Abstract
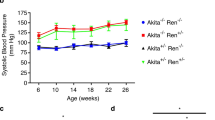
Traditional animal models mimic only the earliest stages of human diabetic nephropathy (DN), which limits their utility to dissect the pathogenesis of progressive disease or test novel therapeutics. In this chapter we describe in detail the experimental procedures required to conduct the Cyp1a1mRen2 rodent model, in which hyperglycemia and renin-dependent hypertension synergize to promote moderate proteinuria, renal fibrosis, and induction of many of the transcriptomic changes observed in the kidney of patients with progressive DN.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brosius FC 3rd, Alpers CE, Bottinger EP et al (2009) Mouse models of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:2503–2512
Betz B, Conway BR (2016) An update on the use of animal models in diabetic nephropathy research. Curr Diab Rep 16:18
Mogensen CE (1998) Combined high blood pressure and glucose in type 2 diabetes: double jeopardy. British trial shows clear effects of treatment, especially blood pressure reduction. BMJ 317:693–694
Berkman J, Rifkin H (1973) Unilateral nodular diabetic glomerulosclerosis (Kimmelstiel-Wilson): report of a case. Metabolism 22:715–722
Beroniade VC, Lefebvre R, Falardeau P (1987) Unilateral nodular diabetic glomerulosclerosis: recurrence of an experiment of nature. Am J Nephrol 7:55–59
Kantachuvesiri S, Fleming S, Peters J et al (2001) Controlled hypertension, a transgenic toggle switch reveals differential mechanisms underlying vascular disease. J Biol Chem 276:36727–36733
Conway BR, Rennie J, Bailey MA et al (2012) Hyperglycemia and renin-dependent hypertension synergize to model diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:405–411
Conway BR, Betz B, Sheldrake TA et al (2014) Tight blood glycaemic and blood pressure control in experimental diabetic nephropathy reduces extracellular matrix production without regression of fibrosis. Nephrology 19:802–813
Liu X, Bellamy CO, Bailey MA et al (2009) Angiotensin-converting enzyme is a modifier of hypertensive end organ damage. J Biol Chem 284:15564–15572
Kantachuvesiri S, Haley CS, Fleming S et al (1999) Genetic mapping of modifier loci affecting malignant hypertension in TGRmRen2 rats. Kidney Int 56:414–420
Kelly DJ, Wilkinson-Berka JL, Allen TJ et al (1998) A new model of diabetic nephropathy with progressive renal impairment in the transgenic (mRen-2)27 rat (TGR). Kidney Int 54:343–352
Hartner A, Cordasic N, Klanke B et al (2007) Renal injury in streptozotocin-diabetic Ren2-transgenic rats is mainly dependent on hypertension, not on diabetes. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 292:F820–F827
Keppler A, Gretz N, Schmidt R et al (2007) Plasma creatinine determination in mice and rats: an enzymatic method compares favorably with a high-performance liquid chromatography assay. Kidney Int 71:74–78
Qi Z, Whitt I, Mehta A et al (2004) Serial determination of glomerular filtration rate in conscious mice using FITC-inulin clearance. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 286:F590–F596
Herrera Perez Z, Weinfurter S, Gretz N (2016) Transcutaneous assessment of renal function in conscious rodents. J Vis Exp 109:e53767
Acknowledgments
Dr. Conway was supported by a MRC Clinician Scientist Award, a Scottish Senior Clinical Fellowship, a British Heart Foundation Transition Fellowship Award, and grants from Kidney Research UK and the Edinburgh and Lothians Health Foundation Renal Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Cairns, C., Conway, B. (2020). Modeling Human Diabetic Kidney Disease by Combining Hyperglycemia and Hypertension in a Transgenic Rodent Model. In: Gnudi, L., Long, D. (eds) Diabetic Nephropathy. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2067. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9841-8_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9841-8_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-9840-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-9841-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols