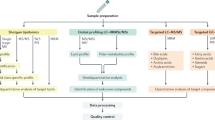
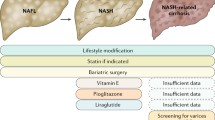
Abstract
The increasing global prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has prompted efforts to identify affected subjects. In particular, the identification of the presence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and fibrosis in patients with NAFLD has become a priority. The widely-recognized limitations of liver biopsy as ‘gold standard’ for NASH diagnosis have encouraged the search for non-invasive biomarkers that facilitate risk stratification of patients and the conduction of clinical trials and drug development. In this chapter, we introduce the emerging ‘omics’ approaches in the biomarker research in NAFLD. We have summarized the latest innovations in lipidomics, proteomics and microRNA biomarkers, and described the most common panels of blood-based biomarkers for the diagnosis of different stages of NAFLD, from simple steatosis to NASH with varying degrees of fibrosis. We also review some examples of the application of circulating biomarkers in clinical trial for drug development.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aby E, Saab S. Nonobese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2017;10(5):130–3.
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41(6):1313–21.
Cohen JC, Horton JD, Hobbs HH. Human fatty liver disease: old questions and new insights. Science. 2011;332(6037):1519–23.
Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):328–57.
European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64(6):1388–402.
Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Rinella M, Sanyal AJ. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. 2018;24(7):908–22.
Filozof C, Goldstein BJ, Williams RN, Sanyal A. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: limited available treatment options but promising drugs in development and recent progress towards a regulatory approval pathway. Drugs. 2015;75(12):1373–92.
Fuchs M. New medical treatment strategies for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2015;13(2):259–73.
Wegermann K, Diehl AM, Moylan CA. Disease pathways and molecular mechanisms of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Liver Dis. 2018;11(4):87–91.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–97.
Pasquinelli AE. MicroRNAs and their targets: recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13(4):271–82.
Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12(12):861–74.
Li Y, Kowdley KV. MicroRNAs in common human diseases. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2012;10(5):246–53.
Gori M, Arciello M, Balsano C. MicroRNAs in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: novel biomarkers and prognostic tools during the transition from steatosis to hepatocarcinoma. Bio Med Res Int. 2014;2014:741465.
Paul P, Chakraborty A, Sarkar D, Langthasa M, Rahman M, Bari M, et al. Interplay between miRNAs and human diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(3):2007–18.
Catalanotto C, Cogoni C, Zardo G. MicroRNA in control of gene expression: an overview of nuclear functions. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(10)
Roberts TC. The MicroRNA biology of the mammalian nucleus. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2014;3:e188.
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(3):228–34.
Du T, Zamore PD. microPrimer: the biogenesis and function of microRNA. Dev Camb Engl. 2005;132(21):4645–52.
Rayner KJ, Hennessy EJ. Extracellular communication via microRNA: lipid particles have a new message. J Lipid Res. 2013;54(5):1174–81.
Baffy G. MicroRNAs in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Med. 2015;4(12):1977–88.
Tan Y, Ge G, Pan T, Wen D, Gan J. A pilot study of serum microRNAs panel as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105192.
Ceccarelli S, Panera N, Gnani D, Nobili V. Dual role of microRNAs in NAFLD. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(4):8437–55.
Zen K, Zhang C-Y. Circulating microRNAs: a novel class of biomarkers to diagnose and monitor human cancers. Med Res Rev. 2012;32(2):326–48.
Bala S, Marcos M, Szabo G. Emerging role of microRNAs in liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(45):5633–40.
Cermelli S, Ruggieri A, Marrero JA, Ioannou GN, Beretta L. Circulating microRNAs in patients with chronic hepatitis C and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23937.
Yamada H, Suzuki K, Ichino N, Ando Y, Sawada A, Osakabe K, et al. Associations between circulating microRNAs (miR-21, miR-34a, miR-122 and miR-451) and non-alcoholic fatty liver. Clin Chim Acta. 2013;424:99–103.
Pirola CJ, Fernández Gianotti T, Castaño GO, Mallardi P, San Martino J, Mora Gonzalez Lopez Ledesma M, et al. Circulating microRNA signature in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: from serum non-coding RNAs to liver histology and disease pathogenesis. Gut. 2015;64(5):800–12.
Csak T, Bala S, Lippai D, Satishchandran A, Catalano D, Kodys K, et al. microRNA-122 regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and vimentin in hepatocytes and correlates with fibrosis in diet-induced steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 2015;35(2):532–41.
Szabo G, Csak T. Role of MicroRNAs in NAFLD/NASH. Dig Dis Sci. 2016;61(5):1314–24.
Becker PP, Rau M, Schmitt J, Malsch C, Hammer C, Bantel H, et al. Performance of serum microRNAs −122, −192 and −21 as biomarkers in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0142661.
Ge W, Yu D-C, Li Q-G, Chen X, Zhang C-Y, Ding Y-T. Expression of serum miR-16, let-7f, and miR-21 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and their clinical significances. Clin Lab. 2014;60(3):427–34.
Francque SM, Ratziu V, Harrison S, Anstee Q, Bedossa P, Cordonnier G, et al. Validation of mir-34a, mir-122 and mir-200a as biomarkers for identification of NASH patients eligible for treatment. Hepatology. 2016;64(6):1119A.
Su Q, Kumar V, Sud N, Mahato RI. MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis and treatment of progressive liver injury in NAFLD and liver fibrosis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;129:54–63.
Castro RE, Ferreira DMS, Afonso MB, Borralho PM, Machado MV, Cortez-Pinto H, et al. miR-34a/SIRT1/p53 is suppressed by ursodeoxycholic acid in the rat liver and activated by disease severity in human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2013;58(1):119–25.
Ding J, Li M, Wan X, Jin X, Chen S, Yu C, et al. Effect of miR-34a in regulating steatosis by targeting PPARα expression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13729.
Ren F-H, Yang H, He R-Q, Lu J-N, Lin X-G, Liang H-W, et al. Analysis of microarrays of miR-34a and its identification of prospective target gene signature in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):12.
Cordonnier G, Texier F, Noel B, Degallaix N, Sudrick FB, Brozek J, et al. Expression profiling of 728 miRNAs in a NASH model identifies excellent correlations of hepatic and circulation miR-34a levels with histological lesions in rats and men. J Hepatol. 2018;68:S347–8.
Jiang L, Cheng Q, Zhang B-H, Zhang M-Z. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma screening: a validation set from China. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(10):e603.
Sun C, Huang F, Liu X, Xiao X, Yang M, Hu G, et al. miR-21 regulates triglyceride and cholesterol metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by targeting HMGCR. Int J Mol Med. 2015;35(3):847–53.
Wu H, Ng R, Chen X, Steer CJ, Song G. MicroRNA-21 is a potential link between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma via modulation of the HBP1-p53-Srebp1c pathway. Gut. 2016;65(11):1850–60.
Wen Y, Han J, Chen J, Dong J, Xia Y, Liu J, et al. Plasma miRNAs as early biomarkers for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2015;137(7):1679–90.
Povero D, de Araujo Horcel L, Eguchi A, Johnson C, Kneiber D, Feldstein AE. MiR-128-3p is enriched in the liver of murine models of NASH and is a key contributor to liver fibrosis via modulation of hepatic stellate cell phenotype. Proceedings of The 66th Annual Meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: The Liver Meeting. San Francisco, CA; 2015. p. 13–7.
Lambrecht J, Jan Poortmans P, Verhulst S, Reynaert H, Mannaerts I, van Grunsven LA. Circulating ECV-associated miRNAs as potential clinical biomarkers in early stage HBV and HCV induced liver fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:56.
Matsuura K, De Giorgi V, Schechterly C, Wang RY, Farci P, Tanaka Y, et al. Circulating let-7 levels in plasma and extracellular vesicles correlate with hepatic fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol Baltim Md. 2016;64(3):732–45.
Amacher DE. Progress in the search for circulating biomarkers of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Biomarkers. 2014;19(7):541–52.
Yilmaz Y. Serum proteomics for biomarker discovery in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2012;413(15–16):1190–3.
Nuño-Lámbarri N, Barbero-Becerra VJ, Uribe M, Chávez-Tapia NC. Mitochondrial molecular pathophysiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a proteomics approach. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(3):281.
Pratt DS, Kaplan MM. Evaluation of abnormal liver-enzyme results in asymptomatic patients. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(17):1266–71.
Angulo P, Hui JM, Marchesini G, Bugianesi E, George J, Farrell GC, et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology. 2007;45(4):846–54.
Fracanzani AL, Valenti L, Bugianesi E, Andreoletti M, Colli A, Vanni E, et al. Risk of severe liver disease in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with normal aminotransferase levels: a role for insulin resistance and diabetes. Hepatology. 2008;48(3):792–8.
Mofrad P, Contos MJ, Haque M, Sargeant C, Fisher RA, Luketic VA, et al. Clinical and histologic spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associated with normal ALT values. Hepatology. 2003;37(6):1286–92.
Papagianni M, Sofogianni A, Tziomalos K. Non-invasive methods for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Hepatol. 2015;7(4):638–48.
Neuman MG, Cohen LB, Nanau RM. Biomarkers in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;28(11):607–18.
Sookoian S, Castaño GO, Scian R, Fernández Gianotti T, Dopazo H, Rohr C, et al. Serum aminotransferases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are a signature of liver metabolic perturbations at the amino acid and Krebs cycle level. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;103(2):422–34.
Feldstein AE, Wieckowska A, Lopez AR, Liu Y-C, Zein NN, McCullough AJ. Cytokeratin-18 fragment levels as noninvasive biomarkers for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a multicenter validation study. Hepatology. 2009;50(4):1072–8.
Bantel H, Lügering A, Heidemann J, Volkmann X, Poremba C, Strassburg CP, et al. Detection of apoptotic caspase activation in sera from patients with chronic HCV infection is associated with fibrotic liver injury. Hepatology. 2004;40(5):1078–87.
Kramer G, Erdal H, Mertens HJMM, Nap M, Mauermann J, Steiner G, et al. Differentiation between cell death modes using measurements of different soluble forms of extracellular cytokeratin 18. Cancer Res. 2004;64(5):1751–6.
Wieckowska A, Zein NN, Yerian LM, Lopez AR, McCullough AJ, Feldstein AE. In vivo assessment of liver cell apoptosis as a novel biomarker of disease severity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2006;44(1):27–33.
Kawanaka M, Nishino K, Nakamura J, Urata N, Oka T, Goto D, et al. Correlation between serum cytokeratin-18 and the progression or regression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann Hepatol. 2015;14(6):837–44.
Mandelia C, Collyer E, Mansoor S, Lopez R, Lappe S, Nobili V, et al. Plasma cytokeratin-18 level as a novel biomarker for liver fibrosis in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2016;63(2):181–7.
Cusi K, Chang Z, Harrison S, Lomonaco R, Bril F, Orsak B, et al. Limited value of plasma cytokeratin-18 as a biomarker for NASH and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2014;60(1):167–74.
Chen J, Zhu Y, Zheng Q, Jiang J. Serum cytokeratin-18 in the diagnosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a meta-analysis. Hepatol Res. 2014;44(8):854–62.
Pimentel CFMG, Jiang ZG, Otsubo T, Feldbrügge L, Challies TL, Nasser I, et al. Poor inter-test reliability between CK18 kits as a biomarker of NASH. Dig Dis Sci. 2016;61(3):905–12.
Li H, Fang Q, Gao F, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang X, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 levels are increased in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients and are correlated with hepatic triglyceride. J Hepatol. 2010;53(5):934–40.
Yan H, Xia M, Chang X, Xu Q, Bian H, Zeng M, et al. Circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 levels are closely associated with hepatic fat content: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24895.
Yilmaz Y, Eren F, Yonal O, Kurt R, Aktas B, Celikel CA, et al. Increased serum FGF21 levels in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur J Clin Investig. 2010;40(10):887–92.
Dushay J, Chui PC, Gopalakrishnan GS, Varela-Rey M, Crawley M, Fisher FM, et al. Increased fibroblast growth factor 21 in obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(2):456–63.
Zhang X, Yeung DCY, Karpisek M, Stejskal D, Zhou Z-G, Liu F, et al. Serum FGF21 levels are increased in obesity and are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in humans. Diabetes. 2008;57(5):1246–53.
Shen J, Chan HL-Y, Wong GL-H, Choi PC-L, Chan AW-H, Chan H-Y, et al. Non-invasive diagnosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by combined serum biomarkers. J Hepatol. 2012;56(6):1363–70.
Wu G, Li H, Fang Q, Zhang J, Zhang M, Zhang L, et al. Complementary role of fibroblast growth factor 21 and cytokeratin 18 in monitoring the different stages of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5095.
Yang M, Xu D, Liu Y, Guo X, Li W, Guo C, et al. Combined serum biomarkers in non-invasive diagnosis of non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0131664.
Newcomer ME, Ong DE. Plasma retinol binding protein: structure and function of the prototypic lipocalin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1482(1–2):57–64.
Graham TE, Yang Q, Blüher M, Hammarstedt A, Ciaraldi TP, Henry RR, et al. Retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in lean, obese, and diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(24):2552–63.
Terra X, Auguet T, Broch M, Sabench F, Hernández M, Pastor RM, et al. Retinol binding protein-4 circulating levels were higher in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease vs. histologically normal liver from morbidly obese women. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013;21(1):170–7.
Stefan N, Hennige AM, Staiger H, Machann J, Schick F, Schleicher E, et al. High circulating retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with elevated liver fat but not with total, subcutaneous, visceral, or intramyocellular fat in humans. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(5):1173–8.
Seo JA, Kim NH, Park SY, Kim HY, Ryu OH, Lee KW, et al. Serum retinol-binding protein 4 levels are elevated in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Endocrinol. 2008;68(4):555–60.
Chen X, Shen T, Li Q, Chen X, Li Y, Li D, et al. Retinol binding protein-4 levels and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a community-based cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. 2017;7:45100.
Bell LN, Theodorakis JL, Vuppalanchi R, Saxena R, Bemis KG, Wang M, et al. Serum proteomics and biomarker discovery across the spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;51(1):111–20.
Polyzos SA, Toulis KA, Goulis DG, Zavos C, Kountouras J. Serum total adiponectin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism. 2011;60(3):313–26.
Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Mantzoros CS. Leptin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a narrative review. Metabolism. 2015;64(1):60–78.
Adolph TE, Grander C, Grabherr F, Tilg H. Adipokines and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: multiple interactions. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(8):1649.
Senn JJ, Klover PJ, Nowak IA, Zimmers TA, Koniaris LG, Furlanetto RW, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS-3), a potential mediator of interleukin-6-dependent insulin resistance in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(16):13740–6.
Kim J-H, Bachmann RA, Chen J. Interleukin-6 and insulin resistance. Vitam Horm. 2009;80:613–33.
Jarrar MH, Baranova A, Collantes R, Ranard B, Stepanova M, Bennett C, et al. Adipokines and cytokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27(5):412–21.
Wieckowska A, Papouchado BG, Li Z, Lopez R, Zein NN, Feldstein AE. Increased hepatic and circulating interleukin-6 levels in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103(6):1372–9.
García-Galiano D, Sánchez-Garrido MA, Espejo I, Montero JL, Costán G, Marchal T, et al. IL-6 and IGF-1 are independent prognostic factors of liver steatosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in morbidly obese patients. Obes Surg. 2007;17(4):493–503.
Jamali R, Arj A, Razavizade M, Aarabi MH. Prediction of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via a novel panel of serum adipokines. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(5):e2630.
Vonghia L, Francque S. Cross talk of the immune system in the adipose tissue and the liver in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: pathology and beyond. World J Hepatol. 2015;7(15):1905–12.
Tamimi TIA-R, Elgouhari HM, Alkhouri N, Yerian LM, Berk MP, Lopez R, et al. An apoptosis panel for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis diagnosis. J Hepatol. 2011;54(6):1224–9.
Feldstein AE, Canbay A, Guicciardi ME, Higuchi H, Bronk SF, Gores GJ. Diet associated hepatic steatosis sensitizes to Fas mediated liver injury in mice. J Hepatol. 2003;39(6):978–83.
Alkhouri N, Alisi A, Okwu V, Matloob A, Ferrari F, Crudele A, et al. Circulating soluble fas and fas ligand levels are elevated in children with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60(8):2353–9.
Manousou P, Kalambokis G, Grillo F, Watkins J, Xirouchakis E, Pleguezuelo M, et al. Serum ferritin is a discriminant marker for both fibrosis and inflammation in histologically proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Liver Int. 2011;31(5):730–9.
Kowdley KV, Belt P, Wilson LA, Yeh MM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Chalasani N, et al. Serum ferritin is an independent predictor of histologic severity and advanced fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2012;55(1):77–85.
Yoneda M, Nozaki Y, Endo H, Mawatari H, Iida H, Fujita K, et al. Serum ferritin is a clinical biomarker in Japanese patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) independent of HFE gene mutation. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55(3):808–14.
Yu C, Xu C, Xu L, Yu J, Miao M, Li Y. Serum proteomic analysis revealed diagnostic value of hemoglobin for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2012;56(1):241–7.
Nielsen MJ, Nedergaard AF, Sun S, Veidal SS, Larsen L, Zheng Q, et al. The neo-epitope specific PRO-C3 ELISA measures true formation of type III collagen associated with liver and muscle parameters. Am J Transl Res. 2013;5(3):303–15.
Tanwar S, Trembling PM, Guha IN, Parkes J, Kaye P, Burt AD, et al. Validation of terminal peptide of procollagen III for the detection and assessment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2013;57(1):103–11.
Karsdal MA, Henriksen K, Nielsen MJ, Byrjalsen I, Leeming DJ, Gardner S, et al. Fibrogenesis assessed by serological type III collagen formation identifies patients with progressive liver fibrosis and responders to a potential antifibrotic therapy. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016;311(6):G1009–17.
Younossi ZM, Loomba R, Anstee QM, Rinella ME, Bugianesi E, Marchesini G, et al. Diagnostic Modalities for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and Associated Fibrosis. Hepatology. 2018;68(1):349–60.
Kamada Y, Ono M, Hyogo H, Fujii H, Sumida Y, Mori K, et al. A novel noninvasive diagnostic method for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis using two glycobiomarkers. Hepatology. 2015;62(5):1433–43.
Boga S, Koksal AR, Alkim H, Yilmaz Ozguven MB, Bayram M, Ergun M, et al. Plasma Pentraxin 3 Differentiates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) from Non-NASH. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2015;13(9):393–9.
Yeniova AO, Küçükazman M, Ata N, Dal K, Kefeli A, Başyiğit S, et al. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is a strong predictor of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2014;61(130):422–5.
Akbal E, Koçak E, Akyürek Ö, Köklü S, Batgi H, Şenes M. Liver fatty acid-binding protein as a diagnostic marker for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2016;128(1–2):48–52.
Colak Y, Senates E, Ozturk O, Yilmaz Y, Coskunpinar E, Kahraman OT, et al. Plasma fibrinogen-like protein 2 levels in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2011;58(112):2087–90.
Nicholson JK, Lindon JC. Systems biology: metabonomics. Nature. 2008;455(7216):1054–6.
Mato JM, Martínez-Chantar ML, Lu SC. Systems biology for hepatologists. Hepatology. 2014;60(2):736–43.
Holmes E, Wijeyesekera A, Taylor-Robinson SD, Nicholson JK. The promise of metabolic phenotyping in gastroenterology and hepatology. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;12(8):458–71.
Patti GJ, Yanes O, Siuzdak G. Innovation: metabolomics: the apogee of the omics trilogy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(4):263–9.
Cano A, Alonso C. Deciphering non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through metabolomics. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014;42(5):1447–52.
Alonso C, Fernández-Ramos D, Varela-Rey M, Martínez-Arranz I, Navasa N, Van Liempd SM, et al. Metabolomic identification of subtypes of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(6):1449–1461.e7.
Iruarrizaga-Lejarreta M, Varela-Rey M, Fernández-Ramos D, Martínez-Arranz I, Delgado TC, Simon J, et al. Role of aramchol in steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice. Hepatol Commun. 2017;1(9):911–27.
Psychogios N, Hau DD, Peng J, Guo AC, Mandal R, Bouatra S, et al. The human serum metabolome. PLoS One. 2011;6(2):e16957.
Quehenberger O, Armando AM, Brown AH, Milne SB, Myers DS, Merrill AH, et al. Lipidomics reveals a remarkable diversity of lipids in human plasma. J Lipid Res. 2010;51(11):3299–305.
Puri P, Wiest MM, Cheung O, Mirshahi F, Sargeant C, Min H-K, et al. The plasma lipidomic signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2009;50(6):1827–38.
Barr J, Vázquez-Chantada M, Alonso C, Pérez-Cormenzana M, Mayo R, Galán A, et al. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based parallel metabolic profiling of human and mouse model serum reveals putative biomarkers associated with the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Proteome Res. 2010;9(9):4501–12.
Feldstein AE, Lopez R, Tamimi TA-R, Yerian L, Chung Y-M, Berk M, et al. Mass spectrometric profiling of oxidized lipid products in human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Lipid Res. 2010;51(10):3046–54.
Kalhan SC, Guo L, Edmison J, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ, Hanson RW, et al. Plasma metabolomic profile in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism. 2011;60(3):404–13.
Gorden DL, Ivanova PT, Myers DS, McIntyre JO, VanSaun MN, Wright JK, et al. Increased diacylglycerols characterize hepatic lipid changes in progression of human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; comparison to a murine model. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22775.
Barr J, Caballería J, Martínez-Arranz I, Domínguez-Díez A, Alonso C, Muntané J, et al. Obesity-dependent metabolic signatures associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression. J Proteome Res. 2012;11(4):2521–32.
Orešič M, Hyötyläinen T, Kotronen A, Gopalacharyulu P, Nygren H, Arola J, et al. Prediction of non-alcoholic fatty-liver disease and liver fat content by serum molecular lipids. Diabetologia. 2013;56(10):2266–74.
Gorden DL, Myers DS, Ivanova PT, Fahy E, Maurya MR, Gupta S, et al. Biomarkers of NAFLD progression: a lipidomics approach to an epidemic. J Lipid Res. 2015;56(3):722–36.
Loomba R, Quehenberger O, Armando A, Dennis EA. Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolites as novel lipidomic biomarkers for noninvasive diagnosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Lipid Res. 2015;56(1):185–92.
Pietiläinen KH, Sysi-Aho M, Rissanen A, Seppänen-Laakso T, Yki-Järvinen H, Kaprio J, et al. Acquired obesity is associated with changes in the serum lipidomic profile independent of genetic effects--a monozygotic twin study. PLoS One. 2007;2(2):e218.
Kim JY, Park JY, Kim OY, Ham BM, Kim H-J, Kwon DY, et al. Metabolic profiling of plasma in overweight/obese and lean men using ultra performance liquid chromatography and Q-TOF mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF MS). J Proteome Res. 2010;9(9):4368–75.
Zhang A, Sun H, Wang X. Power of metabolomics in biomarker discovery and mining mechanisms of obesity. Obes Rev. 2013;14(4):344–9.
Xie B, Waters MJ, Schirra HJ. Investigating potential mechanisms of obesity by metabolomics. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:805683.
Kimberly WT, O’Sullivan JF, Nath AK, Keyes M, Shi X, Larson MG, et al. Metabolite profiling identifies anandamide as a biomarker of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. JCI Insight. 2017;2(9)
Tokushige K, Hashimoto E, Kodama K, Tobari M, Matsushita N, Kogiso T, et al. Serum metabolomic profile and potential biomarkers for severity of fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol. 2013;48(12):1392–400.
Charlton M, Angulo P, Chalasani N, Merriman R, Viker K, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, et al. Low circulating levels of dehydroepiandrosterone in histologically advanced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2008;47(2):484–92.
Puri P, Baillie RA, Wiest MM, Mirshahi F, Choudhury J, Cheung O, et al. A lipidomic analysis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2007;46(4):1081–90.
Dennis EA, Norris PC. Eicosanoid storm in infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15(8):511–23.
Zhou Y, Orešič M, Leivonen M, Gopalacharyulu P, Hyysalo J, Arola J, et al. Noninvasive detection of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis using clinical markers and circulating levels of lipids and metabolites. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(10):1463–1472.e6.
Chalasani N, Guo X, Loomba R, Goodarzi MO, Haritunians T, Kwon S, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants associated with histologic features of nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(5):1567–76, 1576.e1–6
Luukkonen PK, Zhou Y, Hyötyläinen T, Leivonen M, Arola J, Orho-Melander M, et al. The MBOAT7 variant rs641738 alters hepatic phosphatidylinositols and increases severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in humans. J Hepatol. 2016;65(6):1263–5.
Alonso C, Mato JM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. In: Nicholls A, Theodoridis G, Wilson ID, editors. Global metabolic profiling: clinical applications: Future Science Ltd; 2014. p. 110–22.
Mayo R, Crespo J, Martínez-Arranz I, Banales JM, Arias M, Mincholé I, et al. Metabolomic-based noninvasive serum test to diagnose nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: results from discovery and validation cohorts. Hepatol Commun. 2018;2(7):807–20.
Bril F, Millán L, Kalavalapalli S, McPhaul MJ, Caulfield MP, Martinez-Arranz I, et al. Use of a metabolomic approach to non-invasively diagnose non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20(7):1702–9.
Rinella ME, Sanyal AJ. NAFLD in 2014: genetics, diagnostics and therapeutic advances in NAFLD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;12(2):65–6.
Buzzetti E, Pinzani M, Tsochatzis EA. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism. 2016;65(8):1038–48.
Machado MV, Cortez-Pinto H. Non-invasive diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. A critical appraisal. J Hepatol. 2013;58(5):1007–19.
Poynard T, Imbert-Bismut F, Munteanu M, Ratziu V. FibroTest-FibroSURE: towards a universal biomarker of liver fibrosis? Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2005;5(1):15–21.
Munteanu M, Tiniakos D, Anstee Q, Charlotte F, Marchesini G, Bugianesi E, et al. Diagnostic performance of FibroTest, SteatoTest and ActiTest in patients with NAFLD using the SAF score as histological reference. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;44(8):877–89.
Bedogni G, Bellentani S, Miglioli L, Masutti F, Passalacqua M, Castiglione A, et al. The Fatty Liver Index: a simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006;6:33.
Bedogni G, Kahn HS, Bellentani S, Tiribelli C. A simple index of lipid overaccumulation is a good marker of liver steatosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010;10:98.
Kotronen A, Seppänen-Laakso T, Westerbacka J, Kiviluoto T, Arola J, Ruskeepää A-L, et al. Hepatic stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD)-1 activity and diacylglycerol but not ceramide concentrations are increased in the nonalcoholic human fatty liver. Diabetes. 2009;58(1):203–8.
Lee J-H, Kim D, Kim HJ, Lee C-H, Yang JI, Kim W, et al. Hepatic steatosis index: a simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2010;42(7):503–8.
Poynard T, Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Messous D, Munteanu M, Imbert-Bismut F, et al. Diagnostic value of biochemical markers (NashTest) for the prediction of non alcoholo steato hepatitis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006;6:34.
Younossi ZM, Page S, Rafiq N, Birerdinc A, Stepanova M, Hossain N, et al. A biomarker panel for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and NASH-related fibrosis. Obes Surg. 2011;21(4):431–9.
Kaswala DH, Lai M, Afdhal NH. Fibrosis Assessment in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in 2016. Dig Dis Sci. 2016;61(5):1356–64.
Cheah MC, McCullough AJ, Goh GB-B. Current modalities of fibrosis assessment in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2017;5(3):261–71.
Enomoto H, Bando Y, Nakamura H, Nishiguchi S, Koga M. Liver fibrosis markers of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(24):7427–35.
Buzzetti E, Lombardi R, De Luca L, Tsochatzis EA. Noninvasive assessment of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:343828.
Halfon P, Munteanu M, Poynard T. FibroTest-ActiTest as a non-invasive marker of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2008;32(6 Suppl 1):22–39.
Ratziu V, Massard J, Charlotte F, Messous D, Imbert-Bismut F, Bonyhay L, et al. Diagnostic value of biochemical markers (FibroTest-FibroSURE) for the prediction of liver fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006;6:6.
Lassailly G, Caiazzo R, Hollebecque A, Buob D, Leteurtre E, Arnalsteen L, et al. Validation of noninvasive biomarkers (FibroTest, SteatoTest, and NashTest) for prediction of liver injury in patients with morbid obesity. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;23(6):499–506.
McPherson S, Stewart SF, Henderson E, Burt AD, Day CP. Simple non-invasive fibrosis scoring systems can reliably exclude advanced fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut. 2010;59(9):1265–9.
Shah AG, Lydecker A, Murray K, Tetri BN, Contos MJ, Sanyal AJ. Use of the Fib-4 index for non-invasive evaluation of fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7(10):1104–12.
Musso G, Gambino R, Cassader M, Pagano G. Meta-analysis: natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive tests for liver disease severity. Ann Med. 2011;43(8):617–49.
Treeprasertsuk S, Björnsson E, Enders F, Suwanwalaikorn S, Lindor KD. NAFLD fibrosis score: a prognostic predictor for mortality and liver complications among NAFLD patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(8):1219–29.
Lichtinghagen R, Pietsch D, Bantel H, Manns MP, Brand K, Bahr MJ. The Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) score: normal values, influence factors and proposed cut-off values. J Hepatol. 2013;59(2):236–42.
Guha IN, Parkes J, Roderick P, Chattopadhyay D, Cross R, Harris S, et al. Noninvasive markers of fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: validating the European liver fibrosis panel and exploring simple markers. Hepatology. 2008;47(2):455–60.
Calès P, Boursier J, Oberti F, Gallois Y, Rousselet M-C, Moal V, et al. [FibroMeters: a family of blood tests for liver fibrosis with high diagnostic performance and applicability in clinical practice]. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2009;57(6):459–62.
Cichoż-Lach H, Celiński K, Prozorow-Król B, Swatek J, Słomka M, Lach T. The BARD score and the NAFLD fibrosis score in the assessment of advanced liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Med Sci Monit. 2012;18(12):CR735–40.
Lee TH, Han SH, Yang JD, Kim D, Ahmed M. Prediction of advanced fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an enhanced model of BARD score. Gut Liver. 2013;7(3):323–8.
Ruffillo G, Fassio E, Alvarez E, Landeira G, Longo C, Domínguez N, et al. Comparison of NAFLD fibrosis score and BARD score in predicting fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2011;54(1):160–3.
Loaeza-del-Castillo A, Paz-Pineda F, Oviedo-Cárdenas E, Sánchez-Avila F, Vargas-Vorácková F. AST to platelet ratio index (APRI) for the noninvasive evaluation of liver fibrosis. Ann Hepatol. 2008;7(4):350–7.
Ratziu V, Giral P, Charlotte F, Bruckert E, Thibault V, Theodorou I, et al. Liver fibrosis in overweight patients. Gastroenterology. 2000;118(6):1117–23.
Ampuero J, Aller R, Gallego-Durán R, Bañales J, Crespo J, Villar-Gomez E, et al. Hepamet score: a new non-invasive method for NAFLD-related fibrosis screening in clinical practice. J Hepatol. 2018;68:S97–8.
Subasi CF, Aykut UE, Yilmaz Y. Comparison of noninvasive scores for the detection of advanced fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;27(2):137–41.
Adams LA, George J, Bugianesi E, Rossi E, De Boer WB, van der Poorten D, et al. Complex non-invasive fibrosis models are more accurate than simple models in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26(10):1536–43.
Sun W, Cui H, Li N, Wei Y, Lai S, Yang Y, et al. Comparison of FIB-4 index, NAFLD fibrosis score and BARD score for prediction of advanced fibrosis in adult patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis study. Hepatol Res. 2016;46(9):862–70.
Boursier J, Vergniol J, Guillet A, Hiriart J-B, Lannes A, Le Bail B, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic significance of blood fibrosis tests and liver stiffness measurement by FibroScan in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;65(3):570–8.
Siddiqui MS, Harrison SA, Abdelmalek MF, Anstee QM, Bedossa P, Castera L, et al. Case definitions for inclusion and analysis of endpoints in clinical trials for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through the lens of regulatory science. Hepatology. 2018;67(5):2001–12.
Sanyal AJ, Abdelmalek MF, Suzuki A, Cummings OW, Chojkier M, EPE-A Study Group. No significant effects of ethyl-eicosapentanoic acid on histologic features of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in a phase 2 trial. Gastroenterology. 2014;147(2):377–384.e1.
Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Loomba R, Sanyal AJ, Lavine JE, Van Natta ML, Abdelmalek MF, et al. Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;385(9972):956–65.
Mudaliar S, Henry RR, Sanyal AJ, Morrow L, Marschall H-U, Kipnes M, et al. Efficacy and safety of the farnesoid X receptor agonist obeticholic acid in patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(3):574–582.e1.
Cusi K, Orsak B, Bril F, Lomonaco R, Hecht J, Ortiz-Lopez C, et al. Long-term pioglitazone treatment for patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and prediabetes or type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2016;165(5):305–15.
Bril F, Kalavalapalli S, Clark VC, Lomonaco R, Soldevila-Pico C, Liu I-C, et al. Response to pioglitazone in patients with nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis with vs without type 2 diabetes. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(4):558–566.e2.
Friedman S, Sanyal A, Goodman Z, Lefebvre E, Gottwald M, Fischer L, et al. Efficacy and safety study of cenicriviroc for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adult subjects with liver fibrosis: CENTAUR Phase 2b study design. Contemp Clin Trials. 2016;47:356–65.
Friedman SL, Ratziu V, Harrison SA, Abdelmalek MF, Aithal GP, Caballeria J, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of cenicriviroc for treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with fibrosis. Hepatology. 2018;67(5):1754–67.
Ratziu V, Harrison SA, Francque S, Bedossa P, Lehert P, Serfaty L, et al. Elafibranor, an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α and -δ, induces resolution of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis without fibrosis worsening. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(5):1147–1159.e5.
Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Mantzoros CS, Polymerou V, Katsinelos P. Effects of combined low-dose spironolactone plus vitamin E vs vitamin E monotherapy on insulin resistance, non-invasive indices of steatosis and fibrosis, and adipokine levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19(12):1805–9.
Loomba R, Lawitz E, Mantry PS, Jayakumar S, Caldwell SH, Arnold H, et al. The ASK1 inhibitor selonsertib in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, phase 2 trial. Hepatology. 2017;67(2):549–59.
Chalasani N, Vuppalanchi R, Rinella M, Middleton MS, Siddiqui MS, Barritt AS, et al. Randomised clinical trial: a leucine-metformin-sildenafil combination (NS-0200) vs placebo in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;47(12):1639–51.
Sanyal AJ, Cordonnier G, Brozek J, Roudot A, Deledicque S, Barbazanges M, et al. A new method including the quantification of circulating miRNAs allows the efficient identification of NASH at risk who should be treated. J Hepatol. 2016;64(2):S717.
Harrison S, Praca C, Brozek J, Cordonnier G, Sudrik FB, Roudot A, et al. A new non-invasive diagnostic score to monitor change in disease activity and predict fibrosis evolution in patients with NASH. J Hepatol. 2018;66:S110.
Hanf R, Pierre C, Zouher M, Cordonnier G, Brozek J, Praca E, et al. Validation of NIS4 algorithm for detection of NASH at risk of cirrhosis in 467 NAFLD patients prospectively screened for inclusion in the RESOLVE-IT trial. J Hepatol. 2018;68:S115–6.
Financial Support
This work was supported by NIH grants R01AT001576 (SCL and JMM) and R01DK092407 (SCL), the Agencia Estatal de Investigación of MINECO SAF 2017-88041R (JMM), MINECO-ISCiii PIE14/00031 (JMM), CIBERehd-ISCiii (JMM), Basque Government through the projects Hazitek ZL-2016/00444 and ZL-2017/00018 (PO), Etorgai ER-2015/00015 (CA), Plan de Promoción de la Innovación 2015 – Diputación Foral de Bizkaia, 6/12/IN/2015/00131 (CA) and Horizon 2020 Framework Program of the European Union (under grant agreement number 777377 for the project LITMUS (PO, JMM and CA)). We thank Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness MINECO for CIC bioGUNE Severo Ochoa Excellence Accreditation (SEV-2016-0644).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Iruarrizaga-Lejarreta, M. et al. (2019). Emerging Circulating Biomarkers for The Diagnosis and Assessment of Treatment Responses in Patients with Hepatic Fat Accumulation, Nash and Liver Fibrosis. In: Krentz, A., Weyer, C., Hompesch, M. (eds) Translational Research Methods in Diabetes, Obesity, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11748-1_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11748-1_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-11747-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-11748-1
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)