Abstract
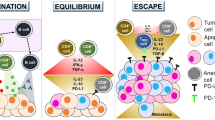
Colorectal cancer is a common malignancy around the world, with an important mortality rate among other malignancies. The cornerstone of treatment is curative surgery as 40% of patients are diagnosed with localized disease. Patients who were diagnosed with advanced disease have a dismal prognosis. Conventional chemotherapy is the standard treatment in an advanced setting with important development of strategies that combine biological agents (bevacizumab, cetuximab, panitumumab, ramucirumab, etc.). Recently the better understanding of immune system interaction in carcinogenesis has led to the development of new therapeutic strategies based on immune modulators that activate the immune system. With the current evidence we have, probably a combination of these strategies will result in better outcomes in the fight against this malignancy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E FJ. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0. International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization, Lyon, France; 2013. http://globocan.iarc.fr/Default.aspx Accessed 18 Mar 2016.
Las Cifras del Cáncer en España en 2016. Accessed 18 Mar 2016. http://seom.org/seomcms/images/stories/recursos/LA_CIFRAS_DEL_CANCER_EN_2016.pdf.
American Cancer Society. Colorectal cancer facts & figures 2014–2016. Atlanta: American Cancer Society. 2014. Accessed 18 Mar 2016. http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/documents/document/acspc-042280.pdf.
Hellinger MD, Santiago CA. Reoperation for recurrent colorectal cancer. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2006;19(4):228–36.
Kocián P, Šedivcová M, Drgáč J, Cerná K, Hoch J, Kodet R, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and dendritic cells in human colorectal cancer: their relationship to KRAS mutational status and disease recurrence. Hum Immunol. 2011;72(11):1022–8.
Gonzalez-Pons M, Cruz-Correa M. Colorectal cancer biomarkers: where are we now? Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:149014.
Deschoolmeester V, Baay M, Specenier P, Lardon F, Vermorken JB. A review of the most promising biomarkers in colorectal cancer: one step closer to targeted therapy. Oncologist AlphaMed Press. 2010;15(7):699–731.
Pernot S, Terme M, Voron T, Colussi O, Marcheteau E, Tartour E, et al. Colorectal cancer and immunity: what we know and perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(14):3738–50.
Frisch M. Association of cancer with AIDS-related immunosuppression in adults. JAMA. 2001;285(13):1736–45.
Shankaran V, Ikeda H, Bruce AT, White JM, Swanson PE, Old LJ, et al. IFNgamma and lymphocytes prevent primary tumour development and shape tumour immunogenicity. Nature. 2001;410(6832):1107–11.
Dunn GP, Bruce AT, Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat Immunol. 2002;3(11):991–8.
Markman JL, Shiao SL. Impact of the immune system and immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015;6(1):208–23.
Malmberg K-J, Bryceson YT, Carlsten M, Andersson S, Björklund A, Björkström NK, et al. NK cell-mediated targeting of human cancer and possibilities for new means of immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2008;57(10):1541–52.
Carbone E, Neri P, Mesuraca M, Fulciniti MT, Otsuki T, Pende D, et al. HLA class I, NKG2D, and natural cytotoxicity receptors regulate multiple myeloma cell recognition by natural killer cells. Blood Am Soc Hematol. 2005;105(1):251–8.
Terme M, Fridman WH, Tartour E. NK cells from pleural effusions are potent antitumor effector cells. Eur J Immunol. 2013;43(2):331–4.
Coca S, Perez-Piqueras J, Martinez D, Colmenarejo a SM a, Vallejo C, et al. The prognostic significance of intratumoral natural killer cells in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 1997;79(12):2320–8.
Tachibana T, Onodera H, Tsuruyama T, Mori A, Nagayama S, Hiai H, et al. Increased intratumor Valpha24-positive natural killer T cells: a prognostic factor for primary colorectal carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(20):7322–7.
Pollard JW. Tumour-educated macrophages promote tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(1):71–8.
Edin S, Wikberg ML, Rutegård J, Oldenborg P-A, Palmqvist R. Phenotypic skewing of macrophages in vitro by secreted factors from colorectal cancer cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74982.
Erreni M, Mantovani A, Allavena P. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) and inflammation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Microenviron. 2011;4(2):141–54.
Jacobs J, Smits E, Lardon F, Pauwels P, Deschoolmeester V. Immune checkpoint modulation in colorectal cancer: what’s new and what to expect. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:158038.
Golubovskaya V, Wu L. Different subsets of T cells, memory, effector functions, and CAR-T immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel). 8(3).
Obermajer N, Dahlke MH. (Compl)Ex-Th17-Treg cell inter-relationship. Oncoimmunology. 2015;5(1):e1040217.
Yao Y, Jiang Q, Jiang L, Wu J, Zhang Q, Wang J, et al. Lnc-SGK1 induced by Helicobacter pylori infection and highsalt diet promote Th2 and Th17 differentiation in human gastric cancer by SGK1/Jun B signaling. Oncotarget. 2016;7(15):20549–60.
Amin M, Lockhart AC. The potential role of immunotherapy to treat colorectal cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015;24(3):329–44.
Mocellin S, Rossi CR, Lise M, Nitti D. Colorectal cancer vaccines: principles, results, and perspectives. Gastroenterology. 2004;127(6):1821–37.
Blankenstein T, Coulie PG, Gilboa E, Jaffee EM. The determinants of tumour immunogenicity. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(4):307–13.
Keenan BP, Jaffee EM. Whole cell vaccines--past progress and future strategies. Semin Oncol. 2012;39(3):276–86.
Koido S, Ohkusa T, Homma S, Namiki Y, Takakura K, Saito K, et al. Immunotherapy for colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(46):8531–42.
Hoover HC, Brandhorst JS, Peters LC, Surdyke MG, Takeshita Y, Madariaga J, et al. Adjuvant active specific immunotherapy for human colorectal cancer: 6.5-year median follow-up of a phase III prospectively randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 1993;11(3):390–9.
Harris J, Ryan L, Hoover H, Stuart R, Oken M, Benson A, et al. Adjuvant active specific immunotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer with an autologous tumor cell vaccine: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E5283. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(1):148–57.
Vermorken J, Claessen A, van Tinteren H, Gall H, Ezinga R, Meijer S, et al. Active specific immunotherapy for stage II and stage III human colon cancer: a randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;353(9150):345–50.
Procaccio L, Schirripa M, Fassan M, Vecchione L, Bergamo F, Prete AA, et al. Immunotherapy in gastrointestinal cancers. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4346576.
Moulton HM, Yoshihara PH, Mason DH, Iversen PL, Triozzi PL. Active specific immunotherapy with a {beta}-human chorionic gonadotropin peptide vaccine in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: antibody response is associated with improved survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8(7):2044–51.
Bilusic M, Heery CR, Arlen PM, Rauckhorst M, Apelian D, Tsang KY, et al. Phase I trial of a recombinant yeast-CEA vaccine (GI-6207) in adults with metastatic CEA-expressing carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014;63(3):225–34.
Posner MC, Niedzwiecki D, Venook AP, Hollis DR, Kindler HL, Martin EW, et al. A phase II prospective multi-institutional trial of adjuvant active specific immunotherapy following curative resection of colorectal cancer hepatic metastases: cancer and leukemia group B study 89903. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15(1):158–64.
Miyagi Y, Imai N, Sasatomi T, Yamada A, Mine T, Katagiri K, et al. Induction of cellular immune responses to tumor cells and peptides in colorectal cancer patients by vaccination with SART3 peptides. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7(12):3950–62.
Speetjens FM, Kuppen PJK, Welters MJP, Essahsah F, Voet van den Brink AMEG, Lantrua MGK, et al. Induction of p53-specific immunity by a p53 synthetic long peptide vaccine in patients treated for metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(3):1086–95.
Kimura T, McKolanis JR, Dzubinski LA, Islam K, Potter DM, Salazar AM, et al. MUC1 vaccine for individuals with advanced adenoma of the colon: a cancer immunoprevention feasibility study. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013;6(1):18–26.
denoue S, Hirohashi Y, Torigoe T, Sato Y, Tamura Y, Hariu H, et al. A potent immunogenic general cancer vaccine that targets survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(4):1474–82.
Schulze T, Kemmner W, Weitz J, Wernecke KD, Schirrmacher V, Schlag PM. Efficiency of adjuvant active specific immunization with Newcastle disease virus modified tumor cells in colorectal cancer patients following resection of liver metastases: results of a prospective randomized trial. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009;58(1):61–9.
Karlsson M, Marits P, Dahl K, Dagöö T, Enerbäck S, Thörn M, et al. Pilot study of sentinel-node-based adoptive immunotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(7):1747–57.
Zhen Y-H, Liu X-H, Yang Y, Li B, Tang J-L, Zeng Q-X, et al. Phase I/II study of adjuvant immunotherapy with sentinel lymph node T lymphocytes in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2015;64:1083–93.
Parkhurst MR, Yang JC, Langan RC, Dudley ME, Nathan D-AN, Feldman SA, et al. T cells targeting carcinoembryonic antigen can mediate regression of metastatic colorectal cancer but induce severe transient colitis. Mol Ther. 2011;19(3):620–6.
Correale P, Tagliaferri P, Fioravanti A, Del Vecchio MT, Remondo C, Montagnani F, et al. Immunity feedback and clinical outcome in colon cancer patients undergoing chemoimmunotherapy with gemcitabine + FOLFOX followed by subcutaneous granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and aldesleukin (GOLFIG-1 Trial). Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(13):4192–9.
Correale P, Botta C, Rotundo MS, Guglielmo A, Conca R, Licchetta A, et al. Gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, levofolinate, 5-fluorouracil, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and interleukin-2 (GOLFIG) versus FOLFOX chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients: the GOLFIG-2 multicentric open-label randomized phase. J Immunother. 2014;37(1):26–35.
Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:515–48.
Rozali EN, Hato SV, Robinson BW, Lake RA, Lesterhuis WJ. Programmed death ligand 2 in cancer-induced immune suppression. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:656340.
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2443–54.
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQM, Hwu W-J, Topalian SL, Hwu P, et al. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2455–65.
Droeser RA, Hirt C, Viehl CT, Frey DM, Nebiker C, Huber X, et al. Clinical impact of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(9):2233–42.
Heinimann K. Toward a molecular classification of colorectal cancer: the role of microsatellite instability status. Front Oncol. 2013;3:272.
Le DT, Uram JN, Wang H, Bartlett BR, Kemberling H, Eyring AD, et al. PD-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(26):2509–20.
Overman MJ, McDermott R, Leach JL, Lonardi S, Lenz HJ, Morse MA, et al. Nivolumab in patients with metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer (CheckMate 142): an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(9):1182–91.
Overman MJ, Lonardi S, Wong KYM, Lenz HJ, Gelsomino F, Aglietta M, et al. Durable clinical benefit with nivolumab plus ipilimumab in DNA mismatch repair-deficient/microsatellite instability-high metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(8):773–9.
Boland PM, Hutson A, Maguire O, Minderman H, Fountzilas C, Iyer RV. A phase Ib/II study of cetuximab and pembrolizumab in RAS-wt mCRC. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36. (suppl 4S; abstr 834).
Betts G, Jones E, Junaid S, El-Shanawany T, Scurr M, Mizen P, et al. Suppression of tumour-specific CD4+ T cells by regulatory T cells is associated with progression of human colorectal cancer. Gut. 2012;61(8):1163–71.
Chung KY, Gore I, Fong L, Venook A, Beck SB, Dorazio P, et al. Phase II study of the anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 monoclonal antibody, tremelimumab, in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(21):3485–90.
Goldberg MV, Drake CG. LAG-3 in cancer immunotherapy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011;344:269–78.
Shin DS, Ribas A. The evolution of checkpoint blockade as a cancer therapy: what’s here, what's next? Curr Opin Immunol. 2015;33:23–35.
Gagliani N, Magnani CF, Huber S, Gianolini ME, Pala M, Licona-Limon P, et al. Coexpression of CD49b and LAG-3 identifies human and mouse T regulatory type 1 cells. Nat Med. 2013;19(6):739–46.
Blackburn SD, Shin H, Haining WN, Zou T, Workman CJ, Polley A, et al. Coregulation of CD8+ T cell exhaustion by multiple inhibitory receptors during chronic viral infection. Nat Immunol. 2009;10(1):29–37.
Chen J, Chen Z. The effect of immune microenvironment on the progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Med Oncol. 2014;31(8):82.
Zhu C, Anderson AC, Schubart A, Xiong H, Imitola J, Khoury SJ, et al. The Tim-3 ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(12):1245–52.
Denoeud J, Moser M. Role of CD27/CD70 pathway of activation in immunity and tolerance. J Leukoc Biol. 2011;89(2):195–203.
Jacobs J, Deschoolmeester V, Zwaenepoel K, Rolfo C, Silence K, Rottey S, et al. CD70: an emerging target in cancer immunotherapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;155:1–10.
Claus C, Riether C, Schürch C, Matter MS, Hilmenyuk T, Ochsenbein AF. CD27 signaling increases the frequency of regulatory T cells and promotes tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2012;72(14):3664–76.
Jacobs J, Zwaenepoel K, Rolfo C, Van den BJ, Deben C, Silence K, et al. Unlocking the potential of CD70 as a novel immunotherapeutic target for non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:13462–75.
Thomas LJ, He L-Z, Marsh H, Keler T. Targeting human CD27 with an agonist antibody stimulates T-cell activation and antitumor immunity. Oncoimmunology. 2014;3(1):e27255.
Schaer DA, Hirschhorn-Cymerman D, Wolchok JD, Hodi F, O’Day S, McDermott D, et al. Targeting tumor-necrosis factor receptor pathways for tumor immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. 2014;2(1):7.
Pedroza-Gonzalez A, Verhoef C, Ijzermans JNM, Peppelenbosch MP, Kwekkeboom J, Verheij J, et al. Activated tumor-infiltrating CD4+ regulatory T cells restrain antitumor immunity in patients with primary or metastatic liver cancer. Hepatology. 2013;57(1):183–94.
Schaer DA, Budhu S, Liu C, Bryson C, Malandro N, Cohen A, et al. GITR pathway activation abrogates tumor immune suppression through loss of regulatory T-cell lineage stability. Cancer Immunol Res. 2013;1(5):320–31.
Weinberg AD, Morris NP, Kovacsovics-Bankowski M, Urba WJ, Curti BD. Science gone translational: the OX40 agonist story. Immunol Rev. 2011;244(1):218–31.
Takeda I, Ine S, Killeen N, Ndhlovu LC, Murata K, Satomi S, et al. Distinct roles for the OX40-OX40 ligand interaction in regulatory and nonregulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2004;172(6):3580–9.
Cepowicz D, Zaręba K, Gryko M, Stasiak-Bermuta A, Kędra B. Determination of the activity of CD134 (OX-40) and CD137 (4-1BB) adhesive nolecules by means of flow cytometry in patients with colorectal cancer metastases to the liver. Polish J Surg. 2011;83(8):424–9.
Redmond WL, Triplett T, Floyd K, Weinberg AD, Watts T, Croft M, et al. Dual anti-OX40/IL-2 therapy augments tumor immunotherapy via IL-2R-mediated regulation of OX40 expression. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34467.
Weinberg AD, Rivera M-M, Prell R, Morris A, Ramstad T, Vetto JT, et al. Engagement of the OX-40 receptor in vivo enhances antitumor immunity. J Immunol. 2000;164(4):2160–9.
Gough MJ, Crittenden MR, Sarff M, Pang P, Seung SK, Vetto JT, et al. Adjuvant therapy with agonistic antibodies to CD134 (OX40) increases local control after surgical or radiation therapy of cancer in mice. J Immunother. 2010;33(8):798–809.
Pan P-Y, Zang Y, Weber K, Meseck ML, Chen S-H. OX40 ligation enhances primary and memory cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in an immunotherapy for hepatic colon metastases. Mol Ther. 2002;6(4):528–36.
Houot R, Levy R. T-cell modulation combined with intratumoral CpG cures lymphoma in a mouse model without the need for chemotherapy. Blood. 2009;113(15):3546–52.
Watanabe A, Hara M, Chosa E, Nakamura K, Sekiya R, Shimizu T, et al. Combination of adoptive cell transfer and antibody injection can eradicate established tumors in mice–an in vivo study using anti-OX40mAb, anti-CD25mAb and anti-CTLA4mAb-. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2010;32(2):238–45.
Garrison K, Hahn T, Lee W-C, Ling LE, Weinberg AD, Akporiaye ET. The small molecule TGF-β signaling inhibitor SM16 synergizes with agonistic OX40 antibody to suppress established mammary tumors and reduce spontaneous metastasis. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012;61(4):511–21.
Curti BD, Kovacsovics-Bankowski M, Morris N, Walker E, Chisholm L, Floyd K, et al. OX40 is a potent immune-stimulating target in late-stage cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2013;73(24):7189–98.
Shuford WW, Klussman K, Tritchler DD, Loo DT, Chalupny J, Siadak AW, et al. 4-1BB costimulatory signals preferentially induce CD8+ T cell proliferation and lead to the amplification in vivo of cytotoxic T cell responses. J Exp Med. 1997;186(1):47–55.
Vinay DS, Kwon BS. 4-1BB signaling beyond T cells. Cell Mol Immunol. 2011;8(4):281–4.
Vinay DS, Kwon BS. Immunotherapy of cancer with 4-1BB. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(5):1062–70.
Melero I, Shuford WW, Newby SA, Aruffo A, Ledbetter JA, Hellström KE, et al. Monoclonal antibodies against the 4-1BB T-cell activation molecule eradicate established tumors. Nat Med. 1997;3(6):682–5.
Sabel MS, Conway TF, Chen FA, Bankert RB. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the T-cell activation molecule CD137 (interleukin-A or 4-1BB) block human lymphocyte-mediated suppression of tumor xenografts in severe combined immunodeficient mice. J Immunother. 2000;23(3):362–8.
Cepowicz D, Gryko M, Zaręba K, Stasiak-Bermuta A, Kędra B. Assessment of activity of an adhesion molecule CD134 and CD137 in colorectal cancer patients. Polish J Surg. 2011;83(12):641–5.
Dimberg J, Hugander A, Wågsäter D. Expression of CD137 and CD137 ligand in colorectal cancer patients. Oncol Rep. 2006;15(5):1197–200.
Chen S. Rejection of disseminated metastases of colon carcinoma by synergism of IL-12 gene therapy and 4-1BB costimulation. Mol Ther. 2000;2(1):39–46.
Segal NH, Gopal AK, Shailender B, Kohrt HE, Levy R, Pishvain MJ, et al. A phase 1 study of PF-05082566 (anti-4-1BB) in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:5s.. (suppl; abstr 3007)
Kohrt HE, Colevas AD, Houot R, Weiskopf K, Goldstein MJ, Lund P, et al. Targeting CD137 enhances the efficacy of cetuximab. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(6):2668–82.
Houot R, Kohrt H. CD137 stimulation enhances the vaccinal effect of anti-tumor antibodies. Oncoimmunology. 2014;3(7):e941740.
Elgueta R, Benson MJ, de Vries VC, Wasiuk A, Guo Y, Noelle RJ. Molecular mechanism and function of CD40/CD40L engagement in the immune system. Immunol Rev. 2009;229(1):152–72.
Barth RJ, Fisher DA, Wallace PK, Channon JY, Noelle RJ, Gui J, et al. A randomized trial of ex vivo CD40L activation of a dendritic cell vaccine in colorectal cancer patients: tumor-specific immune responses are associated with improved survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(22):5548–56.
Honeychurch J, Cheadle EJ, Dovedi SJ, Illidge TM. Immuno-regulatory antibodies for the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(6):787–801.
Georgopoulos NT, Merrick A, Scott N, Selby PJ, Melcher A, Trejdosiewicz LK. CD40-mediated death and cytokine secretion in colorectal cancer: a potential target for inflammatory tumour cell killing. Int J Cancer. 2007;121(6):1373–81.
Palmer DH, Hussain SA, Ganesan R, Cooke PW, Wallace DMA, Young LS, et al. CD40 expression in prostate cancer: a potential diagnostic and therapeutic molecule. Oncol Rep. 2004;12(4):679–82.
Vonderheide RH, Glennie MJ. Agonistic CD40 antibodies and cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(5):1035–43.
Lal N, Beggs AD, Willcox BE, Middleton GW. An immunogenomic stratification of colorectal cancer: implications for development of targeted immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology. 2015;4(3):e976052.
Mlecnik B, Bindea G, Angell HK, et al. Integrative analyses of colorectal cancer show immunoscore is a stronger predictor of patient survival than microsatellite instability. Immunity. 2016;44(3):698–711.
Galon J, Pages F, Marincola FM, Angell HK, Thurin M, Lugli A, et al. Cancer classification using the Immunoscore: a worldwide task force. J Transl Med. 2012;10:205.
Deschoolmeester V, Smits E, Peeters M, Vermorken JB. Status of active specific immunotherapy for stage II, stage III, and resected stage IV colon cancer. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2013;9(4):380–90.
Ilieva KM, Correa I, Josephs DH, Karagiannis P, Egbuniwe IU, Cafferkey MJ, et al. Effects of BRAF mutations and BRAF inhibition on immune responses to melanoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(12):2769–83.
Fields AL, Keller A, Schwartzberg L, Bernard S, Kardinal C, Cohen A, Schulz J, Eisenberg P, Forster J, Wissel P. Adjuvant therapy with the monoclonal antibody Edrecolomab plus fluorouracil-based therapy does not improve overall survival of patients with stage III colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(12):1941–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Callata-Carhuapoma, H.R., García-Foncillas López, J. (2019). Immunological Treatment in Gastrointestinal Cancers. In: Yalcin, S., Philip, P. (eds) Textbook of Gastrointestinal Oncology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18890-0_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18890-0_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-18888-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-18890-0
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)