Abstract
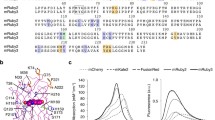
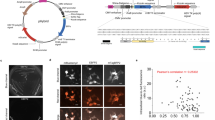
Since the discovery of the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria, outstanding fluorescent labeling tools with numerous applications in vastly different areas of life sciences have been developed. To optimize GFP for diverse life science applications, a large variety of GFP derivatives with different environmental characteristics have been generated by mutagenesis. The enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) is a well-known GFP derivative with highly increased fluorescence intensity compared to the GFP wild-type molecule. Further optimization strategies include numerous GFP derivatives with blue- and yellow-shifted fluorescence and increased pH-stability. The methods reported herein describe in detail the construction of customized fluorescent GFP reporter plasmids where the fluorescence gene is expressed under the control of a certain bacterial promoter of interest. Special attention is given to the GFP derivatives EGFP and Sirius. We explain how to generate EGFP/Sirius expressing streptococci and how to employ recombinantly labeled streptococci in different downstream fluorescent applications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chudakov DM, Matz MV, Lukyanov S, Lukyanov KA (2010) Fluorescent proteins and their applications in imaging living cells and tissues. Physiol Rev 90(3):1103–1163. doi:10.1152/physrev.00038.2009
Chalfie M, Tu Y, Euskirchen G, Ward WW, Prasher DC (1994) Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science 263(5148):802–805
Zimmer M (2002) Green fluorescent protein (GFP): applications, structure, and related photophysical behavior. Chem Rev 102(3):759–781
Tsien RY (1998) The green fluorescent protein. Annu Rev Biochem 67:509–544. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.509
Cormack BP, Valdivia RH, Falkow S (1996) FACS-optimized mutants of the green fluorescent protein (GFP). Gene 173((1 Spec No)):33–38
Bokman SH, Ward WW (1981) Renaturation of Aequorea green-fluorescent protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 101(4):1372–1380
Cody CW, Prasher DC, Westler WM, Prendergast FG, Ward WW (1993) Chemical structure of the hexapeptide chromophore of the Aequorea green-fluorescent protein. Biochemistry 32(5):1212–1218
Hansen MC, Palmer RJ Jr, Udsen C, White DC, Molin S (2001) Assessment of GFP fluorescence in cells of Streptococcus gordonii under conditions of low pH and low oxygen concentration. Microbiology 147(Pt 5):V1383–1391
Smith CB, Anderson JE, Fischer RL, Webb SR (2002) Stability of green fluorescent protein using luminescence spectroscopy: is GFP applicable to field analysis of contaminants? Environ Pollut 120(3):517–520
Tomosugi W, Matsuda T, Tani T, Nemoto T, Kotera I, Saito K, Horikawa K, Nagai T (2009) An ultramarine fluorescent protein with increased photostability and pH insensitivity. Nat Methods 6(5):351–353. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1317
Trieu-Cuot P, Carlier C, Poyart-Salmeron C, Courvalin P (1990) A pair of mobilizable shuttle vectors conferring resistance to spectinomycin for molecular cloning in Escherichia coli and in gram-positive bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res 18(14):4296
Gleich-Theurer U, Aymanns S, Haas G, Mauerer S, Vogt J, Spellerberg B (2009) Human serum induces streptococcal c5a peptidase expression. Infect Immun 77(9):3817–3825. doi:10.1128/iai.00826-08
Asam D, Mauerer S, Spellerberg B (2015) Streptolysin S of Streptococcus anginosus exhibits broad-range hemolytic activity. Med Microbiol Immunol 204(2):227–237. doi:10.1007/s00430-014-0363-0
Aymanns S, Mauerer S, van Zandbergen G, Wolz C, Spellerberg B (2011) High-level fluorescence labeling of gram-positive pathogens. PLoS One 6(6):e19822. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019822
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Shabayek, S., Spellerberg, B. (2017). Making Fluorescent Streptococci and Enterococci for Live Imaging. In: Nordenfelt, P., Collin, M. (eds) Bacterial Pathogenesis. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1535. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6673-8_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6673-8_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-6671-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-6673-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols