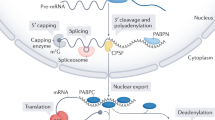
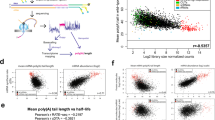
Abstract
Polyadenylation is a posttranscriptional modification present throughout all the kingdoms of life with important roles in regulation of RNA stability, translation, and quality control. Functions of polyadenylation in prokaryotic and organellar RNA metabolism are still not fully characterized, and poly(A) tails appear to play contrasting roles in different systems. Here we present a general overview of the polyadenylation process and the factors involved in its regulation, with an emphasis on the diverse functions of 3′ end modification in the control of gene expression in different biological systems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dyall SD, Brown MT, Johnson PJ (2004) Ancient invasions: from endosymbionts to organelles. Science 304:253–257
Just A, Butter F, Trenkmann M et al (2008) A comparative analysis of two conserved motifs in bacterial poly(A) polymerase and CCA-adding enzyme. Nucleic Acids Res 36:5212–5220
Cao GJ, Sarkar N (1992) Identification of the gene for an Escherichia coli poly(A) polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89: 10380–10384
Sarkar D, Park ES, Emdad L et al (2005) Defining the domains of human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPaseOLD-35) mediating cellular senescence. Mol Cell Biol 25:7333–7343
Raynal LC, Carpousis AJ (1999) Poly(A) polymerase I of Escherichia coli: characterization of the catalytic domain, an RNA binding site and regions for the interaction with proteins involved in mRNA degradation. Mol Microbiol 32:765–775
Yehudai-Resheff S, Schuster G (2000) Characterization of the E. coli poly(A) polymerase: nucleotide specificity, RNA-binding affinities and RNA structure dependence. Nucleic Acids Res 28:1139–1144
Mohanty BK, Kushner SR (2000) Polynucleotide phosphorylase functions both as a 3′ right-arrow 5′ exonuclease and a poly(A) polymerase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:11966–11971
Zimmer SL, Schein A, Zipor G et al (2009) Polyadenylation in Arabidopsis and Chlamydomonas organelles: the input of nucleotidyltransferases, poly(A) polymerases and polynucleotide phosphorylase. Plant J 59:88–99
Schuster G, Stern D (2009) RNA polyadenylation and decay in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 85: 393–422
Groot GS, Flavell RA, Van Ommen GJ et al (1974) Yeast mitochondrial RNA does not contain poly(A). Nature 252:167–169
Wang SW, Toda T, MacCallum R et al (2000) Cid1, a fission yeast protein required for S-M checkpoint control when DNA polymerase delta or epsilon is inactivated. Mol Cell Biol 20:3234–3244
Etheridge RD, Aphasizheva I, Gershon PD et al (2008) 3′ adenylation determines mRNA abundance and monitors completion of RNA editing in T. brucei mitochondria. EMBO J 27:1596–1608
Tomecki R, Dmochowska A, Gewartowski K et al (2004) Identification of a novel human nuclear-encoded mitochondrial poly(A) polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res 32:6001–6014
Nagaike T, Suzuki T, Katoh T et al (2005) Human mitochondrial mRNAs are stabilized with polyadenylation regulated by mitochondria-specific poly(A) polymerase and polynucleotide phosphorylase. J Biol Chem 280:19721–19727
Bai Y, Srivastava SK, Chang JH et al (2011) Structural basis for dimerization and activity of human PAPD1, a noncanonical poly(A) polymerase. Mol Cell 41:311–320
Aphasizheva I, Maslov D, Wang X et al (2011) Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins stimulate mRNA adenylation/uridylation to activate mitochondrial translation in trypanosomes. Mol Cell 42:106–117
Grunberg-Manago M, Oritz PJ, Ochoa S (1955) Enzymatic synthesis of nucleic acidlike polynucleotides. Science 122:907–910
Mohanty BK, Kushner SR (2011) Bacterial/archaeal/organellar polyadenylation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2:256–276
Symmons MF, Jones GH, Luisi BF (2000) A duplicated fold is the structural basis for polynucleotide phosphorylase catalytic activity, processivity, and regulation. Structure 8: 1215–1226
Liu Q, Greimann JC, Lima CD (2006) Reconstitution, activities, and structure of the eukaryotic RNA exosome. Cell 127: 1223–1237
Lorentzen E, Dziembowski A, Lindner D et al (2007) RNA channelling by the archaeal exosome. EMBO Rep 8:470–476
Rossmanith W (2012) Of P and Z: mitochondrial tRNA processing enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819:1017–1026
Rorbach J, Minczuk M (2012) The post-transcriptional life of mammalian mitochondrial RNA. Biochem J 444:357–373
Borowski LS, Szczesny RJ, Brzezniak LK et al (2010) RNA turnover in human mitochondria: more questions than answers? Biochim Biophys Acta 1797:1066–1070
Mackie GA (2013) RNase E: at the interface of bacterial RNA processing and decay. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:45–57
Arraiano CM, Matos RG, Barbas A (2010) RNase II: the finer details of the modus operandi of a molecular killer. RNA Biol 7:276–281
Rorbach J, Nicholls TJ, Minczuk M (2011) PDE12 removes mitochondrial RNA poly(A) tails and controls translation in human mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res 39:7750–7763
Poulsen JB, Andersen KR, Kjaer KH et al (2011) Human 2′-phosphodiesterase localizes to the mitochondrial matrix with a putative function in mitochondrial RNA turnover. Nucleic Acids Res 39:3754
Vogel J, Luisi BF (2011) Hfq and its constellation of RNA. Nat Rev Microbiol 9: 578–589
Hankins JS, Denroche H, Mackie GA (2010) Interactions of the RNA-binding protein Hfq with cspA mRNA, encoding the major cold shock protein. J Bacteriol 192:2482–2490
Feng Y, Huang H, Liao J et al (2001) Escherichia coli poly(A)-binding proteins that interact with components of degradosomes or impede RNA decay mediated by polynucleotide phosphorylase and RNase E. J Biol Chem 276:31651–31656
Yohn CB, Cohen A, Danon A et al (1998) A poly(A) binding protein functions in the chloroplast as a message-specific translation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:2238–2243
Kazak L, Reyes A, Duncan AL et al (2013) Alternative translation initiation augments the human mitochondrial proteome. Nucleic Acids Res 41:2354–2369
Schmitz-Linneweber C, Small I (2008) Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins: a socket set for organelle gene expression. Trends Plant Sci 13:663–670
Chujo T, Ohira T, Sakaguchi Y et al (2012) LRPPRC/SLIRP suppresses PNPase-mediated mRNA decay and promotes polyadenylation in human mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res 40:8033–8047
Ruzzenente B, Metodiev MD, Wredenberg A et al (2011) LRPPRC is necessary for polyadenylation and coordination of translation of mitochondrial mRNAs. EMBO J 31:443
August JT, Ortiz PJ, Hurwitz J (1962) Ribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleotide incorporation. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem 237:3786–3793
Xu F, Lin-Chao S, Cohen SN (1993) The Escherichia coli pcnB gene promotes adenylylation of antisense RNAI of ColE1-type plasmids in vivo and degradation of RNAI decay intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:6756–6760
He L, Soderbom F, Wagner EG et al (1993) PcnB is required for the rapid degradation of RNAI, the antisense RNA that controls the copy number of ColE1-related plasmids. Mol Microbiol 9:1131–1142
Coburn GA, Miao X, Briant DJ et al (1999) Reconstitution of a minimal RNA degradosome demonstrates functional coordination between a 3′ exonuclease and a DEAD-box RNA helicase. Genes Dev 13:2594–2603
Cohen SN (1995) Surprises at the 3′ end of prokaryotic RNA. Cell 80:829–832
Carpousis AJ, Vanzo NF, Raynal LC (1999) mRNA degradation. A tale of poly(A) and multiprotein machines. Trends Genet 15:24–28
Sarkar N (1997) Polyadenylation of mRNA in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem 66:173–197
O’Hara EB, Chekanova JA, Ingle CA et al (1995) Polyadenylylation helps regulate mRNA decay in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:1807–1811
Coburn GA, Mackie GA (1998) Reconstitution of the degradation of the mRNA for ribosomal protein S20 with purified enzymes. J Mol Biol 279:1061–1074
Goodrich AF, Steege DA (1999) Roles of polyadenylation and nucleolytic cleavage in the filamentous phage mRNA processing and decay pathways in Escherichia coli. RNA 5:972–985
Mohanty BK, Kushner SR (1999) Analysis of the function of Escherichia coli poly(A) polymerase I in RNA metabolism. Mol Microbiol 34:1094–1108
Haugel-Nielsen J, Hajnsdorf E, Regnier P (1996) The rpsO mRNA of Escherichia coli is polyadenylated at multiple sites resulting from endonucleolytic processing and exonucleolytic degradation. EMBO J 15:3144–3152
Bralley P, Jones GH (2002) cDNA cloning confirms the polyadenylation of RNA decay intermediates in Streptomyces coelicolor. Microbiology 148:1421–1425
Campos-Guillen J, Bralley P, Jones GH et al (2005) Addition of poly(A) and heteropolymeric 3′ ends in Bacillus subtilis wild-type and polynucleotide phosphorylase-deficient strains. J Bacteriol 187:4698–4706
Rott R, Zipor G, Portnoy V et al (2003) RNA polyadenylation and degradation in cyanobacteria are similar to the chloroplast but different from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 278:15771–15777
Gould SB, Waller RF, McFadden GI (2008) Plastid evolution. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59: 491–517
Kudla J, Hayes R, Gruissem W (1996) Polyadenylation accelerates degradation of chloroplast mRNA. EMBO J 15:7137–7146
Lisitsky I, Klaff P, Schuster G (1996) Addition of destabilizing poly (A)-rich sequences to endonuclease cleavage sites during the degradation of chloroplast mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:13398–13403
Yehudai-Resheff S, Hirsh M, Schuster G (2001) Polynucleotide phosphorylase functions as both an exonuclease and a poly(A) polymerase in spinach chloroplasts. Mol Cell Biol 21:5408–5416
Lange H, Sement FM, Canaday J et al (2009) Polyadenylation-assisted RNA degradation processes in plants. Trends Plant Sci 14:497–504
Gagliardi D, Stepien PP, Temperley RJ et al (2004) Messenger RNA stability in mitochondria: different means to an end. Trends Genet 20:260–267
Yuckenberg PD, Phillips SL (1982) Oligoadenylate is present in the mitochondrial RNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 2:450–456
Butow RA, Zhu H, Perlman P et al (1989) The role of a conserved dodecamer sequence in yeast mitochondrial gene expression. Genome 31:757–760
Dziembowski A, Piwowarski J, Hoser R et al (2003) The yeast mitochondrial degradosome. Its composition, interplay between RNA helicase and RNase activities and the role in mitochondrial RNA metabolism. J Biol Chem 278:1603–1611
Militello KT, Read LK (2000) UTP-dependent and -independent pathways of mRNA turnover in Trypanosoma brucei mitochondria. Mol Cell Biol 20:2308–2316
Ryan CM, Read LK (2005) UTP-dependent turnover of Trypanosoma brucei mitochondrial mRNA requires UTP polymerization and involves the RET1 TUTase. RNA 11:763–773
Ryan CM, Militello KT, Read LK (2003) Polyadenylation regulates the stability of Trypanosoma brucei mitochondrial RNAs. J Biol Chem 278:32753–32762
Kao CY, Read LK (2005) Opposing effects of polyadenylation on the stability of edited and unedited mitochondrial RNAs in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol 25:1634–1644
Aphasizhev R, Aphasizheva I (2011) Mitochondrial RNA processing in trypanosomes. Res Microbiol 162:655–663
Temperley RJ, Wydro M, Lightowlers RN et al (2010) Human mitochondrial mRNAs-like members of all families, similar but different. Biochim Biophys Acta 1797:1081–1085
Wydro M, Bobrowicz A, Temperley RJ et al (2010) Targeting of the cytosolic poly(A) binding protein PABPC1 to mitochondria causes mitochondrial translation inhibition. Nucleic Acids Res 38:3732–3742
Slomovic S, Schuster G (2008) Stable PNPase RNAi silencing: its effect on the processing and adenylation of human mitochondrial RNA. RNA 14:310–323
Shepard PJ, Choi EA, Lu J et al (2011) Complex and dynamic landscape of RNA polyadenylation revealed by PAS-Seq. RNA 17:761–772
Hajnsdorf E, Braun F, Haugel-Nielsen J et al (1995) Polyadenylylation destabilizes the rpsO mRNA of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:3973–3977
Li Z, Pandit S, Deutscher MP (1998) 3′ exoribonucleolytic trimming is a common feature of the maturation of small, stable RNAs in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:2856–2861
Li Z, Reimers S, Pandit S et al (2002) RNA quality control: degradation of defective transfer RNA. EMBO J 21:1132–1138
Mohanty BK, Maples VF, Kushner SR (2012) Polyadenylation helps regulate functional tRNA levels in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res 40:4589–4603
Joanny G, Le Derout J, Brechemier-Baey D et al (2007) Polyadenylation of a functional mRNA controls gene expression in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res 35:2494–2502
Mohanty BK, Kushner SR (2013) Deregulation of poly(A) polymerase I in Escherichia coli inhibits protein synthesis and leads to cell death. Nucleic Acids Res 41:1757–1766
Mohanty BK, Kushner SR (2013) In vivo analysis of polyadenylation in prokaryotes. In: Rorbach J, Bobrowicz AJ (eds) Polyadenylation, Methods in molecular biology. Humana, New York
Encalade GA, Sukhodolets MV (2013) Polyadenylation of RNA in E. coli: RNA polymerase-associated (rA)n-synthetic activities. In: Rorbach J, Bobrowicz AJ (eds) Polyadenylation, Methods in molecular biology. Humana, New York
Rackham O, Filipovska A (2013) Analysis of the human mitochondrial transcriptome using directional deep sequencing and parallel analysis of RNA ends. In: Rorbach J, Bobrowicz AJ (eds) Polyadenylation, Methods in molecular biology. Humana, New York
Borowski LS, Szczesny RJ (2013) Measurement of mitochondrial RNA stability by metabolic labelling of transcripts with 4-thiouridine. In: Rorbach J, Bobrowicz AJ (eds) Polyadenylation, Methods in molecular biology. Humana, New York
Mohanty BK, Maples VF, Kushner SR (2004) The Sm-like protein Hfq regulates polyadenylation dependent mRNA decay in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 54:905–920
Mohanty BK, Kushner SR (2006) The majority of Escherichia coli mRNAs undergo post-transcriptional modification in exponentially growing cells. Nucleic Acids Res 34: 5695–5704
Temperley RJ, Seneca SH, Tonska K et al (2003) Investigation of a pathogenic mtDNA microdeletion reveals a translation-dependent deadenylation decay pathway in human mitochondria. Hum Mol Genet 12:2341–2348
Chrzanowska-Lightowlers ZM, Temperley RJ, Smith PM et al (2004) Functional polypeptides can be synthesized from human mitochondrial transcripts lacking termination codons. Biochem J 377:725–731
Eckmann CR, Rammelt C, Wahle E (2011) Control of poly(A) tail length. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2:348–361
Sukhodolets MV, Jin DJ (1998) RapA, a novel RNA polymerase-associated protein, is a bacterial homolog of SWI2/SNF2. J Biol Chem 273:7018–7023
Sukhodolets MV, Garges S (2003) Interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with the ribosomal protein S1 and the Sm-like ATPase Hfq. Biochemistry 42:8022–8034
Sukhodolets MV, Garges S, Jin DJ (2003) Purification and activity assays of RapA, the RNA polymerase-associated homolog of the SWI/SNF protein superfamily. Methods Enzymol 370:283–290
Zhi H, Yang W, Jin DJ (2003) Escherichia coli proteins eluted from mono Q chromatography, a final step during RNA polymerase purification procedure. Methods Enzymol 370:291–300
Kansara SG, Sukhodolets MV (2011) Oligomerization of the E. coli core RNA polymerase: formation of (alpha2betabeta′omega)2-DNA complexes and regulation of the oligomerization by auxiliary subunits. PLoS One 6:e18990
Mercer TR, Neph S, Dinger ME et al (2011) The human mitochondrial transcriptome. Cell 146:645–658
German MA, Luo S, Schroth G et al (2009) Construction of parallel analysis of RNA ends (PARE) libraries for the study of cleaved miRNA targets and the RNA degradome. Nat Protoc 4:356–362
German MA, Pillay M, Jeong DH et al (2008) Global identification of microRNA-target RNA pairs by parallel analysis of RNA ends. Nat Biotechnol 26:941–946
Rackham O, Filipovska A (2011) The role of mammalian PPR domain proteins in the regulation of mitochondrial gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819:1008
Davies SM, Lopez Sanchez MI, Narsai R et al (2012) MRPS27 is a pentatricopeptide repeat domain protein required for the translation of mitochondrially encoded proteins. FEBS Lett 586:3555–3561
Rackham O, Mercer TR, Filipovska A (2012) The human mitochondrial transcriptome and the RNA-binding proteins that regulate its expression. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 3: 675–695
Shutt TE, Shadel GS (2010) A compendium of human mitochondrial gene expression machinery with links to disease. Environ Mol Mutagen 51:360–379
Temperley R, Richter R, Dennerlein S et al (2010) Hungry codons promote frameshifting in human mitochondrial ribosomes. Science 327:301
Christian BE, Spremulli LL (2012) Mechanism of protein biosynthesis in mammalian mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819:1035–1054
Aphasizheva I, Aphasizhev R (2010) RET1-catalyzed uridylylation shapes the mitochondrial transcriptome in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol 30:1555–1567
Germain A, Herlich S, Larom S et al (2011) Mutational analysis of Arabidopsis chloroplast polynucleotide phosphorylase reveals roles for both RNase PH core domains in polyadenylation, RNA 3′-end maturation and intron degradation. Plant J 67:381–394
Mohanty BK, Kushner SR (2000) Polynucleotide phosphorylase, RNase II and RNase E play different roles in the in vivo modulation of polyadenylation in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 36:982–994
Carpousis AJ (2002) The Escherichia coli RNA degradosome: structure, function and relationship in other ribonucleolytic multienzyme complexes. Biochem Soc Trans 30: 150–155
Carpousis AJ (2007) The RNA degradosome of Escherichia coli: an mRNA-degrading machine assembled on RNase E. Annu Rev Microbiol 61:71–87
Matos RG, Barbas A, Gomez-Puertas P et al (2011) Swapping the domains of exoribonucleases RNase II and RNase R: conferring upon RNase II the ability to degrade ds RNA. Proteins 79:1853–1867
Li de la Sierra-Gallay I, Zig L, Jamalli A et al (2008) Structural insights into the dual activity of RNase J. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:206–212
Borowski LS, Dziembowski A, Hejnowicz MS et al (2013) Human mitochondrial RNA decay mediated by PNPase-hSuv3 complex takes place in distinct foci. Nucleic Acids Res 41:1223–1240
Baughman JM, Nilsson R, Gohil VM et al (2009) A computational screen for regulators of oxidative phosphorylation implicates SLIRP in mitochondrial RNA homeostasis. PLoS Genet 5:e1000590
Sasarman F, Brunel-Guitton C, Antonicka H et al (2010) LRPPRC and SLIRP interact in a ribonucleoprotein complex that regulates posttranscriptional gene expression in mitochondria. Mol Biol Cell 21:1315–1323
Mattiacio JL, Read LK (2009) Evidence for a degradosome-like complex in the mitochondria of Trypanosoma brucei. FEBS Lett 583:2333–2338
Bollenbach TJ, Schuster G, Stern DB (2004) Cooperation of endo- and exoribonucleases in chloroplast mRNA turnover. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 78:305–337
Yang J, Stern DB (1997) The spinach chloroplast endoribonuclease CSP41 cleaves the 3′-untranslated region of petD mRNA primarily within its terminal stem-loop structure. J Biol Chem 272:12874–12880
Bollenbach TJ, Stern DB (2003) Divalent metal-dependent catalysis and cleavage specificity of CSP41, a chloroplast endoribonuclease belonging to the short chain dehydrogenase/reductase superfamily. Nucleic Acids Res 31:4317–4325
Lupold DS, Caoile AG, Stern DB (1999) Polyadenylation occurs at multiple sites in maize mitochondrial cox2 mRNA and is independent of editing status. Plant Cell 11: 1565–1578
Gagliardi D, Perrin R, Marechal-Drouard L et al (2001) Plant mitochondrial polyadenylated mRNAs are degraded by a 3′- to 5′-exoribonuclease activity, which proceeds unimpeded by stable secondary structures. J Biol Chem 276:43541–43547
Nagaike T, Suzuki T, Ueda T (2008) Polyadenylation in mammalian mitochondria: insights from recent studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1779:266–269
Piechota J, Tomecki R, Gewartowski K et al (2006) Differential stability of mitochondrial mRNA in HeLa cells. Acta Biochim Pol 53: 157–168
Bobrowicz AJ, Lightowlers RN, Chrzanowska-Lightowlers Z (2008) Polyadenylation and degradation of mRNA in mammalian mitochondria: a missing link? Biochem Soc Trans 36:517–519
Slomovic S, Laufer D, Geiger D et al (2005) Polyadenylation and degradation of human mitochondrial RNA: the prokaryotic past leaves its mark. Mol Cell Biol 25:6427–6435
Slomovic S, Laufer D, Geiger D et al (2006) Polyadenylation of ribosomal RNA in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res 34:2966–2975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Rorbach, J., Bobrowicz, A., Pearce, S., Minczuk, M. (2014). Polyadenylation in Bacteria and Organelles. In: Rorbach, J., Bobrowicz, A. (eds) Polyadenylation. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1125. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-971-0_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-971-0_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-62703-970-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-62703-971-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols