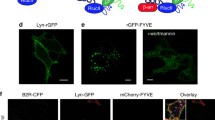
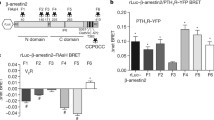
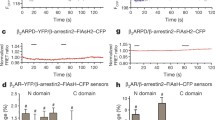
Abstract
Information contained in the structure of extracellular ligands is transmitted across the cell membrane through allosterically induced changes in G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) conformation that occur upon ligand binding. These changes, in turn, are imprinted upon intracellular effectors like arrestins and help determine which of its many functions are performed. Intramolecular fluorescein arsenical hairpin (FlAsH) bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET), in which both the fluorescence donor and acceptor are contained within the same protein, can be used to report on activation-induced changes in protein conformation. Here, we describe a method using a series of Rluc-arrestin3-FlAsH-BRET biosensors to measure stimulus-induced changes in arrestin conformation in live cells. Each Rluc-arrestin3-FlAsH-BRET construct contains an N-terminal Renilla luciferase fluorescence donor that excites a fluorescent arsenical targeted to a different position within the protein by mutational insertion of a tetracysteine tag motif. Changes in net BRET upon GPCR stimulation can thus be viewed from multiple vantage points within the protein and used to develop an arrestin3 “conformational signature” that is receptor- and ligand-specific. This method can be used to determine how differences in GPCR and ligand structure influence information transfer across the plasma membrane and to classify GPCRs and/or ligands based on their capacity to induce different arrestin3 activation modes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peterson YK, Luttrell LM (2017) The diverse roles of arrestin scaffolds in G protein-coupled receptor signaling. Pharmacol Rev 69:256–297
Han M, Gurevich VV, Vishnivetskiy SA, Sigler PB, Schubert C (2001) Crystal structure of beta-arrestin at 1.9 A: possible mechanism of receptor binding and membrane translocation. Structure 9:869–880
Zhan X, Gimenez LE, Gurevich VV, Spiller BW (2011) Crystal structure of arrestin-3 reveals the basis of the difference in receptor binding between two non-visual subtypes. J Mol Biol 406:467–478
Shukla AK, Manglik A, Kruse AC, Xiao K, Reis RI, Tseng WC, Staus DP, Hilger D, Uysal S, Huang LY, Paduch M, Tripathi-Shukla P, Koide A, Koide S, Weis WI, Kossiakoff AA, Kobilka BK, Lefkowitz RJ (2013) Structure of active β-arrestin-1 bound to a G-protein-coupled receptor phosphopeptide. Nature 497:137–141
Kim YJ, Hofmann KP, Ernst OP, Scheerer P, Choe HW, Sommer ME (2013) Crystal structure of pre-activated arrestin p44. Nature 497:142–146
Kang Y, Zhou XE, Gao X, He Y, Liu W, Ishchenko A, Barty A, White TA, Yefanov O, Han GW, Xu Q, de Waal PW, Ke J, Tan MH, Zhang C, Moeller A, West GM, Pascal BD, Van Eps N, Caro LN, Vishnivetskiy SA, Lee RJ, Suino-Powell KM, Gu X, Pal K, Ma J, Zhi X, Boutet S, Williams GJ, Messerschmidt M, Gati C, Zatsepin NA, Wang D, James D, Basu S, Roy-Chowdhury S, Conrad CE, Coe J, Liu H, Lisova S, Kupitz C, Grotjohann I, Fromme R, Jiang Y, Tan M, Yang H, Li J, Wang M, Zheng Z, Li D, Howe N, Zhao Y, Standfuss J, Diederichs K, Dong Y, Potter CS, Carragher B, Caffrey M, Jiang H, Chapman HN, Spence JC, Fromme P, Weierstall U, Ernst OP, Katritch V, Gurevich VV, Griffin PR, Hubbell WL, Stevens RC, Cherezov V, Melcher K, Xu HE (2015) Crystal structure of rhodopsin bound to arrestin by femtosecond X-ray laser. Nature 523:561–567
Charest PG, Bouvier M (2003) Palmitoylation of the V2 vasopressin receptor carboxyl tail enhances beta-arrestin recruitment leading to efficient receptor endocytosis and ERK1/2 activation. J Biol Chem 278:41541–41551
Charest PG, Terrillon S, Bouvier M (2005) Monitoring agonist-promoted conformational changes of beta-arrestin in living cells by intramolecular BRET. EMBO Rep 6:334–340
Vilardaga JP, Bünemann M, Krasel C, Castro M, Lohse MJ (2003) Measurement of the millisecond activation switch of G protein-coupled receptors in living cells. Nat Biotechnol 21:807–812
Hoffmann C, Gaietta G, Bünemann M, Adams SR, Oberdorff-Maass S, Behr B, Vilardaga JP, Tsien RY, Ellisman MH, Lohse MJ (2005) A FlAsH-based FRET approach to determine G protein-coupled receptor activation in living cells. Nat Methods 2:171–176
Lee M-H, Appleton KM, Strungs EG, Kwon JY, Morinelli TA, Peterson YK, Laporte SA, Luttrell LM (2016) The conformational signature of activated arrestin3 predicts its trafficking and signaling functions. Nature 531:665–668
Nuber S, Zabel U, Lorenz K, Nuber A, Milligan G, Tobin AB, Lohse MJ, Hoffmann C (2016) FRET-based β-arrestin biosensors reveal a rapid, receptor-dependent activation/deactivation cycle in living cells. Nature 531:661–664
Perroy J, Adam L, Qanbar R, Chenier S, Bouvier M (2003) Phosphorylation-independent desensitization of GABA(B) receptor by GRK4. EMBO J 22:3816–3824
Yon J, Fried M (1989) Precise gene fusion by PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 17:4895
Devost D, Sleno R, Pétrin D, Zhang A, Shinjo Y, Okde R, Aoki J, Inoue A, Hébert TE (2017) Conformational profiling of the AT1 angiotensin II receptor reflects biased agonism, G protein coupling, and cellular context. J Biol Chem 292:5443–5456
Oakley RH, Laporte SA, Holt JA, Caron MG, Barak LS (2000) Differential affinities of visual arrestin, beta arrestin1, and beta arrestin2 for G protein-coupled receptors delineate two major classes of receptors. J Biol Chem 275:17201–17210
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants R01 DK055524 (LML), R01 GM095497 (LML), Department of Veterans Affairs Merit Review Grant I01 BX003188 (LML), and the Research Service of the Charleston, SC Veterans Affairs Medical Center. The contents of this article do not represent the views of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Strungs, E.G., Luttrell, L.M., Lee, MH. (2019). Probing Arrestin Function Using Intramolecular FlAsH-BRET Biosensors. In: Scott, M., Laporte, S. (eds) Beta-Arrestins. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1957. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9158-7_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9158-7_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-9157-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-9158-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols