Abstract
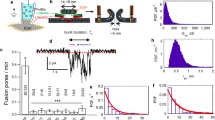
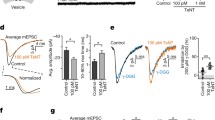
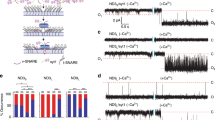
During exocytosis, vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents. The fusion pore is the initial, nanometer-sized connection between the plasma membrane and the cargo-laden vesicle. A growing body of evidence points toward the fusion pore being a regulator of exocytosis, but the shortcomings of current experimental techniques to investigate single-fusion pores make it difficult to study factors governing pore behavior. Here we describe an assay that fuses v-SNARE-reconstituted nanodiscs with cells ectopically expressing “flipped” t-SNAREs to monitor dynamics of single fusion pores in a biochemically defined system using electrical recordings. We also describe a fluorescence microscopy-based approach to monitor nanodisc-cell fusion that is much simpler to employ, but cannot resolve single pores.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chernomordik LV, Kozlov MM (2008) Mechanics of membrane fusion. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:675–683
Jahn R, Fasshauer D (2012) Molecular machines governing exocytosis of synaptic vesicles. Nature 490:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11320
Sudhof TC, Rothman JE (2009) Membrane fusion: grappling with SNARE and SM proteins. Science 323:474–477. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1161748
Lindau M, de Toledo GA (2003) The fusion pore. BBA-Mol Cell Res 1641:167–173
Jackson MB, Chapman ER (2008) The fusion pores of Ca2+ −triggered exocytosis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:684–689. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1449
Weber T et al (1998) SNAREpins: minimal machinery for membrane fusion. Cell 92:759–772
Gao Y et al (2012) Single reconstituted neuronal SNARE complexes zipper in three distinct stages. Science 337:1340–1343. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1224492
Lindau M (2012) High resolution electrophysiological techniques for the study of calcium-activated exocytosis. BBA-Gen Subjects 1820:1234–1242
Fulop T, Radabaugh S, Smith C (2005) Activity-dependent differential transmitter release in mouse adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurosci 25:7324–7332
Hastoy B, Clark A, Rorsman P, Lang J (2017) Fusion pore in exocytosis: more than an exit gate? A beta-cell perspective. Cell Calcium 68:45–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2017.10.005
Collins SC et al (2016) Increased expression of the diabetes gene SOX4 reduces insulin secretion by impaired fusion pore expansion. Diabetes 65:1952–1961. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-1489
Staal RGW, Mosharov EV, Sulzer D (2004) Dopamine neurons release transmitter via a flickering fusion pore. Nat Neurosci 7:341–346
Pawlu C, DiAntonio A, Heckmann M (2004) Postfusional control of quantal current shape. Neuron 42:607–618
Chapochnikov NM et al (2014) Uniquantal release through a dynamic fusion pore is a candidate mechanism of hair cell exocytosis. Neuron 83:1389–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.08.003
He LM, Wu XS, Mohan R, Wu LG (2006) Two modes of fusion pore opening revealed by cell-attached recordings at a synapse. Nature 444:102–105
Alabi AA, Tsien RW (2013) Perspectives on kiss-and-run: role in exocytosis, endocytosis, and neurotransmission. Annu Rev Physiol 75:393–422. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-020911-153305
Travis ER, Wightman RM (1998) Spatio-temporal resolution of exocytosis from individual cells. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 27:77–103. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biophys.27.1.77
Kyoung M, Zhang Y, Diao J, Chu S, Brunger AT (2013) Studying calcium-triggered vesicle fusion in a single vesicle-vesicle content and lipid-mixing system. Nat Protoc 8:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2012.134
Yoon TY, Okumus B, Zhang F, Shin YK, Ha T (2006) Multiple intermediates in SNARE-induced membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:19731–19736
Lai Y et al (2013) Fusion pore formation and expansion induced by Ca2+ and synaptotagmin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:1333–1338. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1218818110
Kiessling V, Liang B, Kreutzberger AJ, Tamm LK (2017) Planar supported membranes with mobile SNARE proteins and quantitative fluorescence microscopy assays to study synaptic vesicle fusion. Front Mol Neurosci 10:72. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00072
Karatekin E et al (2010) A fast, single-vesicle fusion assay mimics physiological SNARE requirements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:3517–3521. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914723107
Karatekin E, Rothman JE (2012) Fusion of single proteoliposomes with planar, cushioned bilayers in microfluidic flow cells. Nat Protoc 7:903–920. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2012.019
Smith MB et al (2011) Interactive, computer-assisted tracking of speckle trajectories in fluorescence microscopy: application to actin polymerization and membrane fusion. Biophys J 101:1794–1804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2011.09.007
Stratton BS et al (2016) Cholesterol increases the openness of SNARE-mediated flickering fusion pores. Biophys J 110:1538–1550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2016.02.019
Wu Z et al (2016) Nanodisc-cell fusion: control of fusion pore nucleation and lifetimes by SNARE protein transmembrane domains. Sci Rep 6:27287. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27287
Wu Z et al (2017) Dilation of fusion pores by crowding of SNARE proteins. elife 6:e22964. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22964
Shi L et al (2012) SNARE proteins: one to fuse and three to keep the nascent fusion pore open. Science 335:1355–1359
Hu C et al (2003) Fusion of cells by flipped SNAREs. Science 300:1745–1749
Sakmann B, Neher E (2009) Single-channel recording, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Bello OD, Auclair SM, Rothman JE, Krishnakumar SS (2016) Using ApoE Nanolipoprotein particles to analyze SNARE-induced fusion pores. Langmuir 32:3015–3023. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b00245
Stroeva E, Krishnakumar SS (2018) Using nanodiscs to probe Ca2+-dependent membrane interaction of Synaptotagmin-1. In: Fratti R (ed) SNAREs, Methods and protocols. Springer, New York
Breckenridge LJ, Almers W (1987) Currents through the fusion pore that forms during exocytosis of a secretory vesicle. Nature 328:814–817
Acknowledgments
We thank all members of the Karatekin laboratory for stimulating discussions, D. Zenisek and F. Sigworth (Cellular and Molecular Physiology, Yale University) for expert advice and discussions, and James E. Rothman, Oscar Bello, Shyam Krishnakumar, and other members of the Rothman laboratory (Cell Biology, Yale University) for critical advice and introducing us to the use of nanodiscs. This work was supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (grant R01GM108954), and a Kavli Foundation Neuroscience Scholar Award (to EK). NRD was supported by NIH Training Grant T32 NS41228 funded by the Jointly Sponsored NIH Predoctoral Training Program in the Neurosciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Dudzinski, N.R., Wu, Z., Karatekin, E. (2019). A Nanodisc-Cell Fusion Assay with Single-Pore Sensitivity and Sub-millisecond Time Resolution. In: Fratti, R. (eds) SNAREs. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1860. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8760-3_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8760-3_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-8759-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-8760-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols