Home Network
References
Bradner S, Mankin A (1995) The recommendation for the IP next generation protocol. RFC 1752
http://www.networkworld.com/article/2198933/lan-wan/yahoo-worries-ipv6-upgrade-could-shut-out-1-million-internet-users-initially.html. Last visited on 2017-12-10
http://www.networkworld.com/article/2179637/lan-wan/yahoo%2D%2Dfacebook-and-google-to-ietf%2D%2Dwhere-are-the-ipv6-users-.html. Last visited on 2017-12-19
https://www.google.com/intl/en/ipv6/statistics.html. Retrieved 5.1.2018
“The IPv6 Forum”. The IPv6 Forum. Retrieved 2017-01-20
“Internet Society, Number Resource Organization, and Regional Internet Registries Reinforce Importance of IPv6 Deployment for the Future of the Internet”. Internet Society, 2012
http://www.alliedtelesis.com/media/fount/white_paper/ipv6_WP_RevD.pdf
http://www.ipv6.ru/english/presscenter/project.php. Last visited on 2016-3-12
Bound J, Toutain L, Richier JL (2005) Dual Stack IPv6 Dominant Transition Mechanism (DSTM), draft-bound-dstm-exp-04.txt
Tsirtsis G, Park V, Soliman H (2008) “Dual Stack Mobile IPv4”. Internet draft draft-ietf-mip4-dsmipv4-06, IETF
Hesham Solima (2008) Mobile IPv6 support for dual stack Hosts and Routers. Internet Draft draft-ietf-mext-nemo-v4traversal-03, IETF
Turanyi ZR, Szabo C (2001) Global internet roaming with RoamIP. ACM J Mobile Comput Commun Rev 4(3):58–68
Changwen Liu (2004) Support mobile IPv6 in IPv4 domains. In: IEEE proceedings of the international conference on Vehicular Technology (VTC). ISBN:7803-8255-2/04, pp 2700–2704
Ssang-Hee Seo In-Yeup Kong (2005) A performance analysis model of PC- based software router supporting IPv6-IPv4 translation for residential gateway. In: Proceedings of the fourth annual ACIS International Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS’05) 0-7695- 2296-3/05
Aoun C, Davies E (2007) Reasons to move the network address translator – protocol translator. RFC 4966
Bangnulo M, Matthews P, van Beijnum I (2008) NAT64/DNS64: network address and protocol translation from IPv6 clients to IPv4 servers. Draft-bagnulo-behave-nat64-00
Srisuresh P, Egevang K (2001) Traditional IP Network Address Translator (Traditional NAT). RFC 3022
Nordmark E (2000) Stateless IP/ICMP Translation Algorithm (SIIT), RFC 2765
Ra’ed AlJa’afreh, John Mellor, Irfan Awan (2008) Implementation of IPv4/IPv6 BDMS translation mechanism. In: IEEE second UKSIM European symposium on computer modeling and simulation. ISBN:978-0-7695-3325-4/08, pp 512–517
Hagino J, Yamamoto K (2001) An IPv6-to-IPv4 transport relay translator. RFC 3142
Kitamura H (2001) A SOCKS-based IPv6/IPv4 gateway mechanism. RFC 3089
Lee S, Shin M-K, Kim Y-J, Nordmark E, Durand A (2002) Dual stack hosts using “Bump-in-the-API” (BIA). RFC3338
Choi HH, Cho DH (2003) Mobility management based on mobile IP in mixed IPv4/IPv6 networks. In: IEEE 58th proceedings of VTC 2003- Fall, pp 2048–2052
Wu P, Cui Y, Xu M, Wu J, Li X, Metz C, Wang S (2010) PET: prefixing encapsulation and translation for IPv4-IPv6 coexistence. In: The Proceedings of Global Telecommunications Conference (GLOBECOM). ISSN.1930-529X, pp 1–5
Bagnulo M, Sullivan A, Matthews P, van Beijnum I (2011) DNS64: DNS Extensions for Network Address Translation from IPv6 Clients to IPv4 Servers. RFC 6147
Bagnulo M, Matthews P, van Beijnum I (2011) Stateful NAT64: network address and protocol translation from IPv6 clients to IPv4 servers. RFC 6146
Baker F, Li X, Bao C, Yin K (2011) Framework for IPv4/IPv6 translation. RFC 6144
Mawatari M, Kawashima M, Byrne C (2013) 464XLAT: combination of stateful and stateless translation. RFC 6877
Li X, Troan O, Matsushima S, Murakami T (2015) Mapping of Address and Port using Translation (MAP-T). RFC 7599
Anderson T, Steffann S. Stateless IP/ICMP Translation for IPv6 Internet Data Center Environments (SIIT-DC): dual translation mode. RFC 7756, 016
Li X, Bao C, Baker F (2016) IP/ICMP translation algorithm. RFC 6145
Meynell K (2017) Local-use IPv4/IPv6 translation prefix. RFC 8215
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Manimozhi, S., Gnana Jayanthi, J. (2020). Performance Study of IPv6/IPv4 MANET (64MANET) Architecture. In: Kumar, L., Jayashree, L., Manimegalai, R. (eds) Proceedings of International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Smart Grid and Smart City Applications. AISGSC 2019 2019. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24051-6_59
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24051-6_59
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-24050-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-24051-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)