Abstract
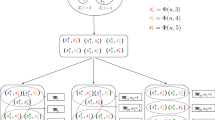
Neural embedding has been widely applied as an effective category of vectorization methods in real-world recommender systems. However, its exploration of users’ explicit feedback on items, to create good quality user and item vectors is still limited. Existing neural embedding methods only consider the items that are accessed by the users, but neglect the scenario when a user gives high or low rating to a particular item. In this paper, we propose Pref2Vec, a method to generate vector representations of pairwise item preferences, users and items, which can be directly utilized for machine learning tasks. Specifically, Pref2Vec considers users’ pairwise item preferences as elementary units. It vectorizes users’ pairwise preferences by maximizing the likelihood estimation of the conditional probability of each pairwise item preference given another one. With the pairwise preference matrix and the generated preference vectors, the vectors of users are yielded by minimizing the difference between users’ observed preferences and the product of the user and preference vectors. Similarly, the vectorization of items can be achieved with the user-item rating matrix and the users vectors. We conducted extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets to assess the quality of item vectors and the initialization independence of the user and item vectors. The utility of our vectorization results is shown by the recommendation performance achieved using them. Our experimental results show significant improvement over state-of-the-art baselines.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barkan, O., Koenigstein, N.: Item2Vec: neural item embedding for collaborative filtering. In: MLSP, pp. 1–6 (2016)
Bengio, Y., Ducharme, R., Vincent, P., Janvin, C.: A neural probabilistic language model. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 3, 1137–1155 (2003)
Bhingardive, S., Singh, D., V, R., Redkar, H.H., Bhattacharyya, P.: Unsupervised most frequent sense detection using word embeddings. In: HLT-NAACL, pp. 1238–1243 (2015)
Bordes, A., Usunier, N., Garcia-Durán, A., Weston, J., Yakhnenko, O.: Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. In: NIPS, pp. 2787–2795 (2013)
Breese, J.S., Heckerman, D., Kadie, C.: Empirical analysis of predictive algorithms for collaborative filtering. In: UAI, pp. 43–52 (1998)
Choi, S., Cha, S., Tapper, C.C.: A survey of binary similarity and distance measures. J. Systemics Cybern. Inform. 8(1), 43–48 (2010)
Cohen, W.W., Schapire, R.E., Singer, Y.: Learning to order things. J. Art. Int. Res. 10(1), 243–270 (1999)
Collobert, R., Weston, J., Bottou, L., Karlen, M., Kavukcuoglu, K., Kuksa, P.: Natural language processing (almost) from scratch. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2493–2537 (2011)
Djuric, N., Wu, H., Radosavljevic, V., Grbovic, M., Bhamidipati, N.: Hierarchical neural language models for joint representation of streaming documents and their content. In: WWW, pp. 248–255 (2015)
Garey, M.R., Johnson, D.S.: Computers and Intractability; A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness. W. H. Freeman & Co., New York (1990)
Grbovic, M., et al.: E-commerce in your inbox: Product recommendations at scale. In: SIGKDD, pp. 1809–1818 (2015)
Grover, A., Leskovec, J.: Node2vec: scalable feature learning for networks. In: SIGKDD, pp. 855–864 (2016)
He, X., Liao, L., Zhang, H., Nie, L., Hu, X., Chua, T.S.: Neural collaborative filtering. In: WWW, pp. 173–182 (2017)
He, X., Zhang, H., Kan, M.Y., Chua, T.S.: Fast matrix factorization for online recommendation with implicit feedback. In: SIGIR, pp. 549–558 (2016)
Herlocker, J., Konstan, J.A., Riedl, J.: An empirical analysis of design choices in neighborhood-based collaborative filtering algorithms. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 5, 287–310 (2002)
Hosmer Jr., D.W., Lemeshow, S., Sturdivant, R.X.: Applied Logistic Regression, vol. 398. Wiley, Hoboken (2013)
Järvelin, K., Kekäläinen, J.: Cumulated gain-based evaluation of IR techniques. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 20(4), 422–446 (2002)
Koren, Y., Bell, R., Volinsky, C.: Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer 42(8), 30–37 (2009)
Lample, G., Ballesteros, M., Subramanian, S., Kawakami, K., Dyer, C.: Neural architectures for named entity recognition. In: HLT-NAACL, pp. 260–270 (2016)
Le, Q., Mikolov, T.: Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In: ICML, pp. 1188–1196 (2014)
Liu, N.N., Yang, Q.: Eigenrank: a ranking-oriented approach to collaborative filtering. In: SIGIR, pp. 83–90 (2008)
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., Dean, J.: Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. CoRR abs/1301.3781 (2013)
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G.S., Dean, J.: Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: NIPS, pp. 3111–3119 (2013)
Perozzi, B., Al-Rfou, R., Skiena, S.: Deepwalk: online learning of social representations. In: SIGKDD, pp. 701–710 (2014)
Schwenk, H.: Continuous space language models. Comput. Speech Lang. 21(3), 492–518 (2007)
Socher, R., Chen, D., Manning, C.D., Ng, A.: Reasoning with neural tensor networks for knowledge base completion. In: NIPS, pp. 926–934 (2013)
Socher, R., Lin, C.C., Ng, A.Y., Manning, C.D.: Parsing natural scenes and natural language with recursive neural networks. In: ICML (2011)
Turian, J., Ratinov, L., Bengio, Y.: Word representations: a simple and general method for semi-supervised learning. In: ACL, pp. 384–394 (2010)
Turney, P.D.: Distributional semantics beyond words: supervised learning of analogy and paraphrase. TACL 1, 353–366 (2013)
Zou, W.Y., Socher, R., Cer, D.M., Manning, C.D.: Bilingual word embeddings for phrase-based machine translation. In: EMNLP, pp. 1393–1398 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pandey, G., Wang, S., Ren, Z., Chang, Y. (2019). Vectors of Pairwise Item Preferences. In: Azzopardi, L., Stein, B., Fuhr, N., Mayr, P., Hauff, C., Hiemstra, D. (eds) Advances in Information Retrieval. ECIR 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11437. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15712-8_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15712-8_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-15711-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-15712-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)