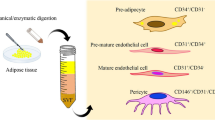
Abstract
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a population of multipotent cells that can be isolated from various adult and fetal tissues, including adipose tissue. These cells contain enormous clinical and basic research appeal due to their plasticity to differentiate into cells of all germ layers in vitro, cross allogeneic barriers in vivo, and suppress inflammation. Methods to isolate adipose-derived MSCs (ADSCs) primarily rely on enzymatic digestion of the adipose tissue using harsh enzymes such as collagenase. However, these harsh enzymes are expensive and can have detrimental effects on the ADSCs, including risks of using xenograft components in clinical application. This chapter focuses on methods of isolating ADSCs from adipose tissue without enzymatic digestion.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitchell JB et al (2006) Immunophenotype of human adipose-derived cells: temporal changes in stromal-associated and stem cell-associated markers. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio) 24:376–385
Bourin P et al (2013) Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: a joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy 15:641–648
Baptista LS et al (2009) An alternative method for the isolation of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from lipoaspirate samples. Cytotherapy 11:706–715
Condé-Green A et al (2014) Comparison between stromal vascular cells’ isolation with enzymatic digestion and mechanical processing of aspirated adipose tissue. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 134:4
Mattar P, Bieback K (2015) Comparing the immunomodulatory properties of bone marrow, adipose tissue, and birth-associated tissue mesenchymal stromal cells. Front Immunol 6:560
Conde-Green A et al (2016) Shift toward mechanical isolation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction: review of upcoming techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 4:e1017
Chang H et al (2013) Safety of adipose-derived stem cells and collagenase in fat tissue preparation. Aesthet Plast Surg 37:802–808
Spees JL et al (2004) Internalized antigens must be removed to prepare hypoimmunogenic mesenchymal stem cells for cell and gene therapy. Mol Ther 9:747–756
Horwitz EM et al (2002) Isolated allogeneic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells engraft and stimulate growth in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: Implications for cell therapy of bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:8932–8937
Tsuji K et al (2017) Effects of different cell-detaching methods on the viability and cell surface antigen expression of synovial mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant 26:1089–1102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Sherman, L.S., Condé-Green, A., Kotamarti, V.S., Lee, E.S., Rameshwar, P. (2018). Enzyme-Free Isolation of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. In: Singh, S., Rameshwar, P. (eds) Somatic Stem Cells. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1842. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8697-2_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8697-2_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-8696-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-8697-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols