Abstract
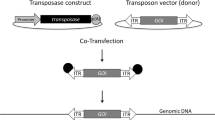
Stable mammalian, namely human, suspension cell lines play a pivotal role in red biotechnology production scenarios for the generation of state-of-the-art biologics. However, selection of genetically modified and highly productive cell populations – prior to the establishment of clonal lines – is often challenging. To overcome this limitation, we first describe an optimized transient transfection protocol using the inexpensive reagent polyethylenimine (PEI) and human 293F cells. Transposon donor vectors derived from Sleeping Beauty encompassing a cassette with the reporter gene encoding for the green fluorescent protein (GFP) coupled with an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) to the expression of puromycin-resistance are employed to readily detect transfected cells. Upon stable transfection in the presence and absence of transposase expression, respectively, and subsequent antibiotic selection, GFP expression using flow cytometry analysis, cell viability, and cell density can be examined over a range of up to 3 weeks. Owing to the integration of high vector copy numbers into the target cell genome, transposase-mediated transposition of transposon donor vectors is instrumental in the faster establishment of recombinant cell population as compared to the classical stable transfection of plasmid DNA.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wurm FM (2004) Production of recombinant protein therapeutics in cultivated mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol 22(11):1393–1398
Baldi L, Hacker DL, Adam M et al (2007) Recombinant protein production by large-scale transient gene expression in mammalian cells: state of the art and future perspectives. Biotechnol Lett 29(5):677–684
Cervera L, Kamen AA (2018) Large-scale transient transfection of suspension mammalian cells for VLP production. Methods Mol Biol 1674:117–127
Robinson DK, Memmert KW (1991) Kinetics of recombinant immunoglobulin production by mammalian cells in continuous culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 38(9):972–976
Gutiérrez-Granados S, Cervera L, Kamen AA et al (2018) Advancements in mammalian cell transient gene expression (TGE) technology for accelerated production of biologics. Crit Rev Biotechnol 38(6):918–940
Schlaeger EJ, Christensen K (1999) Transient gene expression in mammalian cells grown in serum-free suspension culture. Cytotechnology 30(1–3):71–83
Pham PL, Perret S, Doan HC et al (2003) Large-scale transient transfection of serum-free suspension-growing HEK293 EBNA1 cells: peptone additives improve cell growth and transfection efficiency. Biotechnol Bioeng 84(3):332–342
Gorman C, Bullock C (2000) Site-specific gene targeting for gene expression in eukaryotes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11(5):455–460
Jordan M, Wurm F (2004) Transfection of adherent and suspended cells by calcium phosphate. Methods 33(2):136–143
Geisse S (2009) Reflections on more than 10 years of TGE approaches. Protein Expr Purif 64(2):99–107
Boussif O, Lezoualc’h F, Zanta MA et al (1995) A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(16):7297–7301
Ho SCL, Bardor M, Feng H et al (2012) IRES-mediated tricistronic vectors for enhancing generation of high monoclonal antibody expressing CHO cell lines. J Biotechnol 157(1):130–139
Grabundzija I, Irgang M, Mátés L et al (2010) Comparative analysis of transposable element vector systems in human cells. Mol Ther 18(6):1200–1209
Ammar I, Izsvák Z, Ivics Z (2012) The sleeping beauty transposon toolbox. Methods Mol Biol 859:229–240
Mátés L, Chuah MKL, Belay E et al (2009) Molecular evolution of a novel hyperactive sleeping beauty transposase enables robust stable gene transfer in vertebrates. Nat Genet 41(6):753–761
Yant SR, Meuse L, Chiu W et al (2000) Somatic integration and long-term transgene expression in normal and haemophilic mice using a DNA transposon system. Nat Genet 25(1):35–41
Donello JE, Loeb JE, Hope TJ (1998) Woodchuck hepatitis virus contains a tripartite posttranscriptional regulatory element. J Virol 72(6):5085–5092
Zufferey R, Donello JE, Trono D et al (1999) Woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element enhances expression of transgenes delivered by retroviral vectors. J Virol 73(4):2886–2892
Ivics Z, Hackett PB, Plasterk RH et al (1997) Molecular reconstruction of sleeping beauty, a Tc1-like transposon from fish, and its transposition in human cells. Cell 91(4):501–510
Cui Z, Geurts AM, Liu G et al (2002) Structure-function analysis of the inverted terminal repeats of the sleeping beauty transposon. J Mol Biol 318(5):1221–1235
Tom R, Bisson L, Durocher Y (2008) Transfection of HEK293-EBNA1 cells in suspension with linear PEI for production of recombinant proteins. CSH Protoc 2008:pdb.prot4977
Spidel JL, Vaessen B, Chan YY et al (2016) Rapid high-throughput cloning and stable expression of antibodies in HEK293 cells. J Immunol Methods 439:50–58
Acknowledgments
We like to thank Dr. Reto Eggenschwiler and Prof. Dr. Tobias Cantz, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Endocrinology, Hannover Medical School, Germany, for the critical discussion of the manuscript and Danka Bratic for expertise technical support. This work was supported by Grant EFRE-0500031 by the European Regional Development Fund (EFRE) of the European Union to J.S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Berg, K., Schäfer, V.N., Tschorn, N., Stitz, J. (2020). Advanced Establishment of Stable Recombinant Human Suspension Cell Lines Using Genotype–Phenotype Coupling Transposon Vectors. In: Zielonka, S., Krah, S. (eds) Genotype Phenotype Coupling. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2070. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9853-1_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9853-1_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-9852-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-9853-1
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols