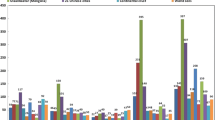
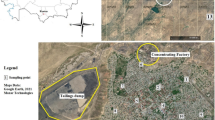
Abstract
Soils contaminated from water or air and by artificially applied toxic substances from pesticides, as well as mineral fertilizers, accumulate toxic elements, including heavy metals, having an extremely adverse impact on the living organisms. Among all kinds of economic activities, mining is the main source of pollution that deteriorates the agrophysical properties of soils and geoecological conditions in whole. The main ecological catastrophic zones in Georgia are discussed, related to the mining industry—Bolnisi metallogenic province (Kvemo Kartli Region) and Chiatura-Zestaponi manganese province (Imereti Region). Besides, pollution of soils and water with pesticides (chlorine-organic compounds) near the former chemical warehouses is considered.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth CC, Pilon JL, Grassman PL, Sluys WGVD (1994) Cobalt, cadmium and lead sorption to hydrous iron oxide: residence time effect. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:1615–1623
Alloway BJ, Jackson AP, Morgan H (1990) The accumulation of Cd by vegetables grown on soils contaminated from variety of sources. Sci Total Environ 91:223–236
Amberger A (1996) Pflanzenernährung, 4th edn. UTB, Stuttgart Bes C, Mench MJ (2008) Remediation of copper contaminated topsoils from a wooden treatment facility using in-situ stabilization. Environ Pollut 156:1–11
BBodSchV (1999) Bundes Bodenschutz und Altlastenverordnung 12 July 1999, Bundesgesetzblatt, Bundesanzeigerverlagsgesellschaft mbH, Köln
Brümmer GW (2010) Böden als Pflanzenstandort. In: Schachtschabel et al (eds) Lehrbuch der Bodenkunde, 16th edn. Spektrum, Heidelberg/Berlin, pp 379–448
Chlopecka A, Adriano DC (1997) Influence of zeolite, apatite and Fe-oxide on Cd and Pb uptake by crops. Sci Total Environ 207:195–206
Commission regulation (EC) No 466/2006. Off J Eur Union Dec 2006 Luxemburg
Contin M, Mondini C, Leita L, De Nobili M (2007) Enhanced soil toxic metal fixation in iron(hydr)oxides by redox cycles. Geoderma 140:164–175
DIN 11466 (1995) Soil quality—extraction of trace elements soluble in aqua regia. Beuth Verlag GmbH, Berlin, Deutsches Institut für Normung
DIN 19684–6: 1977–02 (1977) Methods of soil investigation for agricultural engineering—chemical laboratory tests—part 6: determination of iron soluble in oxalate solution. Beuth Verlag GmbH, Berlin, Deutsches Institut für Normung
DIN 19730: 2009–07 (2009) Soil quality—extraction of trace elements from soil using ammonium nitrate solution. Beuth Verlag GmbH, Berlin, Deutsches Institut für Normung
DIN ISO 10390 2005–12 (2005) Soil quality—determination of pH. Beuth Verlag GmbH, Berlin, Deutsches Institut für Normung
DIN ISO 10693 1997–05 (1997) Soil quality—determination of carbonate content—volumetric method. Beuth Verlag GmbH, Berlin, Deutsches Institut für Normung
DIN ISO 11260 1997–05 (1997) Soil quality—determination of effective cation exchange capacity and base saturation level using barium chloride solution. Beuth Verlag GmbH, Berlin, Deutsches Institut für Normung
DIN EN ISO 14688–1:2003–01 (2003) Geotechnical investigation and testing—identification and classification of soil—part 1: identification and description. Beuth Verlag GmbH, Berlin, Deutsches Institut für Normung
Felix-Henningsen P, Urushadze TF, Narimannidze EI, Wichmann L, Steffens D, Kalandadze B (2007) Heavy metal pollution of soils and food crops due to mining wastes in an irrigation district south of Tbilisi, eastern Georgia. Annal Agrarian Sci 5(3):11–27
Ford RG (2007) Structural dynamics of metal partitioning to mineral surfaces. In: Hamon R, Mc Laughlin M, Lombi E (eds) Natural attenuation of trace element availability. Taylor and Francis, New York, pp 73–88
Friesl W, Horak O (2006) Immobilisierung von Schwermetallen (Metalloide) oberflächennaher, großflächiger Kontaminationen—Technischer Leitfaden. ARC Seibersdorf Research GmbH, Seibersdorf
Friesl W, Friedl J, Platzer K, Horak O, Gerzabek MH (2006) Remediation of contaminated agricultural soils near a former Pb/Zn smelter in Austria: batch pot and field experiments. Environ Pollut 144:40–50
Guo G, Zhou Q, Ma LQ (2006) Availability and assessment of fixing additives for the in situ remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils: a review. Environ Monit Assess 116:513–528
Hanauer T, Shnell S, Steffens D, Kalandadze B, Navrozashvili L, Felix-Henningsen P (2011) In situ remediation of Cd, Cu and Zn contaminated topsoils by different amendments, EGU General Assembly, vol 13. XY488 EGU2011, pp 155–159
Hanauer T, Felix-Henningsen P, Shteffens D, Kalandadze B, Navrozashvili L, Urushadze T (2011a) In situ stabilization of metals (Cu, Cd und Zn) in contaminatedsoils in the region of Bolnisi, Georgia. Plant Soil 341:193–208
Hartley W, Lepp NW (2008) Remediation of arsenic contaminated soils by iron-oxide application, evaluated in terms of plant productivity, arsenic and phytotoxic metal uptake. Sci Total Environ 390:35–44
Janssen RPT, Peijnenburg WJGM, Posthuma L, Magt VDH (1997) Equilibrium partitioning of heavy metals in Dutch fields. I. Relationship between metal partition coefficients and soil characteristics. Env Tox Chem 16:2470–2488
Kabata-Pendyas A, Pendyas H (1989) Microelements in soils and plants. Mir, Moscow
Kalandadze B, Felix-Henningsen P (2014) Pollution of irrigation soils and cultural plants with heavy metals in the basin of the river Kvirila due to mining industry (West Georgia). Eurasian Soil Congress Abs, Istambul, Turkey
Kalandadze B, Matchavariani L (2011) Impact of heavy metals on soils and plants in Mashavera river lowland, Georgia. In: Proceedings of international conference “soil, plant and food interactions. Mendel University, Brno, Chech Rep., 6–8 Sept, pp 587–598
Kalandadze B, Trapaidze V (2015) Quantitative evaluation of the impact of heavy metals on soil productivity on the example of ore-dressing and processing production in east Georgia, SGEM, vol 1I, soils, forest ecosystems, marine and ocean ecosystems, pp 271–278
Kalandadze B, Hanauer T, Felix-Henningsen P, Urushadze T, Narimanidze E, Steffens D (2009) Mining and agriculture in the Mashavera valley (South-East Georgia)—a land use conflict with severte consequences. Biol J Armenia LXI 2:22–29. National Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Armenia
Kandeler E (2010) Bodenorganismen und ihr Lebensraum. In: Schachtschabel et al (eds) Lehrbuch der Bodenkunde, 16th edn. Spektrum, Heidelberg/Berlin, pp 83–119
Khatisashvili G, Matchavariani L, Gakhokidze R (2015) Improving phytoremediation of soil polluted with oil hydrocarbons in Georgia. In: Chapter 19 in book “soil remediation and plants: prospects and challenges”. Elsevier—Amsterdam, Boston, Heidelberg, London, New York, Oxford, Paris, San Diego, San Francisco, Singapore, Sydney, Tokyo, pp 547–569
Knox AS, Seaman J, Adriano DC (2000) Chemostabilization of metals in contaminated soils. In: Wise DL, Trantolo DJ, Cichon EJ, Inyang HI, Stottermeier U (eds) Bioremediation of contaminted soils. Marcel Dekker, New York, Basel, pp 811–836
Kovda V, Rozanov B (1988). Soils science. High school, Moscow (Pochvovedenie. Vishaya shkola, Moskva)
Kretzschmar R (2010) Chemische Eigenschaften. In: Schachtschabel et al (eds) Lehrbuch der Bodenkunde, 16th edn. Spektrum, Heidelberg/Berlin, pp 122–170
Kumpiene J, Ore S, Renella G, Mench M, Lagerkvist A, Maurice C (2006) Assessment of zerovalent iron for stabilization of chromium, copper and arsenic in soil. Environ Pollut 144:62–69
Lezhava VV, Matchavariani LG (1983) Preventing the adverse effects of pesticides on the environment. Georgian scientific-research institute for scientific-technical information, overview information (GSRISTI, OI), vol 3, issue 3, pp 44 (Predotvrashenie otritsatelnogo deistvia estitsidov na okruzhaiushuyu sredu. GruzNIINTI, OI)
Lombi E, Zhao F-J, Wieshammer G, Zhang G, McGrath SP (2002) In situ fixation of metals in soils using bauxite residue: biological effects. Environ Pollut 118:445–452
Marschner B, Müller I, Stolz R, Stempelmann I (2010) Immobilisierung von Schwermetallen in Gartenböden. Bodenschutz 02:34–41
Matchavariani L, Kalandadze B (2012) Pollution of soils by heavy metals from irrigation near mining region of Georgia. vol. Forum Geogr XI(2):127–137
Matchavariani L, Kalandadze B, Lagidze L, Gokhelishvili N, Sulkhanishvili N, Paichadze N, Dvalashvili G (2015) Soil quality changes in response to their pollution of heavy metals in Georgia. J Environ Biol Spec Issue 36(1):85–91
McBride MB (1989) Reactions controlling heavy metals solubility in soils. Adv Soil Sci 10:1–56
Mench M, Manceau A, Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H, Mocquot B (2000) Capacity of soil amendments in lowering the phytoavailability of sludge-born zinc. Agronomie 20:383–397
Müller I (2000) Einfluss eisenoxidhaltiger Bodenzusätze auf die Mobilität von Schwermetallen in kontaminierten Böden. Dissertation, Boden und Landschaft 27. Justus Liebig University
Nurzhanova A, Kalugin S, Zhambakin K (2013) Obsolete pesticides and application of colonizing plant species for remediation of contaminated soil in Kazakhstan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2054–2063
Saet Yu, Basharkevich I, Revich B (1982) Methodical recommendations about a geochemical estimation of sources of environmental pollution. IMGRE
Sastre J, Hernadez E, Rodriguez R, Alcobe X, Vidal M, Rauret G (2004) Use of sorption and extraction tests to predict the dynamics of the interaction of trace elements in agricultural soils contaminated by a mine tailing accident. Sci Total Environ 329:261–281
Sauerbeck D (1982) Welche Schwermetallgehalte in Pflanzen dürfen nicht überschritten werden, um Wachstumsbeeinträchtigungen zu vermeiden? Landwirtsch Forsch Special Edition 39:108–129
Sayed MAHA (2006) Dynamik von Schwermetallen in belasteten schwarzerdeartigen Böden unter Bewässerung in Südost–Georgien. Dissertation, Boden und Landschaft 48, Justus Liebig University
Schatz M, Babaev E, Kalandadze B, Beuhm L, Deuring A (2015) Persistent organic pollutants in transcaucasian soils and sediments—the invisible heritage of former Soviet Union. In: 15th EuCheMS international conference on chemistry and the environment, Leipzig, Germany
VDLUFA (1976) Die chemische Untersuchung von Futtermitteln, 3. print. Verband Deutscher Landwirtschaftlicher Untersuchungs- und Forschungsanstalten, Speyer
Stahr K (2010) Anorganische Komponenten der Böden-Minerale und Gesteine. In: Schachtschabel et al (eds) Lehrbuch der Bodenkunde, 16th edn. Spektrum, Heidelberg/Berlin, pp 7–49
Usman ARAU (2004) Soil reclamation and conservation: evaluation of different additives for remediation and quality improvement of soil. Hohenheimer Bodenkundliche Hefte 73:Stuttgart
Vazhenin I (1987) Methods of definition the microelements in soils and plants. Kolos, Moscow
VDLUFA (1991) Methodenhandbuch I. Verband Deutscher Landwirtschaftlicher Untersuchungs- und Forschungsanstalten, Speyer
VDLUFA (1997) Phosphordüngung nach Bodenuntersuchung und Pflanzenbedarf. Verband Deutscher Landwirtschaftlicher Untersuchungs- und Forschungsanstalten, Darmstadt
Vinogradov AP (1957) Geochemistry of rare and absent-minded chemical elements in soils. ASUSSR, Moscow
Wilke B-M (2010) Gefährdung der Bodenfunktionen. In: Schachtschabel et al (eds) Lehrbuch der Bodenkunde, 16th edn. Spektrum, Heidelberg/Berlin, pp 449–520
Zeien H (1995) Chemische Extraktion zur Bestimmung der Bindungsformen von Schwermetallen in Böden Bonner. Dissertation, Bodenkundliche Abhandlungen, vol 17. Rheinische Friedrichs Wilhelm University
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kalandadze, B., Matchavariani, L. (2019). Soil Pollution. In: Matchavariani, L. (eds) The Soils of Georgia. World Soils Book Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18509-1_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18509-1_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-18508-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-18509-1
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)